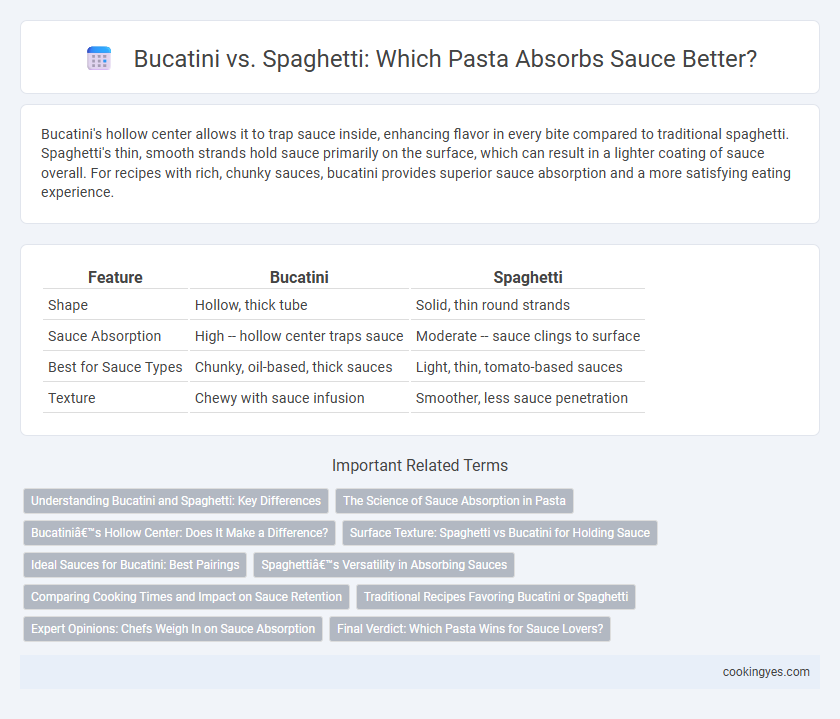
Bucatini's hollow center allows it to trap sauce inside, enhancing flavor in every bite compared to traditional spaghetti. Spaghetti's thin, smooth strands hold sauce primarily on the surface, which can result in a lighter coating of sauce overall. For recipes with rich, chunky sauces, bucatini provides superior sauce absorption and a more satisfying eating experience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bucatini | Spaghetti |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Hollow, thick tube | Solid, thin round strands |
| Sauce Absorption | High -- hollow center traps sauce | Moderate -- sauce clings to surface |
| Best for Sauce Types | Chunky, oil-based, thick sauces | Light, thin, tomato-based sauces |
| Texture | Chewy with sauce infusion | Smoother, less sauce penetration |
Understanding Bucatini and Spaghetti: Key Differences
Bucatini features a hollow center that enhances sauce absorption, making it ideal for thick, chunky sauces, while traditional spaghetti is solid and works best with lighter, oil-based sauces. The tubular shape of bucatini traps more sauce inside, providing a richer flavor experience with every bite compared to spaghetti's surface-coated sauce retention. Understanding these structural differences helps in selecting the perfect pasta to complement specific sauces for optimal taste and texture.
The Science of Sauce Absorption in Pasta
Bucatini's hollow center increases its surface area, allowing sauces to cling both inside and outside the pasta, enhancing flavor absorption compared to traditional spaghetti. The tubular structure traps thicker sauces like amatriciana or carbonara within its core, creating a more uniform sauce distribution in each bite. Spaghetti's solid, slender strands absorb sauce primarily on their exterior, which can result in less integrated flavor and a different texture experience.
Bucatini’s Hollow Center: Does It Make a Difference?
Bucatini's hollow center enhances sauce absorption by allowing liquid to seep inside the pasta, creating a richer and more flavorful bite compared to traditional spaghetti. This tubular structure traps thicker sauces like amatriciana or carbonara, intensifying the sauce-to-pasta ratio in every mouthful. Spaghetti's solid strands rely solely on surface adhesion, making Bucatini the preferred choice for dishes where sauce retention is key.
Surface Texture: Spaghetti vs Bucatini for Holding Sauce
Bucatini features a hollow center that increases surface area, allowing sauces to cling both inside and outside the noodle, enhancing flavor retention. In contrast, traditional spaghetti has a smooth, solid surface that limits sauce absorption primarily to its exterior. The unique texture of bucatini provides superior sauce adherence, making it ideal for thicker, chunkier sauces compared to spaghetti's more uniform coating with lighter sauces.
Ideal Sauces for Bucatini: Best Pairings
Bucatini, with its hollow center, excels at capturing and holding thick, chunky sauces like Amatriciana, carbonara, and rich tomato ragu, making each bite flavorful and well-coated. Its sturdy texture pairs perfectly with creamy sauces and oil-based dressings, allowing the sauce to cling inside and around the pasta strands. Unlike traditional spaghetti, bucatini's tubular shape enhances sauce absorption, elevating dishes that feature hearty, meaty, or robust sauces for an optimal taste experience.
Spaghetti’s Versatility in Absorbing Sauces
Spaghetti's thin, cylindrical shape allows it to effectively absorb a wide range of sauces, making it highly versatile in different culinary applications. Its smooth surface holds lighter sauces like marinara or garlic and oil well, ensuring a balanced coating without overwhelming the pasta. This versatility contrasts with bucatini's hollow center, which traps thicker sauces but may not blend as seamlessly with delicate or thin sauces.
Comparing Cooking Times and Impact on Sauce Retention
Bucatini, thicker and hollow, typically requires 9-12 minutes to cook, while traditional spaghetti cooks in 8-10 minutes, influencing their texture and sauce retention. The hollow center of bucatini allows it to trap more sauce inside, enhancing flavor absorption compared to spaghetti's smooth surface. These cooking time differences and structural contrasts make bucatini superior for thicker, chunky sauces, whereas spaghetti pairs well with lighter, oil-based sauces.
Traditional Recipes Favoring Bucatini or Spaghetti
Bucatini's hollow center allows it to trap and absorb sauces more effectively than traditional spaghetti, making it ideal for rich, thick sauces like Amatriciana or Carbonara often found in Roman cuisine. Spaghetti, with its solid, slender shape, works best with lighter, smoother sauces like classic marinara or aglio e olio, commonly featured in Neapolitan and Southern Italian recipes. Traditional Italian cooking tends to pair bucatini with hearty, robust sauces while reserving spaghetti for simpler, more delicate flavors, highlighting regional preferences in pasta choices.
Expert Opinions: Chefs Weigh In on Sauce Absorption
Chefs widely agree that bucatini's hollow center allows sauces to cling more effectively than traditional spaghetti, creating a more flavorful experience. Renowned culinary experts highlight bucatini's tubular shape as superior for holding thicker, chunkier sauces such as amatriciana or carbonara. Spaghetti, while excellent for smoother sauces like marinara, lacks the same sauce retention capabilities, making bucatini the preferred choice for maximum sauce absorption.
Final Verdict: Which Pasta Wins for Sauce Lovers?
Bucatini's hollow center allows it to trap more sauce, making each bite richly flavored, whereas traditional spaghetti only holds sauce on its surface. For sauce lovers seeking maximum absorption and a more intense taste experience, bucatini offers a superior texture and sauce-holding ability. The thicker, tubular shape of bucatini ultimately wins for those prioritizing sauce retention and flavor integration in their pasta dishes.
Bucatini vs Spaghetti for sauce absorption Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com