Instant pudding mix offers a quick and convenient preparation method by simply whisking the powder with cold milk, resulting in a smooth and creamy dessert without cooking. Cooked pudding mix requires heating milk and stirring the mixture continuously until thickened, creating a richer texture and deeper flavor profile. Choosing between instant and cooked pudding mixes depends on desired preparation time and taste preference.
Table of Comparison
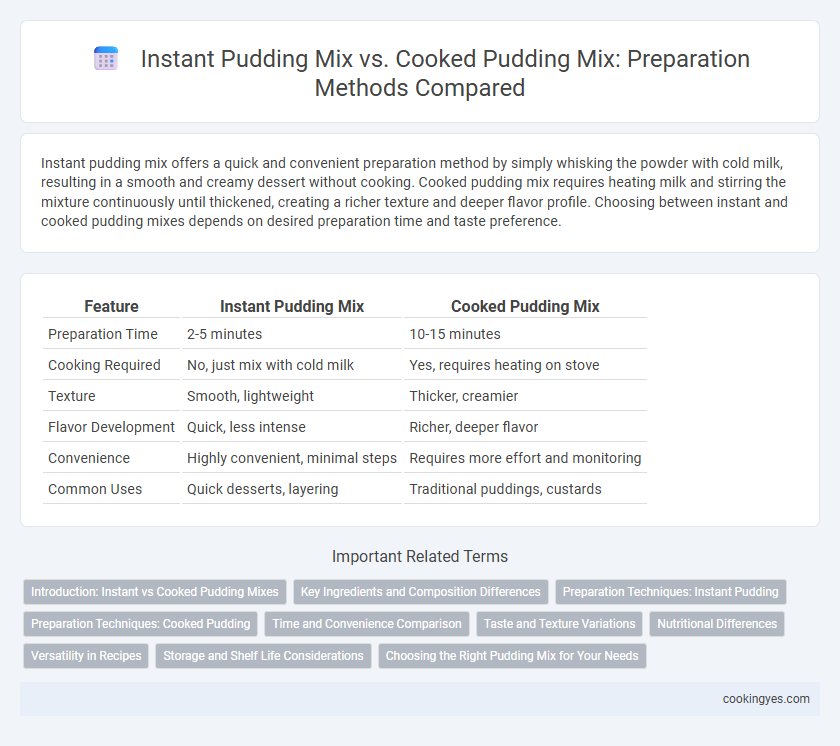
| Feature | Instant Pudding Mix | Cooked Pudding Mix |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Time | 2-5 minutes | 10-15 minutes |
| Cooking Required | No, just mix with cold milk | Yes, requires heating on stove |
| Texture | Smooth, lightweight | Thicker, creamier |
| Flavor Development | Quick, less intense | Richer, deeper flavor |
| Convenience | Highly convenient, minimal steps | Requires more effort and monitoring |
| Common Uses | Quick desserts, layering | Traditional puddings, custards |
Introduction: Instant vs Cooked Pudding Mixes
Instant pudding mix dissolves quickly in cold milk, providing a convenient and time-saving dessert option without the need for cooking. Cooked pudding mix requires heating milk and constant stirring, resulting in a thicker, creamier texture and intensified flavor development. Each method offers distinct preparation experiences, catering to varying preferences for convenience versus traditional cooking.
Key Ingredients and Composition Differences
Instant pudding mix contains pre-gelatinized starches and powdered thickeners that allow it to set quickly without heat, while cooked pudding mix relies on raw starches like cornstarch or flour that gelatinize only when heated. Instant mixes typically include artificial stabilizers and sweeteners to enhance texture and flavor without cooking, whereas cooked pudding ingredients are more traditional, requiring milk and sugar to be combined and heated for proper thickening. The composition differences impact preparation time and texture, with instant pudding delivering a smoother, more gelatinous consistency and cooked pudding offering a creamier, custard-like result.
Preparation Techniques: Instant Pudding
Instant pudding mix requires minimal preparation, simply combining the powder with cold milk and whisking until thickened, eliminating the need for heat. This technique preserves the convenience and speed, making it ideal for quick desserts or last-minute recipes. Instant pudding also offers consistent texture and flavor without the risk of burning or curdling associated with cooked pudding mixtures.
Preparation Techniques: Cooked Pudding
Cooked pudding preparation involves heating the pudding mix with milk on the stove, requiring constant stirring until the mixture thickens to a creamy consistency. This method allows for more control over texture and flavor development, resulting in a richer, smoother dessert compared to instant pudding. Cooking also activates starches more thoroughly, enhancing the pudding's stability and preventing separation during cooling.
Time and Convenience Comparison
Instant pudding mix saves significant preparation time by requiring only mixing with cold milk, making it ready in minutes without cooking. Cooked pudding mix involves heating and constant stirring, extending preparation time but resulting in a creamier texture and richer flavor. Instant mix suits quick desserts and convenience, while cooked mix is preferred for traditional recipes demanding texture and depth.
Taste and Texture Variations
Instant pudding mix offers a smooth, creamy texture with a lighter mouthfeel due to its quick-setting agents, making it ideal for a convenient, no-cook dessert. Cooked pudding mix requires stovetop preparation, producing a thicker, richer texture with a more pronounced, custard-like flavor due to the caramelization and starch gelatinization during cooking. The choice between instant and cooked pudding mix significantly impacts the final dessert's taste depth and texture density, catering to different preferences for convenience versus traditional richness.
Nutritional Differences
Instant pudding mix contains added stabilizers and thickeners, which may slightly alter its nutritional profile by increasing sodium and artificial ingredient content compared to cooked pudding mix. Cooked pudding mix typically uses basic ingredients such as milk, sugar, and cornstarch, resulting in a fresher product with fewer preservatives and potentially lower sodium levels. Both types vary in calorie and sugar content depending on brand formulations, so examining nutrition labels is essential for accurate comparison.
Versatility in Recipes
Instant pudding mix offers superior versatility in recipes, allowing for quick preparation without heat and easy incorporation into no-bake desserts, parfaits, and frostings. Cooked pudding mix, while less convenient, provides a richer texture and depth of flavor that complements baked goods and layered puddings requiring thickening through heating. Both types serve distinct culinary purposes, with instant mixes excelling in time-sensitive recipes and cooked mixes enhancing traditional, cooked dessert profiles.
Storage and Shelf Life Considerations
Instant pudding mix offers extended shelf life and longer storage stability due to its dry, pre-processed ingredients that do not require refrigeration before preparation. Cooked pudding mix, often made from scratch using perishable ingredients like milk and eggs, has a significantly shorter shelf life and must be refrigerated immediately after preparation to prevent spoilage. Proper airtight packaging of instant mixes can maintain freshness for up to two years, while cooked pudding typically lasts only 3 to 4 days when stored in the refrigerator.
Choosing the Right Pudding Mix for Your Needs
Instant pudding mix offers a quick and convenient preparation method by simply whisking the powder with cold milk, making it ideal for fast desserts and beginners. Cooked pudding mix requires heating milk slowly while stirring, resulting in a thicker texture and richer flavor preferred for traditional recipes and more control over consistency. Choosing between these mixes depends on time constraints, desired texture, and flavor intensity for your specific dessert needs.
Instant pudding mix vs Cooked pudding mix for preparation method Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com