Pita bread offers a soft, fluffy texture with a pocket that holds gyro fillings securely, making it an ideal choice for gyros. Tortilla, being thinner and more pliable, wraps around ingredients easily but lacks the traditional authentic feel of a gyro. Choosing pita enhances the classic gyro experience by complementing the savory meats and fresh toppings with its slightly chewy and airy consistency.
Table of Comparison
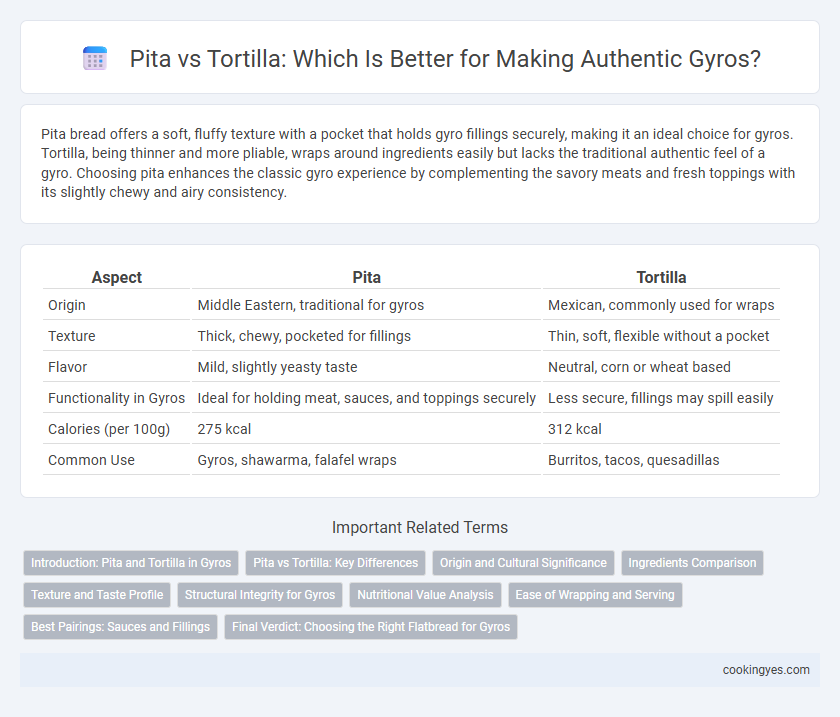
| Aspect | Pita | Tortilla |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Middle Eastern, traditional for gyros | Mexican, commonly used for wraps |
| Texture | Thick, chewy, pocketed for fillings | Thin, soft, flexible without a pocket |
| Flavor | Mild, slightly yeasty taste | Neutral, corn or wheat based |
| Functionality in Gyros | Ideal for holding meat, sauces, and toppings securely | Less secure, fillings may spill easily |
| Calories (per 100g) | 275 kcal | 312 kcal |
| Common Use | Gyros, shawarma, falafel wraps | Burritos, tacos, quesadillas |
Introduction: Pita and Tortilla in Gyros
Pita bread, a traditional Middle Eastern flatbread, offers a soft, pocket-like texture ideal for holding gyro fillings without spilling, making it a popular choice in authentic gyro preparation. Tortillas, primarily a staple in Mexican cuisine, differ with their thinner, flexible structure, which can accommodate gyro ingredients but may not provide the same containment or flavor profile as pita. The distinct texture and cultural origin of pita make it the preferred bread for gyros, enhancing the overall eating experience through its sturdy yet tender characteristics.
Pita vs Tortilla: Key Differences
Pita and tortilla differ significantly in texture and origin, with pita being a soft, leavened flatbread from Middle Eastern cuisine, while tortillas are unleavened and traditionally made from corn or wheat in Mexican cuisine. Pita has a pocket that holds fillings securely, making it ideal for gyros, whereas tortillas are more flexible and wrap around ingredients without a pocket. The choice between pita and tortilla affects the gyro experience; pita offers a slightly chewy bite and authentic flavor, while tortilla provides a thinner, more pliable option.
Origin and Cultural Significance
Pita, originating from the Middle East, holds a deep cultural significance as a traditional bread used in Mediterranean and Levantine cuisines, especially for dishes like gyros. Unlike the tortilla, which hails from Mesoamerican culture and is made from corn or wheat flour, pita is characterized by its pocket that is ideal for stuffing with gyro meat and toppings. The authentic use of pita in gyros reflects centuries-old culinary practices rooted in Greek and Middle Eastern food heritage, emphasizing its authenticity and cultural value.
Ingredients Comparison
Pita and tortilla differ significantly in ingredients, with pita traditionally made from wheat flour, yeast, water, and salt, creating a soft, pocketed bread ideal for holding fillings like gyro meat and toppings. Tortillas, primarily made from corn or wheat flour without yeast, result in a thinner, more flexible flatbread that lacks the pita's characteristic pocket. The yeast in pita contributes to its airy texture, which is preferred for gyros, while tortillas offer a denser, chewier base commonly used in Mexican cuisine.
Texture and Taste Profile
Pita bread offers a soft, pillowy texture with a slight chewiness that complements the juicy, savory flavors of gyro meat, providing an authentic Mediterranean taste experience. Tortillas, typically thinner and more pliable, have a mild, neutral flavor that can sometimes lack the depth and character needed to enhance traditional gyro spices. The slightly toasted, airy pocket of pita traps juices and toppings better, maintaining a balanced bite and preventing sogginess often encountered with tortillas.
Structural Integrity for Gyros
Pita bread offers superior structural integrity compared to tortillas when used for gyros due to its pocket-like design that securely holds fillings without tearing. The thicker, fluffier texture of pita provides enhanced support against the weight and moisture of gyro ingredients such as meat, vegetables, and sauces. Unlike thin, flexible tortillas, pita maintains shape and prevents leakage, ensuring a mess-free gyro eating experience.
Nutritional Value Analysis
Pita bread typically contains around 160 calories, 33 grams of carbohydrates, and 5 grams of protein per serving, offering a moderate glycemic index suitable for sustained energy release in gyros. Tortillas, especially flour varieties, often have higher fat content--about 5 to 8 grams--and similar carbohydrate levels but may contain fewer fibers, influencing digestion and nutrient absorption. Choosing pita over tortillas for gyros provides a slightly better balance of macronutrients and fiber content, enhancing overall nutritional value for a traditional Mediterranean-style meal.
Ease of Wrapping and Serving
Pita bread's pocket design allows easy stuffing and secure wrapping, making it ideal for gyros as it holds fillings firmly during eating. Tortillas are more flexible but lack a sealed pocket, requiring careful folding to prevent ingredients from spilling. Pita's sturdier structure enhances serving convenience and reduces mess, especially for portable or street food settings.
Best Pairings: Sauces and Fillings
Pita bread, with its pocket structure and soft texture, best complements traditional gyro fillings like seasoned lamb, tzatziki sauce, tomatoes, and onions, enhancing the Mediterranean flavor profile. Tortillas offer a flexible wrap ideal for fusion gyros with bold sauces such as spicy harissa or creamy avocado, catering to a variety of global tastes. Choosing pita preserves authentic gyro tastes, while tortillas provide versatility for creative, diverse fillings and sauces.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Flatbread for Gyros
Pita offers a thicker, pocket-style structure ideal for holding traditional gyro fillings like seasoned meat, tzatziki, and fresh vegetables, ensuring minimal spillage. Tortillas provide a thinner, more flexible option that wraps easily but may lack the sturdy support needed for heavier gyro ingredients. For an authentic gyro experience, pita remains the preferred flatbread, balancing texture and functionality perfectly.
Pita vs Tortilla for gyros Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com