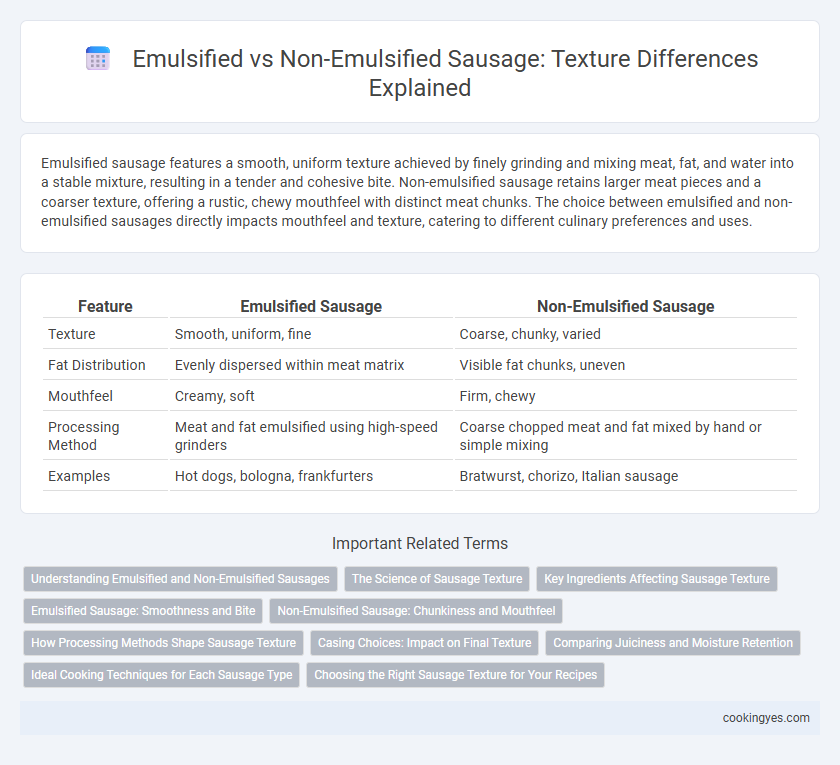
Emulsified sausage features a smooth, uniform texture achieved by finely grinding and mixing meat, fat, and water into a stable mixture, resulting in a tender and cohesive bite. Non-emulsified sausage retains larger meat pieces and a coarser texture, offering a rustic, chewy mouthfeel with distinct meat chunks. The choice between emulsified and non-emulsified sausages directly impacts mouthfeel and texture, catering to different culinary preferences and uses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Emulsified Sausage | Non-Emulsified Sausage |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Smooth, uniform, fine | Coarse, chunky, varied |
| Fat Distribution | Evenly dispersed within meat matrix | Visible fat chunks, uneven |
| Mouthfeel | Creamy, soft | Firm, chewy |
| Processing Method | Meat and fat emulsified using high-speed grinders | Coarse chopped meat and fat mixed by hand or simple mixing |
| Examples | Hot dogs, bologna, frankfurters | Bratwurst, chorizo, Italian sausage |
Understanding Emulsified and Non-Emulsified Sausages
Emulsified sausages like hot dogs and bologna achieve a smooth, uniform texture through finely ground meat blended with water and fat, resulting in a stable mixture that holds together well during cooking. Non-emulsified sausages such as Italian or bratwurst use coarser ground meat, preserving distinct meat and fat textures that provide a firmer bite and more pronounced mouthfeel. The key difference lies in the emulsification process, which affects water retention, texture consistency, and overall sensory experience.
The Science of Sausage Texture
Emulsified sausage achieves a smooth, uniform texture by finely grinding meat and fat particles, allowing proteins to bind water and fat into a stable gel matrix, which enhances juiciness and sliceability. Non-emulsified sausage features a coarser, chunkier texture where larger meat pieces are discernible, providing a hearty mouthfeel but less uniformity in moisture retention. The science of sausage texture hinges on protein extraction and fat distribution, with emulsification creating a consistent microstructure that improves yield and sensory qualities.
Key Ingredients Affecting Sausage Texture
Emulsified sausages, such as hot dogs and bologna, achieve a smooth, uniform texture by finely grinding and mixing lean meat, fat, water, and curing agents, allowing myosin proteins to bind and create a stable matrix. Non-emulsified sausages, like bratwurst and Italian sausage, have a coarser texture due to larger meat and fat particles, relying on protein extraction from meat and salt for cohesion without full emulsification. Key ingredients affecting texture include fat content, type of muscle proteins, salt concentration, and water binding agents, which influence the firmness, juiciness, and bite of the final product.
Emulsified Sausage: Smoothness and Bite
Emulsified sausage features a finely ground texture achieved by blending meat, fat, and water into a stable, homogenous mixture, resulting in exceptional smoothness and a consistent bite. The emulsification process traps fat within the protein matrix, creating a tender yet firm texture that melts in the mouth without crumbliness. In contrast, non-emulsified sausages retain coarser meat chunks, producing a chewier texture with a less uniform bite.
Non-Emulsified Sausage: Chunkiness and Mouthfeel
Non-emulsified sausage features a chunkier texture due to coarsely ground meat and visible fat pieces, enhancing its mouthfeel with a more pronounced chew. The uneven grind allows for a varied bite experience, contributing to a rustic and hearty sensation compared to the smooth, uniform texture of emulsified sausages. This distinctive mouthfeel is preferred in products like Italian sausage and bratwurst, where texture plays a crucial role in flavor perception and satisfaction.
How Processing Methods Shape Sausage Texture
Emulsified sausages, such as hot dogs and bologna, undergo fine grinding and mixing with water and fat, creating a smooth, uniform texture due to the stable emulsion of fat and proteins. Non-emulsified sausages like Italian sausage or bratwurst maintain a coarser, chunkier texture because the meat and fat are simply ground and mixed without forming an emulsion. The processing methods, including cutting speed, temperature control, and mixing intensity, directly influence the final bite, mouthfeel, and cohesiveness of sausage varieties.
Casing Choices: Impact on Final Texture
Emulsified sausages use fine meat and fat particles suspended in a stable mixture, resulting in a smooth texture that's enhanced by thin, edible casings like collagen or collagen-based films, which allow for even cooking and moisture retention. Non-emulsified sausages consist of coarser meat chunks, with natural casings such as hog or beef intestines that contribute to a chewier, more rustic bite and provide varied permeability affecting moisture and smoke absorption. Choosing between natural and synthetic casings directly impacts the mouthfeel and firmness, making casing selection crucial for achieving the desired texture in both emulsified and non-emulsified sausages.
Comparing Juiciness and Moisture Retention
Emulsified sausages, such as hot dogs and bologna, exhibit superior juiciness and moisture retention due to the fine dispersion of fat and water stabilized by emulsifiers, resulting in a smooth and cohesive texture. Non-emulsified sausages like bratwurst and Italian sausage maintain a coarser texture with larger meat chunks, leading to lower moisture retention and a less uniform juiciness. The emulsification process enhances water-binding capacity and fat distribution, which directly improves the overall moistness and bite of the sausage.
Ideal Cooking Techniques for Each Sausage Type
Emulsified sausages, such as hot dogs and bologna, require precise, low-temperature cooking methods like simmering or steaming to maintain their smooth, uniform texture and prevent fat separation. Non-emulsified sausages, including bratwurst and Italian sausage, benefit from grilling or pan-frying, which enhances their coarser texture and creates a flavorful, crispy exterior. Understanding these cooking techniques ensures optimal texture retention and flavor development for each sausage type.
Choosing the Right Sausage Texture for Your Recipes
Emulsified sausages, such as hot dogs and bologna, offer a smooth, uniform texture achieved by finely grinding meat and fat into a stable mixture, ideal for recipes requiring a consistent mouthfeel. Non-emulsified sausages, like Italian or bratwurst, retain coarser meat chunks, providing a chewier, more rustic texture suitable for grilling or sauteing. Selecting the right sausage texture depends on the desired bite and cooking method, with emulsified varieties enhancing spreadability and creaminess, while non-emulsified sausages bring robust, distinct meatiness to dishes.
Emulsified sausage vs non-emulsified sausage for texture Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com