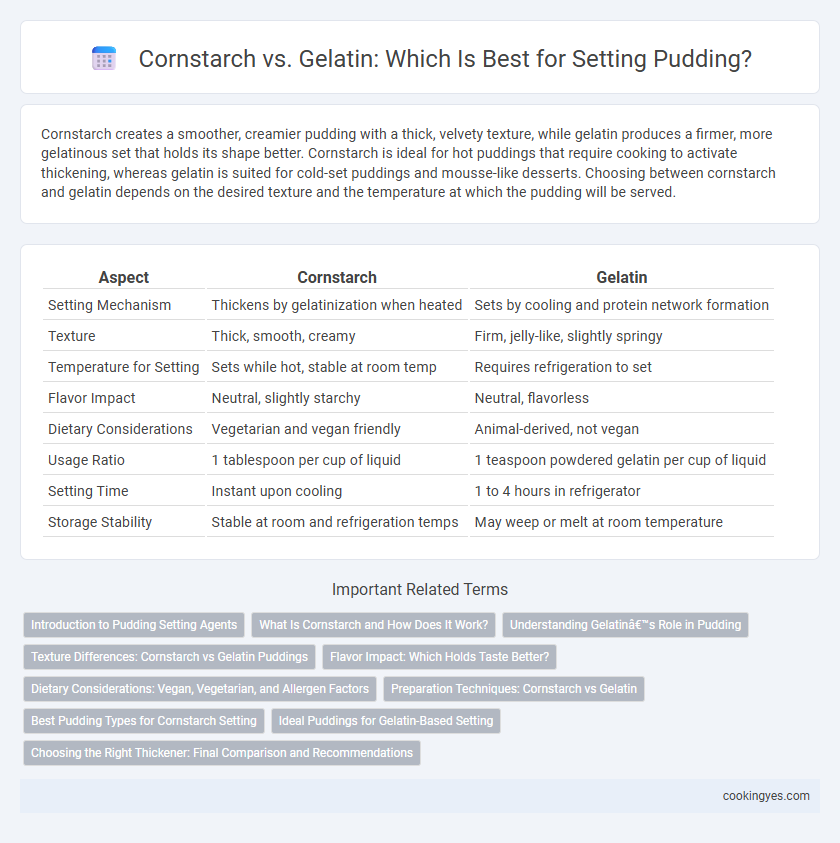
Cornstarch creates a smoother, creamier pudding with a thick, velvety texture, while gelatin produces a firmer, more gelatinous set that holds its shape better. Cornstarch is ideal for hot puddings that require cooking to activate thickening, whereas gelatin is suited for cold-set puddings and mousse-like desserts. Choosing between cornstarch and gelatin depends on the desired texture and the temperature at which the pudding will be served.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cornstarch | Gelatin |
|---|---|---|
| Setting Mechanism | Thickens by gelatinization when heated | Sets by cooling and protein network formation |
| Texture | Thick, smooth, creamy | Firm, jelly-like, slightly springy |
| Temperature for Setting | Sets while hot, stable at room temp | Requires refrigeration to set |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, slightly starchy | Neutral, flavorless |
| Dietary Considerations | Vegetarian and vegan friendly | Animal-derived, not vegan |
| Usage Ratio | 1 tablespoon per cup of liquid | 1 teaspoon powdered gelatin per cup of liquid |
| Setting Time | Instant upon cooling | 1 to 4 hours in refrigerator |
| Storage Stability | Stable at room and refrigeration temps | May weep or melt at room temperature |
Introduction to Pudding Setting Agents
Cornstarch and gelatin are common pudding setting agents that influence texture and stability. Cornstarch thickens pudding through gelatinization when heated with liquid, producing a smooth and creamy consistency. Gelatin, derived from collagen, sets pudding by forming a gel as it cools, resulting in a more elastic and firm texture.
What Is Cornstarch and How Does It Work?
Cornstarch is a fine, powdery starch derived from the endosperm of corn kernels, widely used as a thickening agent in puddings due to its ability to gelatinize when heated with liquid. Upon heating, cornstarch granules absorb water and swell, creating a viscous network that thickens and sets the pudding with a smooth, creamy texture. Unlike gelatin, cornstarch produces a more stable, opaque pudding that withstands heat and reheating without losing its firmness.
Understanding Gelatin’s Role in Pudding
Gelatin acts as a protein-based gelling agent in pudding, creating a smooth, elastic texture by forming a network that traps water molecules. Unlike cornstarch, which thickens pudding through starch gelatinization and results in a creamy, opaque consistency, gelatin provides a clearer, more stable set with a slight jiggle. Understanding gelatin's role helps achieve a delicate, melt-in-the-mouth pudding that holds its shape well when chilled.
Texture Differences: Cornstarch vs Gelatin Puddings
Cornstarch creates puddings with a creamy, thick texture that is smooth and slightly dense, offering a more opaque appearance. Gelatin-based puddings set firmer and have a more jiggly, translucent quality, providing a lighter, more gelatinous mouthfeel. The choice between cornstarch and gelatin significantly impacts the pudding's final texture, with cornstarch yielding a traditional custard-like consistency and gelatin producing a delicate, wobblier dessert.
Flavor Impact: Which Holds Taste Better?
Cornstarch-based pudding preserves the natural flavor of ingredients due to its neutral taste and smooth texture, allowing the primary flavors to shine without interference. Gelatin, while providing a clearer and firmer set, can sometimes impart a subtle aftertaste that alters delicate flavors. For recipes prioritizing pure taste retention, cornstarch is generally the preferred setting agent.
Dietary Considerations: Vegan, Vegetarian, and Allergen Factors
Cornstarch is a plant-based thickener suitable for vegan and vegetarian diets, making it an excellent allergy-friendly option free from animal-derived ingredients. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, is unsuitable for vegans and vegetarians and may pose allergen concerns for those with sensitivities to animal proteins. Choosing cornstarch supports dietary restrictions while providing a smooth, stable pudding texture without compromising on allergen safety.
Preparation Techniques: Cornstarch vs Gelatin
Cornstarch sets pudding through heat-activated thickening, requiring cooking the starch with liquid until it reaches a translucent, gel-like consistency; precise temperature control prevents clumping and ensures smooth texture. Gelatin sets pudding by cooling a dissolved protein solution, creating a firm yet delicate gel without heat, ideal for recipes that benefit from a melt-in-the-mouth feel. Proper preparation techniques for cornstarch involve gradual heating and constant stirring, while gelatin requires blooming in cold liquid before dissolving in warmth, each affecting the pudding's final texture and stability.
Best Pudding Types for Cornstarch Setting
Cornstarch is ideal for creamy puddings like vanilla, chocolate, and butterscotch because it creates a smooth, stable texture without gelatin's bounce. It excels in custard-style desserts that require gentle thickening and can withstand reheating without losing firmness. Cornstarch-based puddings are especially suited for eggless recipes, providing a reliable, glossy finish and a rich mouthfeel.
Ideal Puddings for Gelatin-Based Setting
Gelatin-based puddings provide a smooth, melt-in-the-mouth texture that is ideal for creamy desserts like mousse and panna cotta, where a delicate yet firm set is desired. Unlike cornstarch, gelatin creates a transparent, glossy finish and maintains a flexible consistency that holds shape without becoming rubbery. Recipes that benefit most from gelatin include rich, dairy-based puddings and layered parfaits where clarity and lightness enhance the overall presentation and taste.
Choosing the Right Thickener: Final Comparison and Recommendations
Cornstarch provides a smooth, opaque texture and imparts a classic pudding firmness that holds well when chilled, making it ideal for traditional custard-style puddings. Gelatin creates a clearer, jelly-like consistency with a delicate wobble, perfect for fruit-infused or molded puddings requiring a light, airy set. For creamy, stable puddings, cornstarch is preferred, while gelatin is better suited for desserts needing a translucent, delicate finish and quicker setting time.
Cornstarch vs Gelatin for pudding setting Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com