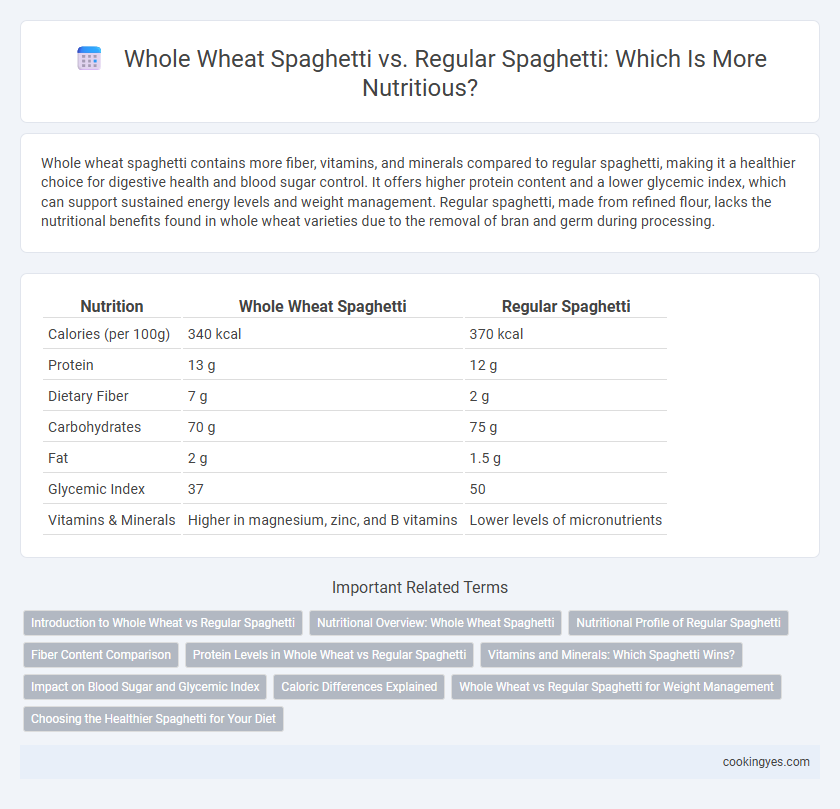
Whole wheat spaghetti contains more fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to regular spaghetti, making it a healthier choice for digestive health and blood sugar control. It offers higher protein content and a lower glycemic index, which can support sustained energy levels and weight management. Regular spaghetti, made from refined flour, lacks the nutritional benefits found in whole wheat varieties due to the removal of bran and germ during processing.
Table of Comparison
| Nutrition | Whole Wheat Spaghetti | Regular Spaghetti |
|---|---|---|
| Calories (per 100g) | 340 kcal | 370 kcal |
| Protein | 13 g | 12 g |
| Dietary Fiber | 7 g | 2 g |
| Carbohydrates | 70 g | 75 g |
| Fat | 2 g | 1.5 g |
| Glycemic Index | 37 | 50 |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Higher in magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins | Lower levels of micronutrients |
Introduction to Whole Wheat vs Regular Spaghetti
Whole wheat spaghetti contains higher fiber content compared to regular spaghetti, offering improved digestive health and sustained energy release. It provides more vitamins and minerals such as magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins due to the inclusion of the entire grain. Regular spaghetti, made from refined flour, tends to be lower in nutrients and has a higher glycemic index, potentially leading to quicker blood sugar spikes.
Nutritional Overview: Whole Wheat Spaghetti
Whole wheat spaghetti offers higher fiber content, providing about 6 grams of fiber per serving compared to 2 grams in regular spaghetti, which supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. It contains more protein, averaging 7 grams per serving, and is richer in essential nutrients like magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins. The lower glycemic index of whole wheat spaghetti contributes to sustained energy release and improved satiety compared to its refined counterpart.
Nutritional Profile of Regular Spaghetti
Regular spaghetti is primarily made from refined durum wheat, resulting in a higher glycemic index and lower fiber content compared to whole wheat varieties. It typically provides around 200 calories per cooked cup, with approximately 7 grams of protein and 1 gram of fiber. Regular spaghetti is richer in simple carbohydrates but lacks significant amounts of essential vitamins and minerals found in whole wheat pasta.
Fiber Content Comparison
Whole wheat spaghetti contains significantly more dietary fiber than regular spaghetti, offering about 6-7 grams of fiber per cooked cup compared to 2 grams in regular spaghetti. This higher fiber content supports better digestive health, promotes satiety, and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Choosing whole wheat spaghetti enhances overall nutrient intake by providing additional vitamins and minerals not present in refined pasta.
Protein Levels in Whole Wheat vs Regular Spaghetti
Whole wheat spaghetti contains approximately 7-8 grams of protein per 2-ounce serving, compared to regular spaghetti, which offers around 5-6 grams. The higher protein content in whole wheat spaghetti is attributed to the inclusion of the entire grain, including the bran and germ. This makes whole wheat spaghetti a more nutrient-dense option, supporting muscle repair and satiety better than refined regular spaghetti.
Vitamins and Minerals: Which Spaghetti Wins?
Whole wheat spaghetti contains higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals compared to regular spaghetti, including increased amounts of B vitamins like niacin and folate, as well as minerals such as iron, magnesium, and zinc. These nutrients support metabolism, red blood cell production, and immune function, making whole wheat spaghetti a nutritionally superior choice. Regular spaghetti, made from refined flour, has fewer micronutrients due to processing, resulting in lower vitamin and mineral content.
Impact on Blood Sugar and Glycemic Index
Whole wheat spaghetti contains higher fiber content and a lower glycemic index than regular spaghetti, leading to a slower digestion process and less pronounced blood sugar spikes. This makes whole wheat spaghetti a better choice for managing blood glucose levels, especially for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes. Regular spaghetti, made from refined flour, typically results in quicker glucose absorption and higher post-meal blood sugar levels.
Caloric Differences Explained
Whole wheat spaghetti contains approximately 174 calories per cup cooked, compared to 200 calories in regular spaghetti, making it a lower-calorie option. The higher fiber content in whole wheat pasta not only aids digestion but also promotes satiety, which can help reduce overall calorie intake. Rich in vitamins and minerals like magnesium and zinc, whole wheat spaghetti offers enhanced nutritional benefits beyond its lower caloric value.
Whole Wheat vs Regular Spaghetti for Weight Management
Whole wheat spaghetti contains higher dietary fiber and protein than regular spaghetti, which enhances satiety and supports weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. The slower digestion rate of whole wheat pasta helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, preventing hunger spikes and promoting fat oxidation. Choosing whole wheat spaghetti over regular can contribute to sustained energy release and effective weight control.
Choosing the Healthier Spaghetti for Your Diet
Whole wheat spaghetti offers higher fiber content, essential vitamins, and minerals compared to regular spaghetti, promoting better digestion and sustained energy levels. Its lower glycemic index helps regulate blood sugar, making it a healthier choice for weight management and diabetes prevention. Opting for whole wheat pasta supports heart health by providing antioxidants and reducing cholesterol levels.
Whole wheat spaghetti vs Regular spaghetti for nutrition Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com