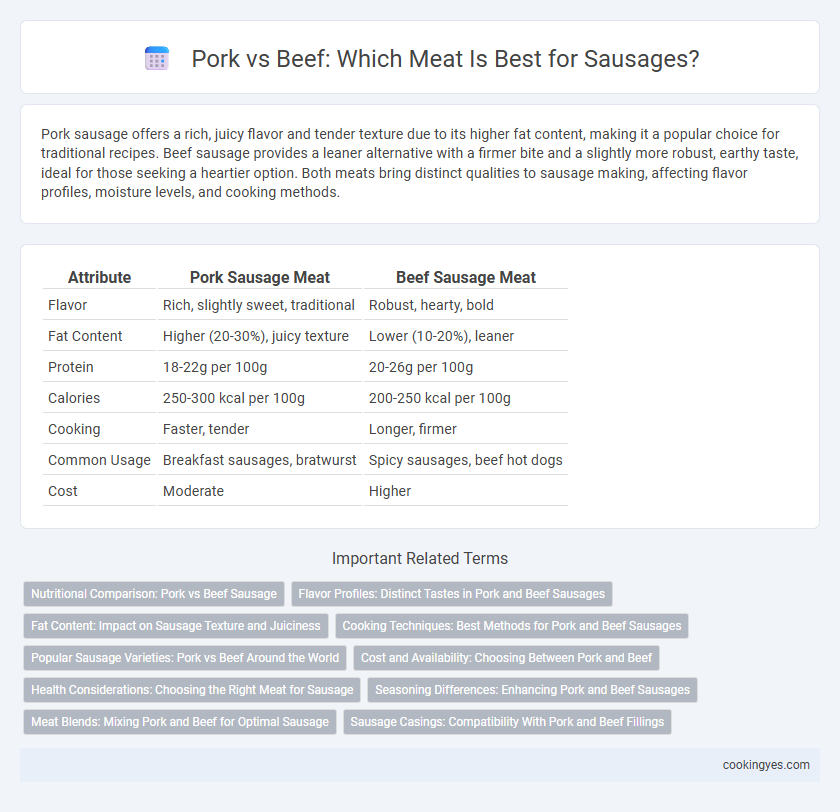
Pork sausage offers a rich, juicy flavor and tender texture due to its higher fat content, making it a popular choice for traditional recipes. Beef sausage provides a leaner alternative with a firmer bite and a slightly more robust, earthy taste, ideal for those seeking a heartier option. Both meats bring distinct qualities to sausage making, affecting flavor profiles, moisture levels, and cooking methods.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Pork Sausage Meat | Beef Sausage Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Rich, slightly sweet, traditional | Robust, hearty, bold |
| Fat Content | Higher (20-30%), juicy texture | Lower (10-20%), leaner |
| Protein | 18-22g per 100g | 20-26g per 100g |
| Calories | 250-300 kcal per 100g | 200-250 kcal per 100g |
| Cooking | Faster, tender | Longer, firmer |
| Common Usage | Breakfast sausages, bratwurst | Spicy sausages, beef hot dogs |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Nutritional Comparison: Pork vs Beef Sausage
Pork sausage generally contains higher fat content, contributing to a richer flavor and increased calorie count compared to beef sausage. Beef sausage offers a higher protein content and lower saturated fat levels, making it a leaner choice for health-conscious consumers. Both types provide essential nutrients like iron and B vitamins, but the specific nutritional profile varies depending on the meat quality and preparation methods.
Flavor Profiles: Distinct Tastes in Pork and Beef Sausages
Pork sausage offers a rich, slightly sweet flavor profile with a tender, juicy texture that enhances traditional seasoning blends like sage and fennel. Beef sausage, on the other hand, delivers a robust, hearty taste with a denser texture, making it ideal for bold spices such as black pepper and smoked paprika. The choice between pork and beef sausages greatly influences the final flavor complexity, with pork providing a milder, more versatile base and beef contributing a deeper, earthier richness.
Fat Content: Impact on Sausage Texture and Juiciness
Pork sausage typically contains a higher fat content, ranging from 20% to 30%, which contributes to a tender, juicy texture and rich flavor. Beef sausage often has a lower fat percentage, around 10% to 15%, resulting in a firmer, leaner bite but less moisture retention. The fat content directly influences the sausage's juiciness, mouthfeel, and ability to bind spices and seasonings effectively.
Cooking Techniques: Best Methods for Pork and Beef Sausages
Pork sausages benefit from slow cooking methods like grilling or pan-frying at medium heat, which help render fat and enhance juiciness, while beef sausages often require higher heat searing or roasting to develop a rich, caramelized crust. Pork's higher fat content demands careful temperature control to prevent drying out, whereas beef's leaner profile responds well to methods that preserve moisture, such as braising or baking with added liquid. Selecting the ideal cooking technique depends on balancing fat content and flavor development specific to pork and beef sausage varieties.
Popular Sausage Varieties: Pork vs Beef Around the World
Pork sausages dominate global cuisine, prized for their juicy texture and rich flavor, with varieties like Italian sausages, German bratwurst, and Spanish chorizo showcasing its versatility. Beef sausages hold significant importance in regions with dietary restrictions on pork, such as Middle Eastern merguez and American beef hot dogs, offering a leaner alternative with a distinct savory profile. Both meats contribute to diverse sausage traditions, reflecting cultural preferences and local culinary practices worldwide.
Cost and Availability: Choosing Between Pork and Beef
Pork sausage meat is generally more cost-effective and widely available compared to beef, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers and large-scale production. Beef sausages tend to be pricier due to higher feed costs and longer raising periods, with availability fluctuating based on regional demand and livestock supply. Both meats offer distinct flavors and textures, but pork's affordability and accessibility often drive its preference in sausage making.
Health Considerations: Choosing the Right Meat for Sausage
Pork sausage typically contains higher fat content, particularly saturated fat, which can impact cardiovascular health, while beef sausage often has a leaner profile with more iron and zinc essential for blood and immune function. Selecting the right meat for sausage depends on dietary goals, as lean beef can support lower cholesterol levels and pork offers a richer source of B vitamins like thiamin and niacin. Considering fat types and micronutrient density helps optimize sausage meat choice for balanced nutrition and health outcomes.
Seasoning Differences: Enhancing Pork and Beef Sausages
Pork sausages benefit from sweeter, aromatic seasonings like sage, thyme, and nutmeg that complement the meat's natural fat and tenderness, while beef sausages often require bolder spices such as black pepper, garlic, and smoked paprika to balance their leaner texture and stronger flavor. The fat content in pork allows it to absorb subtle herbs, whereas beef pairs well with savory and spicy blends that enhance its robustness. Understanding these seasoning differences improves the flavor profile and texture of both pork and beef sausages for a more satisfying culinary experience.
Meat Blends: Mixing Pork and Beef for Optimal Sausage
Blending pork and beef for sausage meat enhances flavor complexity and juiciness, balancing pork's fat content with beef's robust taste. A typical ratio of 70% pork to 30% beef offers optimal texture and moisture retention, ideal for a variety of sausages like bratwurst and Italian links. This meat blend enables sausages to maintain structural integrity during cooking while delivering a rich, savory profile appreciated in gourmet and traditional recipes.
Sausage Casings: Compatibility With Pork and Beef Fillings
Sausage casings made from natural pork intestines are highly compatible with both pork and beef fillings due to their tenderness and elasticity, which enhance the texture and flavor of the sausage. Collagen casings offer a more uniform size and strength, suitable for beef fillings that require a firmer bite. Synthetic casings provide durability and uniformity but may impact the traditional taste profiles favored in pork-based sausages.
Pork vs Beef for sausage meat Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com