Gluten-free pita offers a safe alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, preventing adverse reactions and digestive discomfort. Regular pita, made with wheat flour, contains gluten and is unsuitable for those with gluten sensitivities but provides traditional texture and flavor. Choosing gluten-free pita supports dietary needs without compromising on the enjoyability of pita-based meals.
Table of Comparison
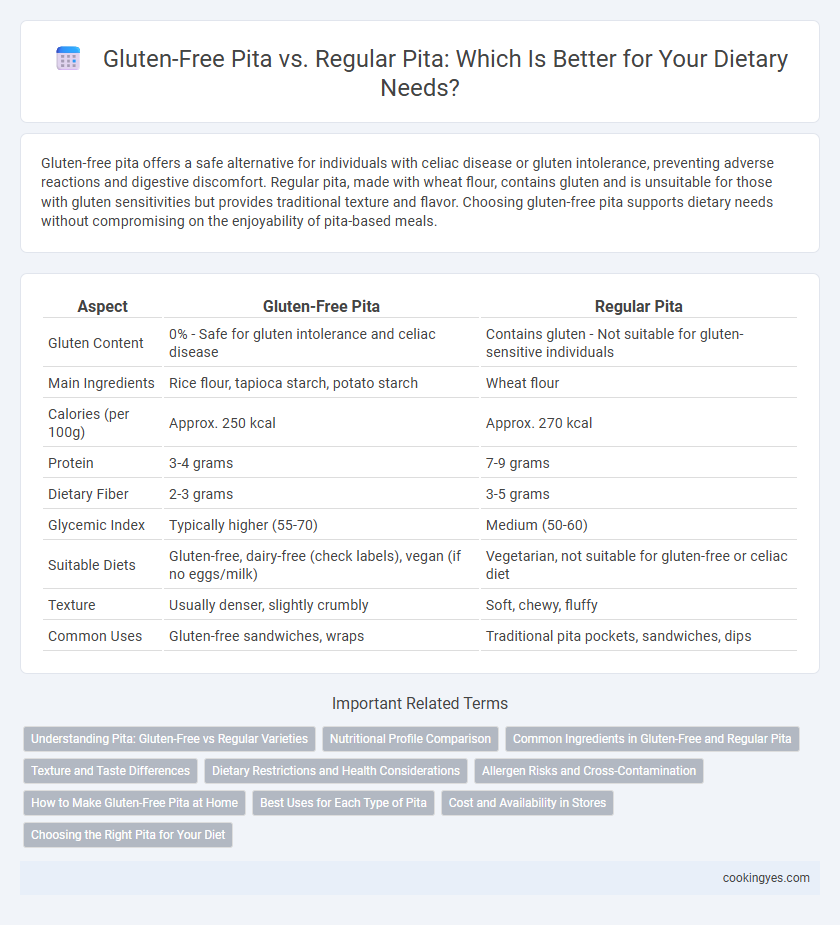
| Aspect | Gluten-Free Pita | Regular Pita |
|---|---|---|
| Gluten Content | 0% - Safe for gluten intolerance and celiac disease | Contains gluten - Not suitable for gluten-sensitive individuals |
| Main Ingredients | Rice flour, tapioca starch, potato starch | Wheat flour |
| Calories (per 100g) | Approx. 250 kcal | Approx. 270 kcal |
| Protein | 3-4 grams | 7-9 grams |
| Dietary Fiber | 2-3 grams | 3-5 grams |
| Glycemic Index | Typically higher (55-70) | Medium (50-60) |
| Suitable Diets | Gluten-free, dairy-free (check labels), vegan (if no eggs/milk) | Vegetarian, not suitable for gluten-free or celiac diet |
| Texture | Usually denser, slightly crumbly | Soft, chewy, fluffy |
| Common Uses | Gluten-free sandwiches, wraps | Traditional pita pockets, sandwiches, dips |
Understanding Pita: Gluten-Free vs Regular Varieties
Gluten-free pita is crafted using alternative flours such as rice, almond, or chickpea, catering to individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance by eliminating gluten proteins found in traditional wheat-based pita. Regular pita contains gluten, a protein that provides elasticity and chewiness, making it unsuitable for those with gluten sensitivities but ideal for those without dietary restrictions seeking classic texture and flavor. Selecting between gluten-free and regular pita hinges on dietary needs and digestive health, with gluten-free options offering safe, inclusive alternatives without compromising the sandwich-style convenience of pita bread.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Gluten-free pita offers a viable alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, typically made from rice flour, tapioca starch, and potato starch, resulting in lower protein and fiber content compared to regular pita. Regular pita, primarily made from wheat flour, contains more gluten, which contributes to higher protein levels and better texture, along with greater amounts of dietary fiber and essential nutrients like B vitamins and iron. Choosing between gluten-free and regular pita depends on the specific dietary needs regarding gluten intolerance and the desired nutritional intake, as gluten-free versions may lack some beneficial nutrients found in traditional wheat-based pita.
Common Ingredients in Gluten-Free and Regular Pita
Gluten-free pita typically contains alternative flours such as rice flour, tapioca starch, and potato starch to replace wheat flour found in regular pita, which contains gluten. Both types often include water, yeast, salt, and olive oil, but gluten-free versions may also incorporate xanthan gum or guar gum to improve texture and elasticity. Understanding these ingredient differences is essential for those managing gluten intolerance or celiac disease while seeking similar flavors and textures.
Texture and Taste Differences
Gluten-free pita often has a denser and crumbly texture compared to the soft, chewy consistency of regular pita, which is due to the absence of gluten's elastic properties. Taste differences are noticeable as gluten-free pita can have a slightly grainy or nutty flavor depending on the alternative flours used, contrasting with the mild, slightly yeasty flavor of traditional wheat-based pita. For dietary needs, gluten-free pita provides a safe option for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, while regular pita offers a familiar texture and taste for those without gluten restrictions.
Dietary Restrictions and Health Considerations
Gluten-free pita is essential for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, as it eliminates the risk of adverse reactions caused by gluten proteins found in regular pita. While regular pita typically contains wheat flour, which provides a higher gluten content, gluten-free versions use alternative flours such as rice, almond, or chickpea, catering to various dietary restrictions. Choosing gluten-free pita supports digestive health and prevents inflammation in sensitive individuals, making it a critical option for maintaining a balanced, allergen-friendly diet.
Allergen Risks and Cross-Contamination
Gluten-free pita offers a safer alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity by eliminating wheat-based gluten proteins that trigger allergic reactions. However, cross-contamination risks remain high if gluten-free pita is produced or stored alongside regular pita containing wheat flour. Strict manufacturing protocols and separate preparation areas are essential to minimize allergen exposure and ensure the safety of gluten-free pita products for sensitive dietary needs.
How to Make Gluten-Free Pita at Home
Making gluten-free pita at home involves using alternative flours such as rice flour, tapioca starch, or a gluten-free flour blend to replicate the traditional dough texture. Incorporating xanthan gum or psyllium husk powder provides elasticity and structure, essential for the characteristic pita pocket formation. Baking the dough at high temperatures on a preheated surface like a cast-iron skillet allows the gluten-free pita to puff up similarly to regular pita, accommodating dietary needs for gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
Best Uses for Each Type of Pita
Gluten-free pita is ideal for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, making it suitable for wraps and sandwiches with naturally gluten-free fillings like grilled vegetables or lean meats. Regular pita, made from wheat flour, offers a softer texture and elasticity beneficial for traditional uses such as stuffing with falafel, gyros, or dipping in hummus. Choosing between gluten-free and regular pita depends on dietary restrictions and the desired texture for recipes like pita chips or pocket sandwiches.
Cost and Availability in Stores
Gluten-free pita typically costs more than regular pita due to specialized ingredients and manufacturing processes, making it less budget-friendly for daily consumption. Availability of gluten-free pita is limited in most grocery stores, often requiring a visit to health food stores or online purchase, whereas regular pita bread is widely stocked in almost all supermarkets. Consumers with dietary needs may face challenges in consistent access and affordability when choosing gluten-free pita compared to regular pita options.
Choosing the Right Pita for Your Diet
Gluten-free pita offers a suitable alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, providing a safe option without compromising taste. Regular pita, made from wheat flour, contains gluten and offers a traditional texture and flavor preferred by those without gluten restrictions. Selecting the right pita depends on your dietary needs, whether prioritizing gluten-free ingredients for health reasons or opting for regular pita to enjoy its familiar taste and nutritional profile.
Gluten-free pita vs regular pita for dietary needs Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com