Bone-in steaks retain more moisture during cooking because the bone acts as a heat barrier, allowing the meat around it to cook slower and stay juicier. Boneless steaks often cook more evenly but can lose moisture faster, resulting in a leaner texture. Choosing bone-in cuts like T-bone or ribeye enhances juiciness and flavor, making them ideal for those seeking a tender, succulent steak experience.
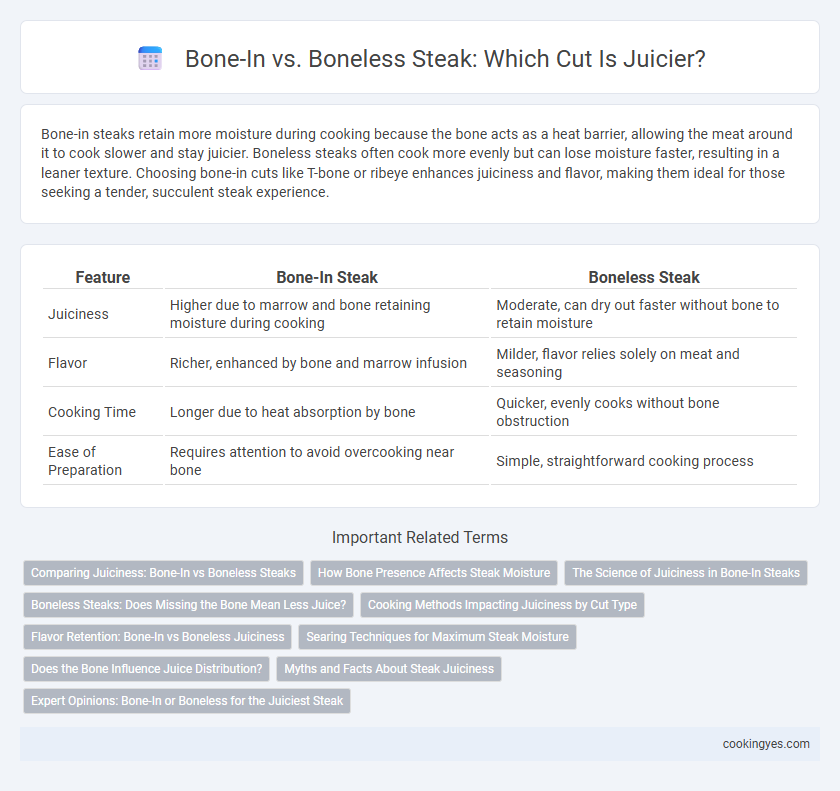
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone-In Steak | Boneless Steak |
|---|---|---|
| Juiciness | Higher due to marrow and bone retaining moisture during cooking | Moderate, can dry out faster without bone to retain moisture |
| Flavor | Richer, enhanced by bone and marrow infusion | Milder, flavor relies solely on meat and seasoning |
| Cooking Time | Longer due to heat absorption by bone | Quicker, evenly cooks without bone obstruction |
| Ease of Preparation | Requires attention to avoid overcooking near bone | Simple, straightforward cooking process |
Comparing Juiciness: Bone-In vs Boneless Steaks
Bone-in steaks retain more moisture during cooking due to the marrow and connective tissues around the bone, enhancing juiciness and flavor. Boneless steaks, while easier to cook evenly, often lose more juices without the insulating effect of the bone. Studies show bone-in cuts generally deliver a richer, more succulent eating experience compared to their boneless counterparts.
How Bone Presence Affects Steak Moisture
The presence of bone in steak slows down heat transfer during cooking, helping the meat retain moisture and stay juicier. Bone-in steaks allow marrow and connective tissues to release flavors and natural juices, enhancing overall succulence. Boneless steaks may cook faster but often lose more moisture, resulting in a drier texture compared to bone-in cuts.
The Science of Juiciness in Bone-In Steaks
Bone-in steaks retain juiciness due to the bone's ability to conduct heat more slowly, creating a more even cooking temperature that preserves moisture. The marrow inside the bone releases gelatin during cooking, which seeps into the surrounding meat, enhancing succulence and tenderness. Scientific studies show that the bone acts as a natural heat sink, reducing moisture loss through evaporation compared to boneless cuts.
Boneless Steaks: Does Missing the Bone Mean Less Juice?
Boneless steaks often retain juiciness through marbling and proper cooking techniques despite lacking the bone, which some believe contributes to moisture retention. Scientific studies show that the bone's presence does not significantly impact the steak's juiciness, as muscle fibers and fat distribution play a larger role. Cooking methods such as sous vide or reverse searing enhance juiciness in boneless cuts by evenly distributing heat and preserving moisture.
Cooking Methods Impacting Juiciness by Cut Type
Bone-in steaks retain more moisture during grilling or roasting because the bone acts as a heat conductor, promoting even cooking and preventing excessive drying. Boneless cuts often release juices faster when pan-seared or broiled due to direct heat exposure on all surfaces, which can reduce overall juiciness if overcooked. Choosing cooking methods like sous vide or low-temperature roasting helps both bone-in and boneless steaks maintain optimal juiciness by preserving internal moisture regardless of cut type.
Flavor Retention: Bone-In vs Boneless Juiciness
Bone-in steaks retain more flavor and juiciness due to the marrow and connective tissues, which release rich, savory juices during cooking. The bone acts as an insulator, promoting even heat distribution and reducing moisture loss compared to boneless cuts. Boneless steaks tend to cook faster but may lose more natural juices, leading to a slightly drier texture.
Searing Techniques for Maximum Steak Moisture
Searing bone-in steaks at high heat creates a flavorful crust while the bone helps retain internal moisture, resulting in juicier meat. Boneless steaks benefit from a two-stage searing technique--initial high heat to lock in juices, followed by lower heat to evenly cook through without drying out. Proper searing techniques, combined with careful temperature control, maximize steak moisture regardless of bone presence.
Does the Bone Influence Juice Distribution?
Bone-in steaks tend to retain more moisture and flavor due to the bone's ability to conduct heat unevenly, which promotes more even cooking and juice retention. The bone acts as a heat barrier, slowing down the cooking process near the edges and helping keep the meat around it juicier. While boneless steaks cook faster and can be easier to handle, they often lose moisture more quickly, resulting in a less juicy final product.
Myths and Facts About Steak Juiciness
Bone-in steaks are often believed to be juicier than boneless cuts due to the bone retaining moisture, but studies show the bone itself does not significantly impact steak juiciness. The true factors affecting juiciness include marbling, cooking technique, and resting time, which allow the meat fibers to reabsorb juices after cooking. Myths about bone-in steaks being inherently juicier overshadow the more important role of internal fat content and proper cooking methods in delivering succulent steak quality.
Expert Opinions: Bone-In or Boneless for the Juiciest Steak
Expert opinions on steak juiciness often highlight bone-in cuts for enhanced flavor retention and moisture due to the bone's heat conduction properties, which help cook the meat evenly. However, boneless steaks allow for more uniform seasoning and marinating, potentially maximizing juiciness when properly prepared. Culinary professionals emphasize that the juiciness difference depends significantly on cooking technique and steak quality rather than solely the presence of a bone.
Bone-in vs Boneless for Steak Juiciness Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com