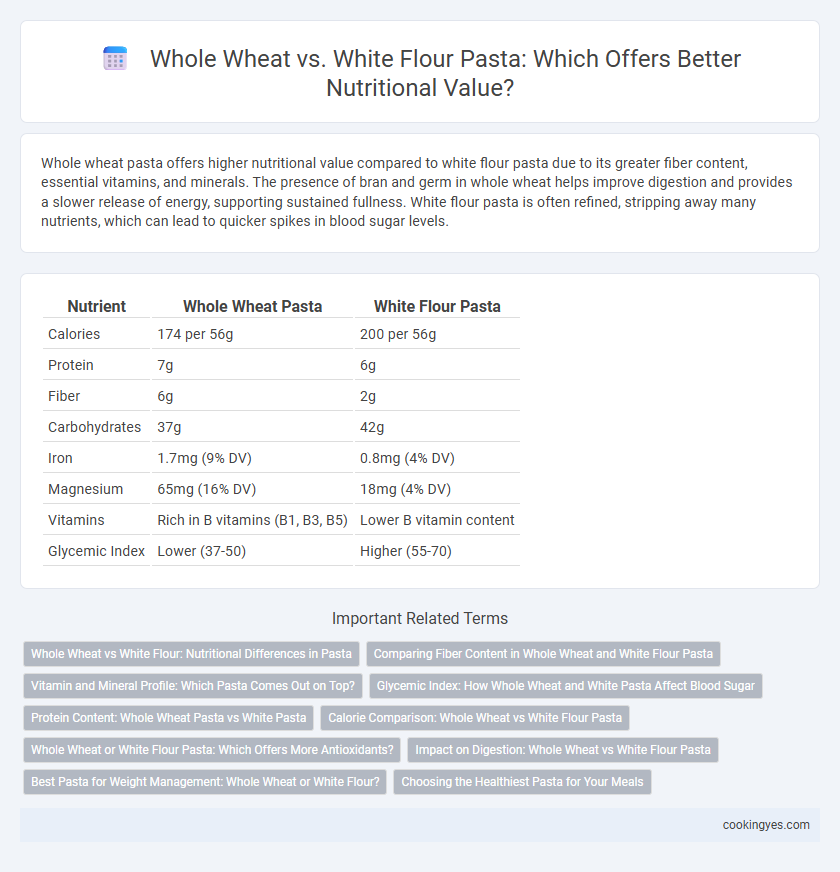
Whole wheat pasta offers higher nutritional value compared to white flour pasta due to its greater fiber content, essential vitamins, and minerals. The presence of bran and germ in whole wheat helps improve digestion and provides a slower release of energy, supporting sustained fullness. White flour pasta is often refined, stripping away many nutrients, which can lead to quicker spikes in blood sugar levels.
Table of Comparison
| Nutrient | Whole Wheat Pasta | White Flour Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 174 per 56g | 200 per 56g |
| Protein | 7g | 6g |
| Fiber | 6g | 2g |
| Carbohydrates | 37g | 42g |
| Iron | 1.7mg (9% DV) | 0.8mg (4% DV) |
| Magnesium | 65mg (16% DV) | 18mg (4% DV) |
| Vitamins | Rich in B vitamins (B1, B3, B5) | Lower B vitamin content |
| Glycemic Index | Lower (37-50) | Higher (55-70) |
Whole Wheat vs White Flour: Nutritional Differences in Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to white flour pasta, providing essential nutrients like magnesium, iron, and B vitamins. The bran and germ in whole wheat flour retain more antioxidants and phytochemicals, which are often lost during the refining process of white flour. White flour pasta has a higher glycemic index, leading to quicker blood sugar spikes, while whole wheat pasta promotes better digestion and sustained energy levels.
Comparing Fiber Content in Whole Wheat and White Flour Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains significantly higher fiber content than white flour pasta, with about 6 grams of dietary fiber per 2-ounce serving compared to only 2 grams in white pasta. The increased fiber in whole wheat pasta promotes better digestive health and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Choosing whole wheat pasta provides essential nutrients and sustained energy release, making it a healthier option for people seeking to increase fiber intake.
Vitamin and Mineral Profile: Which Pasta Comes Out on Top?
Whole wheat pasta offers a superior vitamin and mineral profile compared to white flour pasta, containing higher levels of B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and zinc essential for energy metabolism and immune function. The bran and germ retained in whole wheat contribute to elevated fiber and antioxidant content, which support digestive health and reduce oxidative stress. White flour pasta, stripped of these nutrient-rich components during processing, provides fewer micronutrients but may have a softer texture preferred in some culinary applications.
Glycemic Index: How Whole Wheat and White Pasta Affect Blood Sugar
Whole wheat pasta has a lower glycemic index (GI) ranging from 37 to 50, which helps in slower digestion and a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels compared to white pasta with a higher GI of about 50 to 70. Lower GI foods like whole wheat pasta improve insulin sensitivity and help maintain energy levels, making it a better choice for people managing diabetes or blood sugar issues. Studies indicate that consuming whole wheat pasta reduces post-meal blood glucose spikes, contributing to better long-term metabolic health.
Protein Content: Whole Wheat Pasta vs White Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains approximately 7-8 grams of protein per cooked cup, which is higher than the 5-6 grams found in white pasta made from refined flour. The increased protein content in whole wheat pasta contributes to better muscle repair and prolonged satiety. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports enhanced nutritional benefits by providing more fiber and essential nutrients alongside its superior protein levels.
Calorie Comparison: Whole Wheat vs White Flour Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains approximately 150-170 calories per cooked cup, while white flour pasta typically ranges from 190-220 calories per cooked cup, making whole wheat pasta a lower-calorie option. The higher fiber content in whole wheat pasta contributes to increased satiety and slower digestion compared to refined white flour pasta. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better blood sugar regulation and sustained energy release due to its lower glycemic index and richer nutrient profile.
Whole Wheat or White Flour Pasta: Which Offers More Antioxidants?
Whole wheat pasta contains significantly higher levels of antioxidants like phenolic acids and flavonoids compared to white flour pasta, due to the retention of bran and germ layers in whole wheat. These antioxidants play a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, offering potential health benefits such as improved heart health and reduced risk of chronic diseases. In contrast, white flour pasta is stripped of these nutrient-rich components, resulting in considerably lower antioxidant content and less nutritional value.
Impact on Digestion: Whole Wheat vs White Flour Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains more dietary fiber than white flour pasta, promoting better digestive health by enhancing bowel regularity and preventing constipation. The higher fiber content in whole wheat pasta also supports a slower glucose absorption rate, which can benefit gut microbiota and overall metabolic function. In contrast, white flour pasta lacks sufficient fiber, leading to quicker digestion and potential blood sugar spikes, which may negatively impact digestive comfort and long-term gut health.
Best Pasta for Weight Management: Whole Wheat or White Flour?
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber content and essential nutrients like magnesium and zinc, which promote satiety and support weight management by regulating blood sugar levels. White flour pasta, being more processed, has a higher glycemic index leading to quicker spikes in blood sugar and increased hunger. Choosing whole wheat pasta is generally better for sustained energy release and appetite control during weight management.
Choosing the Healthiest Pasta for Your Meals
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber content and essential nutrients like magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins compared to white flour pasta, which is often stripped of these during processing. The increased fiber in whole wheat pasta supports better digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels, making it a more nutritious choice for balanced meals. Selecting whole wheat pasta contributes to sustained energy release and improved heart health, aligning with dietary goals centered on nutrient density and wellness.
Whole Wheat vs White Flour for Nutritional Value Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com