Traditional pita, made from wheat flour, offers a soft texture and authentic flavor that complements falafel perfectly. Gluten-free pita, crafted from alternative flours like rice or chickpea, caters to those with gluten sensitivities without sacrificing the essential pocket structure. Choosing between the two depends on dietary needs, but both serve as excellent carriers for falafel and fresh toppings.
Table of Comparison
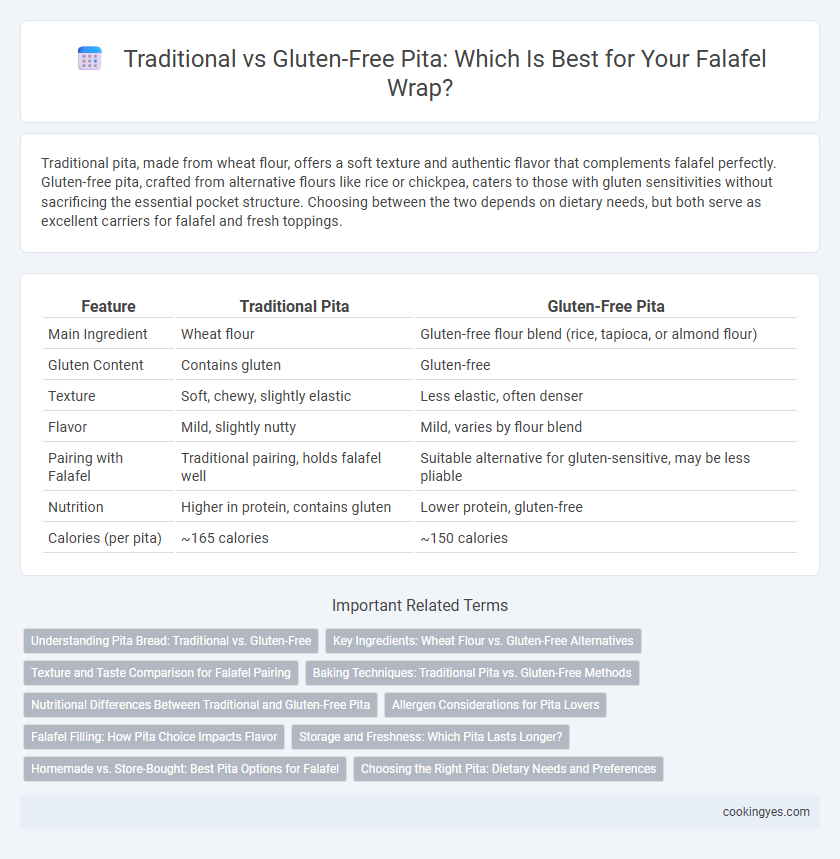
| Feature | Traditional Pita | Gluten-Free Pita |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredient | Wheat flour | Gluten-free flour blend (rice, tapioca, or almond flour) |
| Gluten Content | Contains gluten | Gluten-free |
| Texture | Soft, chewy, slightly elastic | Less elastic, often denser |
| Flavor | Mild, slightly nutty | Mild, varies by flour blend |
| Pairing with Falafel | Traditional pairing, holds falafel well | Suitable alternative for gluten-sensitive, may be less pliable |
| Nutrition | Higher in protein, contains gluten | Lower protein, gluten-free |
| Calories (per pita) | ~165 calories | ~150 calories |
Understanding Pita Bread: Traditional vs. Gluten-Free
Traditional pita bread is made from wheat flour, offering a soft texture and slightly chewy bite that complements the crispy falafel perfectly. Gluten-free pita substitutes wheat with alternative flours like rice, almond, or chickpea, providing a suitable option for those with gluten intolerance while maintaining a similar pocket structure. Both types aim to enhance the falafel experience, balancing taste and dietary needs.
Key Ingredients: Wheat Flour vs. Gluten-Free Alternatives
Traditional pita bread relies on wheat flour, which provides gluten essential for its characteristic soft, chewy texture and ability to puff during baking, making it ideal for holding falafel fillings. Gluten-free pita substitutes use alternative flours such as rice, almond, or tapioca, often combined with binders like xanthan gum to mimic gluten's elasticity. These gluten-free ingredients result in a denser texture but offer an accessible option for those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
Texture and Taste Comparison for Falafel Pairing
Traditional pita offers a soft, chewy texture with a slight elasticity that complements the crispiness of falafel, enhancing the overall mouthfeel. Gluten-free pita often has a denser, crumbly texture due to alternative flours, which can contrast with the falafel's crunch, sometimes overwhelming the taste balance. Taste-wise, traditional pita has a mild, slightly yeasty flavor that harmonizes with savory falafel spices, while gluten-free versions may have a nuttier or earthier profile, influencing the flavor pairing differently.
Baking Techniques: Traditional Pita vs. Gluten-Free Methods
Traditional pita bread for falafel employs high-temperature baking in stone ovens, creating a puffed, airy pocket from a dough rich in gluten, which provides elasticity and structure. Gluten-free pita relies on alternative flours like rice or chickpea, combined with binding agents such as xanthan gum or psyllium husk, requiring lower baking temperatures and longer proofing to achieve similar texture without gluten's elasticity. Advanced gluten-free methods often incorporate steam or hydration techniques during baking to replicate the traditional pita's soft, pliable crust essential for holding falafel fillings.
Nutritional Differences Between Traditional and Gluten-Free Pita
Traditional pita bread, typically made from wheat flour, contains gluten and offers a significant source of carbohydrates, protein, and some dietary fiber, supporting sustained energy release. Gluten-free pita alternatives, often crafted from rice flour, almond flour, or chickpea flour, generally provide lower protein content but may offer higher fiber and healthier fats depending on the ingredients used. Nutritionally, traditional pita tends to have a higher glycemic index, while gluten-free options may support better blood sugar control and accommodate those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
Allergen Considerations for Pita Lovers
Traditional pita bread, made from wheat flour, contains gluten and is unsuitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. Gluten-free pita options, typically crafted from rice flour, chickpea flour, or almond flour, provide a safe alternative for those with allergies or dietary restrictions. Choosing gluten-free pita ensures falafel lovers with allergen sensitivities can enjoy their meal without adverse reactions.
Falafel Filling: How Pita Choice Impacts Flavor
Traditional pita's chewy texture and slightly tangy yeast flavor enhance the savory spices of falafel filling, creating a harmonious taste experience. Gluten-free pita, often made from rice or almond flour, offers a milder, sometimes grainier base that can let the falafel's herbs and spices stand out more distinctly. The pita choice directly influences the overall flavor balance, with traditional pita delivering a robust bite and gluten-free pita providing a lighter, more subtle complement.
Storage and Freshness: Which Pita Lasts Longer?
Traditional pita, made from wheat flour, typically retains freshness for 3-4 days when stored at room temperature and up to a week when refrigerated, thanks to its gluten structure that helps maintain moisture. Gluten-free pita, often made with alternative flours such as rice or almond, has a shorter shelf life and tends to dry out faster, usually remaining fresh for only 1-2 days at room temperature. For longer storage, freezing both types preserves freshness for up to 3 months, though thawed gluten-free pita may exhibit slightly reduced texture quality compared to traditional pita.
Homemade vs. Store-Bought: Best Pita Options for Falafel
Homemade traditional pita offers a soft, chewy texture and authentic flavor that pairs perfectly with falafel, while gluten-free pita provides a necessary alternative for those with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, though it may lack the same pliability. Store-bought traditional pita can be convenient but often contains preservatives and less freshness compared to homemade versions. For gluten-free options, homemade recipes typically yield better control of ingredients and texture than mass-produced store-bought brands, enhancing the overall falafel experience.
Choosing the Right Pita: Dietary Needs and Preferences
Traditional pita made from wheat flour provides a chewy texture and authentic flavor that complements falafel perfectly, but contains gluten, which may trigger sensitivities or celiac disease. Gluten-free pita options use alternative flours like rice, almond, or chickpea flour, offering suitable choices for those with gluten intolerance without sacrificing the ability to hold falafel and toppings. Selecting the right pita depends on balancing taste preference with dietary restrictions to ensure both enjoyment and digestive comfort.
Traditional Pita vs Gluten-Free Pita for falafel Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com