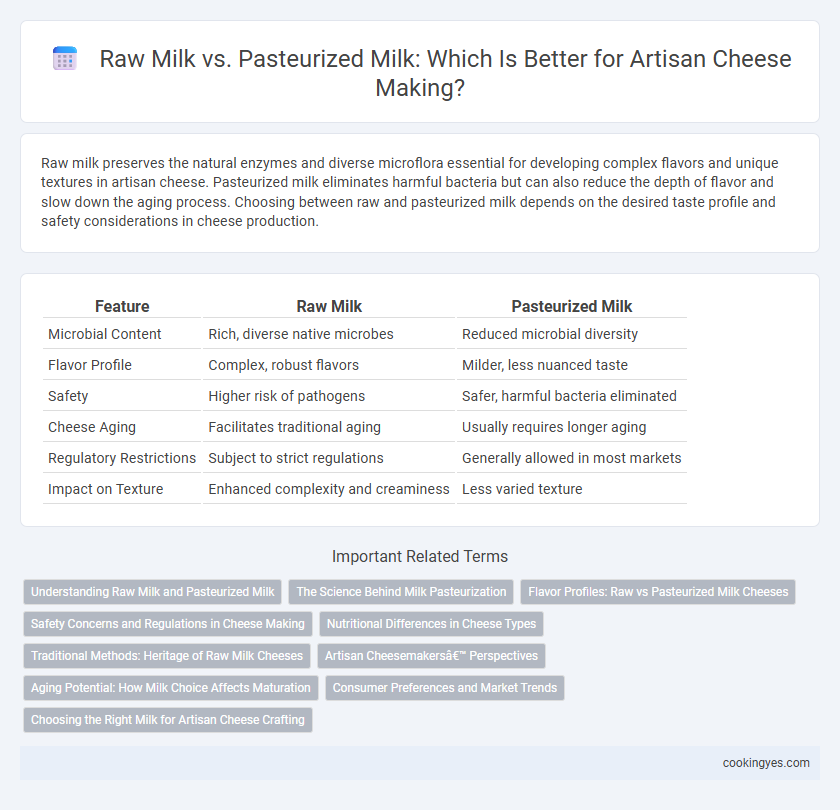
Raw milk preserves the natural enzymes and diverse microflora essential for developing complex flavors and unique textures in artisan cheese. Pasteurized milk eliminates harmful bacteria but can also reduce the depth of flavor and slow down the aging process. Choosing between raw and pasteurized milk depends on the desired taste profile and safety considerations in cheese production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raw Milk | Pasteurized Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Microbial Content | Rich, diverse native microbes | Reduced microbial diversity |
| Flavor Profile | Complex, robust flavors | Milder, less nuanced taste |
| Safety | Higher risk of pathogens | Safer, harmful bacteria eliminated |
| Cheese Aging | Facilitates traditional aging | Usually requires longer aging |
| Regulatory Restrictions | Subject to strict regulations | Generally allowed in most markets |
| Impact on Texture | Enhanced complexity and creaminess | Less varied texture |
Understanding Raw Milk and Pasteurized Milk
Raw milk retains natural enzymes and beneficial microbes essential for developing complex flavors and textures in artisan cheese, while pasteurized milk undergoes heat treatment to eliminate pathogens, ensuring safety but potentially reducing microbial diversity. Understanding the distinctions between raw and pasteurized milk is crucial for cheese makers aiming to balance flavor authenticity, safety regulations, and consumer preferences. The choice impacts aging processes, flavor profiles, and the unique characteristics associated with traditional artisan cheeses.
The Science Behind Milk Pasteurization
Milk pasteurization involves heating raw milk to specific temperatures, typically 161degF (72degC) for 15 seconds, to eliminate harmful pathogens while preserving nutritional quality. This process affects the microbial flora essential for the development of artisan cheese flavor profiles, often reducing complexity compared to raw milk varieties. Understanding the thermal impact on enzymes and beneficial bacteria is key to balancing safety with traditional cheese characteristics in artisan production.
Flavor Profiles: Raw vs Pasteurized Milk Cheeses
Raw milk cheeses deliver complex, rich flavor profiles due to the presence of natural microflora that remain intact during production, enhancing depth and unique terroir expression. Pasteurized milk cheeses offer more consistent and milder flavors, as heat treatment eliminates many bacteria and enzymes that influence taste development. Artisanal cheese makers often favor raw milk to achieve bold, nuanced flavors, while pasteurized options prioritize safety and reproducibility.
Safety Concerns and Regulations in Cheese Making
Raw milk artisan cheeses offer complex flavors due to naturally occurring bacteria, but they pose safety concerns related to potential pathogens like Listeria and Salmonella. Pasteurized milk undergoes heat treatment to eliminate harmful microorganisms, ensuring higher safety standards and compliance with strict FDA and USDA regulations. Cheese makers must balance flavor authenticity with regulatory requirements and consumer health risks when choosing raw or pasteurized milk.
Nutritional Differences in Cheese Types
Artisan cheeses made from raw milk retain higher levels of natural enzymes, beneficial bacteria, and vitamins such as B12 and A, which contribute to enhanced nutritional profiles compared to pasteurized milk cheeses. Pasteurization, while improving safety by eliminating harmful pathogens, can reduce these nutrients and alter the cheese's flavor complexity. Consequently, raw milk cheeses often offer superior probiotic content and a richer nutrient density, appealing to consumers seeking both health benefits and authentic taste experiences.
Traditional Methods: Heritage of Raw Milk Cheeses
Raw milk cheeses preserve the diverse microbial flora essential for developing complex flavors and textures, reflecting centuries-old traditional methods. Artisan producers value raw milk for its natural enzymes and bacteria that contribute to unique regional characteristics often lost in pasteurized versions. This heritage approach supports biodiversity and authenticity, reinforcing the cultural identity of artisanal cheese varieties worldwide.
Artisan Cheesemakers’ Perspectives
Artisan cheesemakers often prefer raw milk for its complex flavor profiles and natural microflora, which are essential for developing distinctive textures and aromas in their cheeses. They argue that pasteurization, while improving safety by eliminating pathogens, can diminish the rich, nuanced characteristics integral to authentic artisan cheese craftsmanship. Emphasizing traditional methods, these cheesemakers uphold raw milk as a critical ingredient in preserving regional heritage and enhancing the sensory depth of their artisanal products.
Aging Potential: How Milk Choice Affects Maturation
Raw milk cheeses contain natural enzymes and native microflora that enhance complex flavor development during aging, contributing to a richer and more distinctive maturation profile. Pasteurized milk, having undergone heat treatment, typically results in more predictable but less diverse microbial activity, which can limit the depth of flavor and texture evolution over extended aging periods. Artisan cheesemakers often select raw milk to maximize aging potential, relying on its inherent bacterial diversity to achieve nuanced ripening and complexity.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences for artisan cheese increasingly favor raw milk varieties due to their perceived richer flavors and traditional production methods, driving niche market growth. Market trends indicate a rising demand for raw milk cheeses, supported by a segment of connoisseurs prioritizing authenticity and unique taste profiles over the safety assurances of pasteurized options. Regulatory landscapes vary globally, influencing availability and shaping consumer access to raw milk artisan cheeses.
Choosing the Right Milk for Artisan Cheese Crafting
Selecting the right milk is crucial for artisan cheese crafting, with raw milk offering richer flavor complexity due to its natural enzymes and diverse microflora. Pasteurized milk provides consistency and safety by eliminating harmful bacteria but can result in milder taste profiles. Balancing these factors helps cheesemakers achieve desired textures and flavors while maintaining food safety standards.
Raw Milk vs Pasteurized Milk for Artisan Cheese Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com