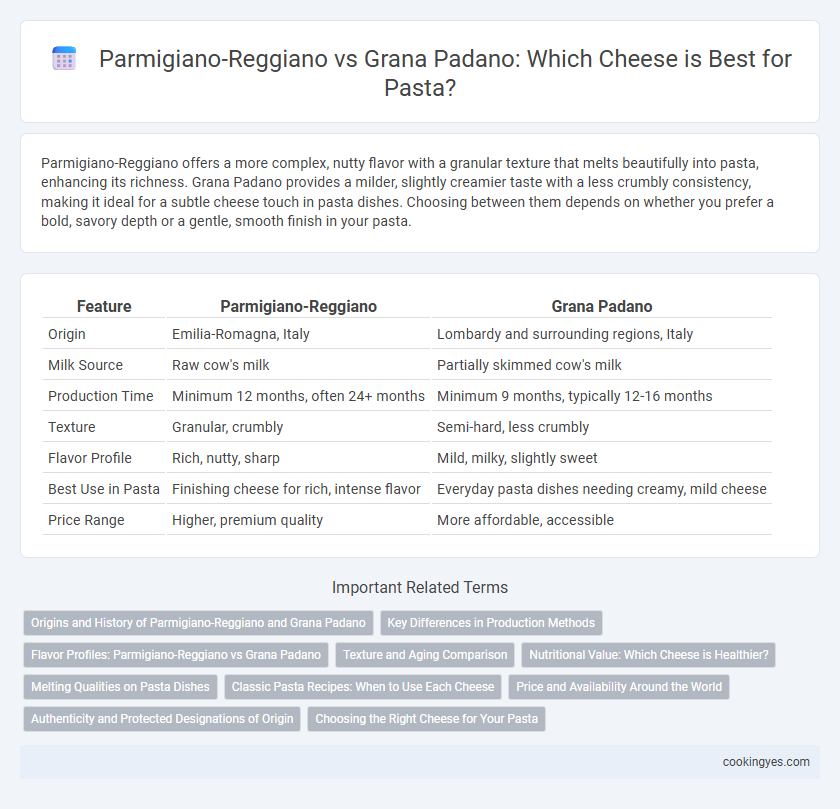
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a more complex, nutty flavor with a granular texture that melts beautifully into pasta, enhancing its richness. Grana Padano provides a milder, slightly creamier taste with a less crumbly consistency, making it ideal for a subtle cheese touch in pasta dishes. Choosing between them depends on whether you prefer a bold, savory depth or a gentle, smooth finish in your pasta.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Parmigiano-Reggiano | Grana Padano |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Emilia-Romagna, Italy | Lombardy and surrounding regions, Italy |
| Milk Source | Raw cow's milk | Partially skimmed cow's milk |
| Production Time | Minimum 12 months, often 24+ months | Minimum 9 months, typically 12-16 months |
| Texture | Granular, crumbly | Semi-hard, less crumbly |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, nutty, sharp | Mild, milky, slightly sweet |
| Best Use in Pasta | Finishing cheese for rich, intense flavor | Everyday pasta dishes needing creamy, mild cheese |
| Price Range | Higher, premium quality | More affordable, accessible |
Origins and History of Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano
Parmigiano-Reggiano, originating from the Parma and Reggio Emilia provinces in Italy, has a documented history dating back to the 12th century, renowned for its strict production rules and aging process of minimum 12 months. Grana Padano, produced mainly in the Po River Valley, traces its origins to Cistercian monks in the 10th century, featuring a slightly faster aging process of 9 to 20 months and a broader production area. Both cheeses share similar textures and granular structures but differ significantly in their historical terroir and regulatory traditions.
Key Differences in Production Methods
Parmigiano-Reggiano undergoes a strict production process requiring cows to be fed only natural forage without silage, resulting in a richer, more complex flavor profile, while Grana Padano allows silage in cow feed, producing a milder taste. The aging period for Parmigiano-Reggiano is a minimum of 12 months, often extending to 24 months or more, compared to Grana Padano's minimum aging of 9 months, which affects texture and depth. Both cheeses use raw cow's milk and share similar techniques like halving the curd with copper tools, but Parmigiano-Reggiano's stringent controls make it more robust and granular, ideal for pasta seasoning.
Flavor Profiles: Parmigiano-Reggiano vs Grana Padano
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a complex, nutty flavor with hints of fruit and umami, enhancing pasta dishes with a robust, savory depth. Grana Padano delivers a milder, slightly sweet and creamy taste, providing a balanced, less intense complement to pasta. The aging process for Parmigiano-Reggiano, typically 12 to 36 months, intensifies its sharpness compared to Grana Padano's shorter aging period of 9 to 24 months, resulting in distinct flavor profiles tailored to different culinary preferences.
Texture and Aging Comparison
Parmigiano-Reggiano features a granular, crystalline texture that becomes more pronounced with aging, typically between 12 to 36 months, resulting in a rich, complex flavor ideal for grating over pasta. Grana Padano, aged from 9 to 24 months, tends to have a smoother, creamier texture with a milder taste, making it a versatile choice for both grating and melting in pasta dishes. The longer aging process of Parmigiano-Reggiano contributes to a more intense umami profile, while Grana Padano offers a subtler, less gritty alternative.
Nutritional Value: Which Cheese is Healthier?
Parmigiano-Reggiano contains higher protein content and more calcium per serving compared to Grana Padano, making it a nutrient-dense choice for pasta dishes. Both cheeses are rich in essential vitamins like B12 and minerals such as phosphorus, but Parmigiano-Reggiano often has a lower fat content and less sodium, contributing to a heart-healthier profile. Selecting Parmigiano-Reggiano can enhance the nutritional value of pasta by providing better support for bone health and muscle maintenance.
Melting Qualities on Pasta Dishes
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers superior melting qualities on pasta due to its granular texture and complex proteins that break down evenly under heat, creating a creamy, rich coating. Grana Padano melts well but tends to be slightly less creamy because of its higher moisture content and milder aging process. Both cheeses enhance pasta dishes with umami depth, yet Parmigiano-Reggiano's melting profile delivers a silkier consistency, ideal for sauces and gratins.
Classic Pasta Recipes: When to Use Each Cheese
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a rich, nutty flavor with granular texture, making it ideal for finishing classic pasta dishes like Spaghetti Carbonara and Risotto alla Milanese that require a bold, aromatic accent. Grana Padano provides a milder, creamier taste with less granular texture, which complements lighter pasta recipes such as Tagliatelle al Limone or simple butter and herb sauces without overpowering delicate flavors. Choosing between the two depends on the pasta sauce complexity and the desired intensity of the cheese's contribution to the dish.
Price and Availability Around the World
Parmigiano-Reggiano is generally more expensive than Grana Padano due to stricter production regulations and longer aging processes, making it a premium choice for pasta dishes. Grana Padano is widely available and more affordable, offering a similar texture and flavor profile that suits everyday cooking. Globally, Grana Padano's broader distribution ensures easier access in international markets, while Parmigiano-Reggiano remains a specialty item often found in gourmet stores.
Authenticity and Protected Designations of Origin
Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano both hold Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status, ensuring strict adherence to traditional production methods in specific Italian regions. Parmigiano-Reggiano is exclusively produced in Parma, Reggio Emilia, Modena, Bologna (left of Reno River), and Mantua (right of Po River), guaranteeing its authenticity and unique flavor profile due to the region's climate and feed regulations. Grana Padano's broader production area covers the Po River Valley with slightly less stringent aging requirements, offering a milder taste while maintaining PDO-certified authenticity for pasta applications.
Choosing the Right Cheese for Your Pasta
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a richer, nuttier flavor and a granular texture that melts beautifully into pasta, enhancing dishes like carbonara and Alfredo. Grana Padano, with its milder, slightly sweeter taste and finer grain, provides a subtler cheese profile ideal for lighter sauces and vegetable-based pastas. Selecting between Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano depends on the desired intensity and texture, balancing the robust character of Parmigiano-Reggiano against the delicate note of Grana Padano for optimal pasta pairing.
Parmigiano-Reggiano vs Grana Padano for pasta Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com