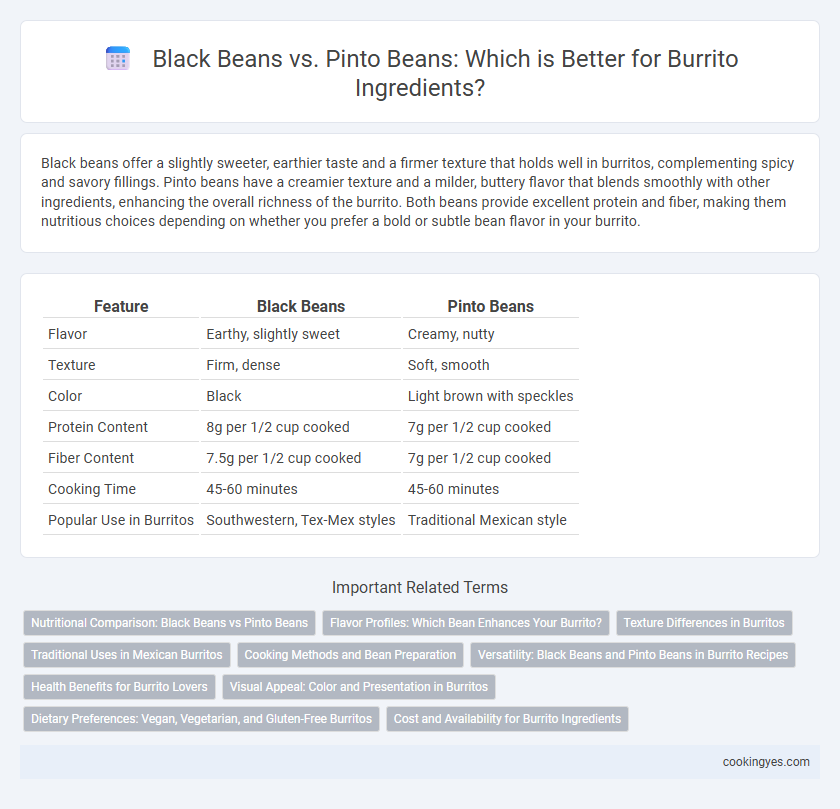
Black beans offer a slightly sweeter, earthier taste and a firmer texture that holds well in burritos, complementing spicy and savory fillings. Pinto beans have a creamier texture and a milder, buttery flavor that blends smoothly with other ingredients, enhancing the overall richness of the burrito. Both beans provide excellent protein and fiber, making them nutritious choices depending on whether you prefer a bold or subtle bean flavor in your burrito.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Black Beans | Pinto Beans |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Earthy, slightly sweet | Creamy, nutty |
| Texture | Firm, dense | Soft, smooth |
| Color | Black | Light brown with speckles |
| Protein Content | 8g per 1/2 cup cooked | 7g per 1/2 cup cooked |
| Fiber Content | 7.5g per 1/2 cup cooked | 7g per 1/2 cup cooked |
| Cooking Time | 45-60 minutes | 45-60 minutes |
| Popular Use in Burritos | Southwestern, Tex-Mex styles | Traditional Mexican style |
Nutritional Comparison: Black Beans vs Pinto Beans
Black beans provide higher protein content and are rich in anthocyanins, which have antioxidant properties beneficial for heart health. Pinto beans contain more folate and fiber, supporting digestion and reducing cholesterol levels. Both beans offer essential nutrients like iron and magnesium, but choosing black beans enhances protein intake while pinto beans boost dietary fiber and B vitamins in burrito fillings.
Flavor Profiles: Which Bean Enhances Your Burrito?
Black beans offer a rich, earthy flavor with a slightly sweet undertone that complements the savory, spicy elements in burritos, providing a robust taste experience. Pinto beans have a creamier texture and a mild, nutty flavor that blends smoothly with other fillings, adding a subtle sweetness without overpowering the dish. Choosing black beans enhances bold, intense flavors, while pinto beans contribute a softer, mellow taste, making each ideal for different burrito flavor profiles.
Texture Differences in Burritos
Black beans offer a denser, creamier texture that holds up well inside burritos without becoming mushy, providing a satisfying bite. Pinto beans tend to have a softer, more buttery consistency that blends smoothly with other ingredients, creating a rich, cohesive filling. The choice between black and pinto beans significantly impacts the overall mouthfeel, influencing whether a burrito feels hearty and firm or smooth and tender.
Traditional Uses in Mexican Burritos
Black beans are commonly used in Mexican burritos for their dense texture and rich, earthy flavor, often paired with rice and seasoned meat to enhance traditional taste profiles. Pinto beans, preferred in northern Mexico, offer a creamier consistency and milder flavor, making them ideal for refried beans or as a filling in classic burritos. Both bean types provide essential nutrients and authentic regional variations, preserving cultural heritage in Mexican cuisine.
Cooking Methods and Bean Preparation
Black beans require soaking for 6-8 hours to reduce cooking time and improve digestibility, then simmering for about 60-90 minutes until tender. Pinto beans benefit from an overnight soak and are typically cooked by boiling for 90-120 minutes, achieving a creamy texture that blends well in burritos. Both beans can be seasoned with garlic, onion, cumin, and chili powder during cooking to enhance flavor and complement the burrito fillings.
Versatility: Black Beans and Pinto Beans in Burrito Recipes
Black beans and pinto beans both offer exceptional versatility in burrito recipes, adapting well to a variety of flavor profiles from smoky chipotle to zesty cumin. Black beans provide a dense, creamy texture and a slightly sweet, earthy taste that complements spicy ingredients, while pinto beans have a softer consistency and mild, buttery flavor that soaks up seasonings. Their interchangeable use in burritos allows for diverse culinary creativity, accommodating dietary preferences and enhancing nutritional value with protein, fiber, and essential minerals.
Health Benefits for Burrito Lovers
Black beans offer a rich source of fiber, protein, and antioxidants, aiding digestion and supporting heart health for burrito lovers. Pinto beans provide essential nutrients such as folate, iron, and magnesium, promoting energy metabolism and muscle function. Incorporating either black or pinto beans into burritos boosts nutritional value while maintaining authentic, delicious flavor.
Visual Appeal: Color and Presentation in Burritos
Black beans provide a deep, rich black color that contrasts strikingly against the vibrant greens, reds, and yellows of typical burrito fillings, enhancing visual appeal. Pinto beans feature a warm, mottled beige and brown pattern that blends more subtly, offering a rustic and hearty look but less dramatic contrast. Choosing black beans elevates burrito presentation by creating a bolder, more colorful plate that attracts the eye while pinto beans contribute to a softer, earthier aesthetic.
Dietary Preferences: Vegan, Vegetarian, and Gluten-Free Burritos
Black beans and pinto beans are both excellent choices for vegan, vegetarian, and gluten-free burritos due to their high protein and fiber content. Black beans offer a slightly richer texture and a lower glycemic index, making them ideal for blood sugar management, while pinto beans provide a creamier consistency favored in traditional Mexican cuisine. Both beans are naturally gluten-free and packed with essential nutrients, perfectly complementing plant-based burrito ingredients without compromising dietary restrictions.
Cost and Availability for Burrito Ingredients
Black beans and pinto beans both offer affordable options for burrito ingredients, but black beans tend to be slightly more expensive due to higher demand in specialty markets. Pinto beans generally boast wider availability in grocery stores across the United States, making them a convenient choice for cost-conscious consumers. The cost difference is minimal, but pinto beans often provide better accessibility without sacrificing nutritional value or flavor in burritos.
Black Beans vs Pinto Beans for Burrito Ingredients Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com