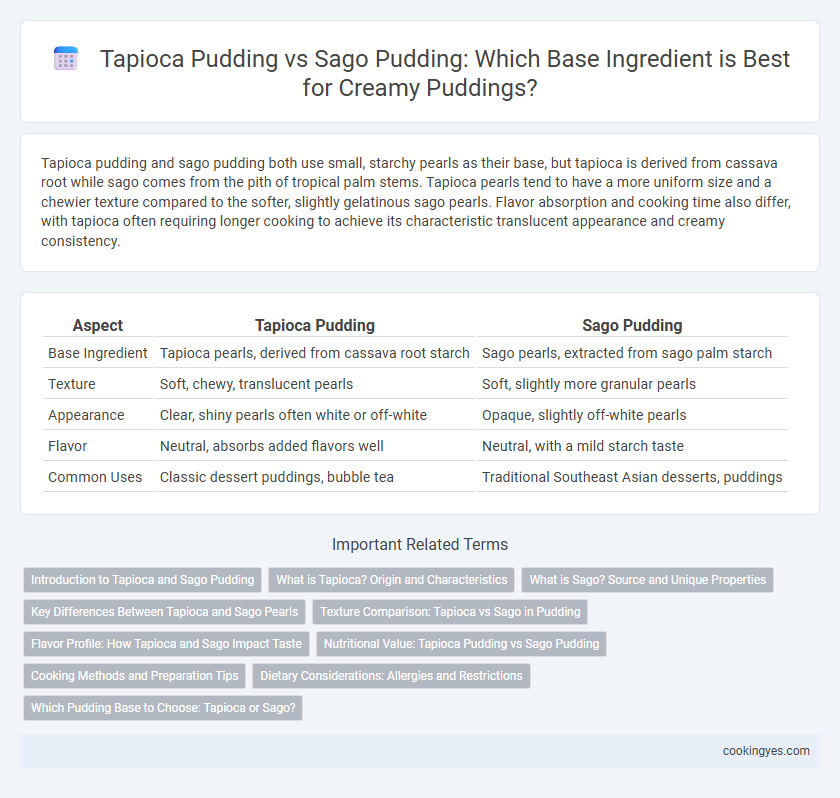
Tapioca pudding and sago pudding both use small, starchy pearls as their base, but tapioca is derived from cassava root while sago comes from the pith of tropical palm stems. Tapioca pearls tend to have a more uniform size and a chewier texture compared to the softer, slightly gelatinous sago pearls. Flavor absorption and cooking time also differ, with tapioca often requiring longer cooking to achieve its characteristic translucent appearance and creamy consistency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tapioca Pudding | Sago Pudding |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredient | Tapioca pearls, derived from cassava root starch | Sago pearls, extracted from sago palm starch |
| Texture | Soft, chewy, translucent pearls | Soft, slightly more granular pearls |
| Appearance | Clear, shiny pearls often white or off-white | Opaque, slightly off-white pearls |
| Flavor | Neutral, absorbs added flavors well | Neutral, with a mild starch taste |
| Common Uses | Classic dessert puddings, bubble tea | Traditional Southeast Asian desserts, puddings |
Introduction to Tapioca and Sago Pudding
Tapioca pudding and sago pudding both use small, starchy pearls derived from different plant sources; tapioca comes from the cassava root, while sago is extracted from the sago palm. Tapioca pearls are typically larger and more translucent, offering a chewier texture compared to the smaller, more opaque sago pearls that provide a softer mouthfeel. Both puddings are popular in various cuisines for their unique textures and ability to absorb sweet flavors, making them classic desserts in Southeast Asian and Western cultures.
What is Tapioca? Origin and Characteristics
Tapioca is a starch extracted from the cassava root, native to South America, and widely used as the base ingredient in tapioca pudding. Characterized by its translucent, jelly-like pearls, tapioca provides a chewy texture and neutral flavor that easily absorbs sweetness and spices. Its versatility and gluten-free nature make tapioca a popular choice compared to sago, which is derived from palm starch and has a different texture and origin.
What is Sago? Source and Unique Properties
Sago is a starch extracted from the pith of tropical palm stems, primarily the sago palm (Metroxylon sagu), and is widely used in Southeast Asian desserts like sago pudding. Unlike tapioca, which is derived from cassava root, sago pearls have a slightly softer texture and a more translucent appearance when cooked. Its unique properties include quick gelatinization and a neutral flavor, making it a versatile base ingredient that absorbs flavors while providing a chewy consistency.
Key Differences Between Tapioca and Sago Pearls
Tapioca pudding uses pearls made from cassava starch, offering a chewier texture and translucent appearance, while sago pudding features pearls derived from sago palm starch with a softer, more opaque consistency. Tapioca pearls tend to be more uniform in size and shape, making them ideal for consistent cooking results, whereas sago pearls often vary in size and require longer cooking times to achieve the desired softness. Nutritionally, tapioca pearls contain more carbohydrates and fewer nutrients compared to sago pearls, which typically have higher fiber content and traces of minerals due to their botanical origin.
Texture Comparison: Tapioca vs Sago in Pudding
Tapioca pudding features a smooth, creamy texture with small, translucent pearls that create a chewy bite, while sago pudding offers a slightly softer consistency with larger, more opaque pearls that provide a gelatinous feel. The smaller size of tapioca pearls results in a more uniform mouthfeel compared to the uneven, slightly grainy experience of sago pearls. Both ingredients absorb liquid well, but tapioca maintains a firmer structure, enhancing the overall pudding texture.
Flavor Profile: How Tapioca and Sago Impact Taste
Tapioca pudding offers a mildly sweet, creamy flavor with a subtle hint of coconut or vanilla that enhances its smooth texture. Sago pudding provides a slightly earthier taste with a more gelatinous consistency, creating a unique mouthfeel that distinguishes it from tapioca. Both bases influence the overall dessert by adding distinct textural elements, with tapioca lending chewiness and sago contributing a bouncier quality.
Nutritional Value: Tapioca Pudding vs Sago Pudding
Tapioca pudding, made from cassava starch, typically offers slightly higher carbohydrate content and calories compared to sago pudding, derived from palm starch. Both contain minimal protein and fat, but sago pudding may provide marginally better fiber content and micronutrients like calcium and iron. Choosing between the two depends on dietary goals, with tapioca favoring energy provision and sago contributing modestly to mineral intake.
Cooking Methods and Preparation Tips
Tapioca pudding is traditionally made with small, translucent pearls derived from cassava starch, requiring soaking or boiling to achieve a chewy texture, whereas sago pudding uses starch extracted from tropical palm stems, with pearls that generally cook faster and become more translucent. Cooking tapioca pearls slowly over low heat while stirring prevents clumping and ensures a smooth, creamy consistency, while sago pearls benefit from rinsing before cooking to remove excess starch and help achieve a glossy finish. Both puddings improve in texture after resting, allowing starches to swell fully, but adjusting liquid ratios is important: tapioca demands more liquid for softness, while sago requires careful control to avoid a gluey texture.
Dietary Considerations: Allergies and Restrictions
Tapioca pudding, made from cassava starch, is naturally gluten-free and suitable for those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease, while sago pudding, derived from palm starch, shares similar allergen-friendly properties but may cause issues for individuals sensitive to tropical starches. Both puddings are free from common allergens like dairy and nuts when prepared traditionally, making them suitable for lactose-intolerant and nut-allergic diets. However, consumers with sensitivities to specific starches should choose carefully, as tapioca and sago can trigger digestive discomfort or allergic reactions in rare cases.
Which Pudding Base to Choose: Tapioca or Sago?
Tapioca pudding uses pearls derived from cassava starch, offering a smooth, slightly chewy texture and a neutral flavor that absorbs added ingredients well. Sago pudding, made from starch extracted from palm stems, features larger, more translucent pearls with a firmer bite and a subtly sweet taste. Choosing between tapioca and sago as a pudding base depends on desired texture and flavor intensity, with tapioca providing creamier consistency and sago delivering a more distinct, pleasantly chewy experience.
Tapioca pudding vs Sago pudding for base ingredient Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com