Domestic shrimp generally offer fresher quality and support local fisheries, while imported shrimp may provide cost savings and greater variety. Choosing between domestic and imported shrimp depends on factors such as price, environmental impact, and availability. Prioritizing sustainably sourced shrimp helps ensure a healthier aquatic habitat and responsible pet care.
Table of Comparison
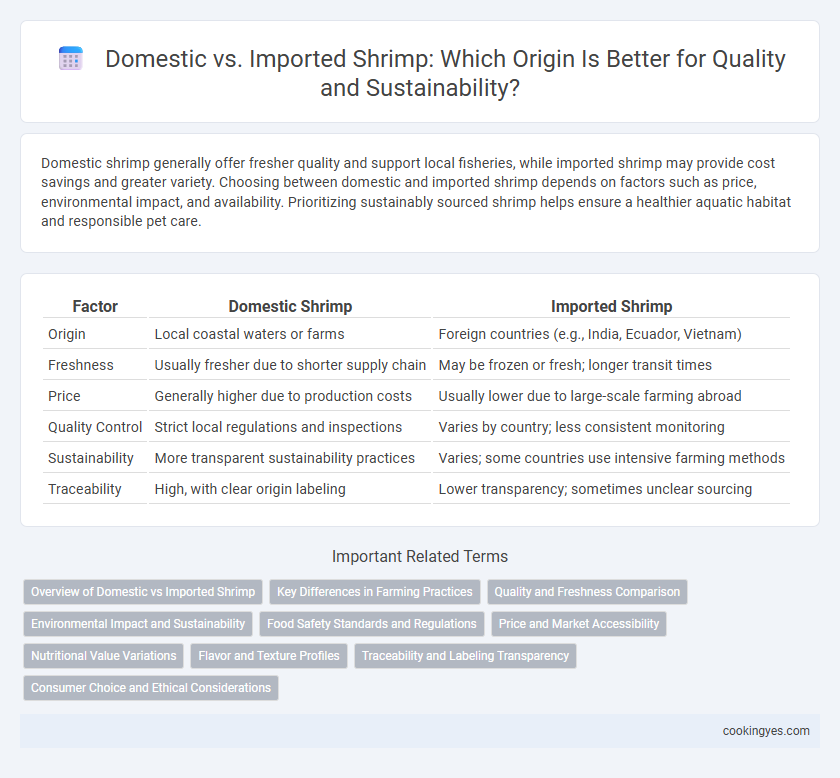
| Factor | Domestic Shrimp | Imported Shrimp |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Local coastal waters or farms | Foreign countries (e.g., India, Ecuador, Vietnam) |
| Freshness | Usually fresher due to shorter supply chain | May be frozen or fresh; longer transit times |
| Price | Generally higher due to production costs | Usually lower due to large-scale farming abroad |
| Quality Control | Strict local regulations and inspections | Varies by country; less consistent monitoring |
| Sustainability | More transparent sustainability practices | Varies; some countries use intensive farming methods |
| Traceability | High, with clear origin labeling | Lower transparency; sometimes unclear sourcing |
Overview of Domestic vs Imported Shrimp
Domestic shrimp are typically harvested from U.S. coastal waters, ensuring fresher products with shorter supply chains and stricter regulatory standards on sustainability and safety. Imported shrimp, primarily from countries like Ecuador, Thailand, and India, often come at lower prices but may vary in quality and face concerns over environmental practices and antibiotic use. Consumer preference balances cost, freshness, and ethical considerations when selecting between domestic and imported shrimp.
Key Differences in Farming Practices
Domestic shrimp farming often emphasizes sustainable aquaculture methods with stringent environmental regulations and controlled water quality monitoring, leading to higher product traceability and safety standards. Imported shrimp typically come from large-scale operations that may utilize intensive farming practices with varied regulatory oversight, potentially impacting biodiversity and antibiotic use. Differences in feed composition, disease management protocols, and harvest cycles distinctly influence the nutritional profile and freshness between domestic and imported shrimp.
Quality and Freshness Comparison
Domestic shrimp often offer superior freshness due to shorter transportation times from harvest to market, preserving their natural texture and flavor. Imported shrimp may vary in quality, as extended shipping and freezing processes can impact their freshness and taste. Consumers prioritizing optimal shrimp quality typically favor domestic sources for immediate freshness and minimal handling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Domestic shrimp farming typically uses more regulated practices that reduce environmental degradation, including lower carbon emissions from transportation and stricter waste management standards. Imported shrimp often come from regions with less stringent environmental regulations, leading to higher risks of mangrove deforestation, water pollution, and habitat destruction. Choosing domestically sourced shrimp supports sustainable aquaculture with minimized ecological footprint compared to many imported options.
Food Safety Standards and Regulations
Domestic shrimp producers in the U.S. adhere to stringent food safety standards regulated by the FDA and USDA, ensuring rigorous testing for contaminants like antibiotics and heavy metals. Imported shrimp, primarily from countries such as Thailand, India, and Ecuador, face variable compliance levels due to differing international standards and occasional lapses in enforcement. Consumers often seek certification labels like the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) and Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP) to verify the safety and quality of imported shrimp.
Price and Market Accessibility
Domestic shrimp generally have higher prices due to stricter quality controls and shorter supply chains, offering fresher products to local markets. Imported shrimp often cost less, benefiting from large-scale production and lower labor expenses in exporting countries, making them widely accessible in global markets. Market accessibility for domestic shrimp is typically limited to regional distribution, whereas imported shrimp dominate international trade channels, increasing availability for consumers worldwide.
Nutritional Value Variations
Domestic shrimp often exhibit higher omega-3 fatty acid levels due to fresher processing techniques and controlled farming environments. Imported shrimp may contain varying nutritional profiles influenced by differing aquaculture practices and feed compositions across countries. Nutrient variations, such as protein content and vitamin concentrations, largely depend on the shrimp's origin and farming conditions.
Flavor and Texture Profiles
Domestic shrimp typically offer a sweeter, more succulent flavor with a firmer texture due to colder waters and shorter supply chains. Imported shrimp often have a milder taste and softer texture, influenced by warmer climates and longer transit times. Consumers seeking robust flavor and crisp bite often prefer domestic varieties, while imported shrimp may be favored for their affordability and consistent size.
Traceability and Labeling Transparency
Domestic shrimp markets often provide greater traceability and labeling transparency due to stringent regulatory standards and oversight by agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Imported shrimp can pose challenges in verifying origin and harvesting methods, as some exporting countries lack comprehensive monitoring systems, leading to potential risks in food safety and sustainability claims. Enhancing traceability technologies and enforcing clear labeling on both domestic and imported shrimp products are crucial for consumer confidence and informed purchasing decisions.
Consumer Choice and Ethical Considerations
Domestic shrimp often appeal to consumers seeking fresher products with a smaller carbon footprint, supporting local fisheries and economies. Imported shrimp, while sometimes more affordable and available year-round, may raise ethical concerns related to labor practices and environmental sustainability in exporting countries. Consumers increasingly weigh these factors, balancing cost, quality, and ethical sourcing when choosing between domestic and imported shrimp.
Domestic vs Imported for shrimp origin Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com