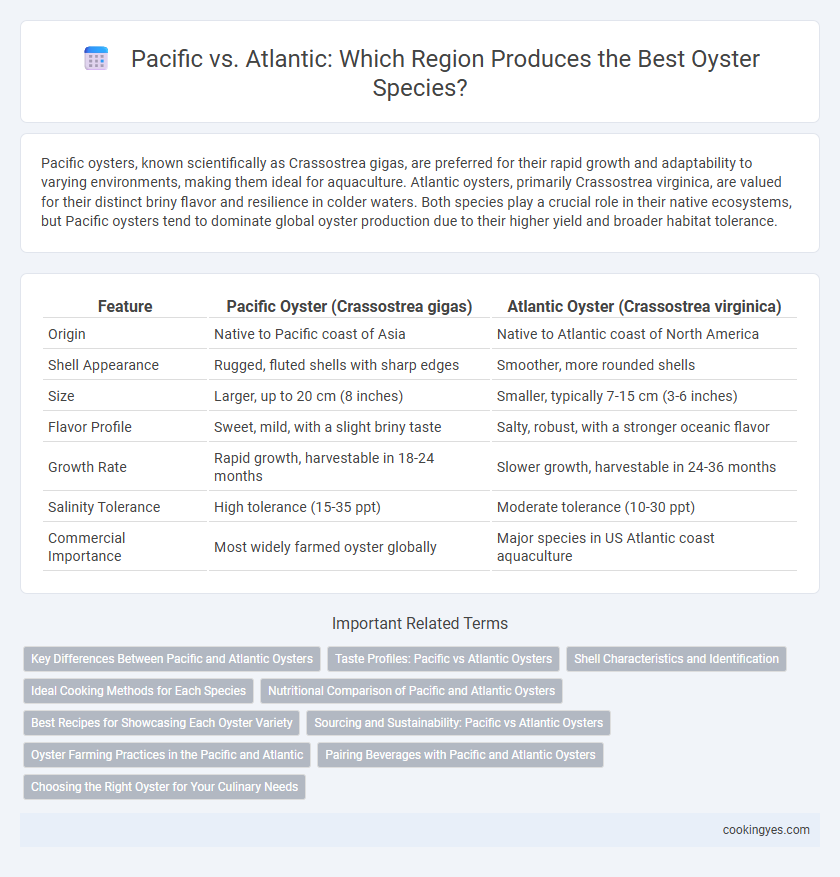
Pacific oysters, known scientifically as Crassostrea gigas, are preferred for their rapid growth and adaptability to varying environments, making them ideal for aquaculture. Atlantic oysters, primarily Crassostrea virginica, are valued for their distinct briny flavor and resilience in colder waters. Both species play a crucial role in their native ecosystems, but Pacific oysters tend to dominate global oyster production due to their higher yield and broader habitat tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) | Atlantic Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Native to Pacific coast of Asia | Native to Atlantic coast of North America |
| Shell Appearance | Rugged, fluted shells with sharp edges | Smoother, more rounded shells |
| Size | Larger, up to 20 cm (8 inches) | Smaller, typically 7-15 cm (3-6 inches) |
| Flavor Profile | Sweet, mild, with a slight briny taste | Salty, robust, with a stronger oceanic flavor |
| Growth Rate | Rapid growth, harvestable in 18-24 months | Slower growth, harvestable in 24-36 months |
| Salinity Tolerance | High tolerance (15-35 ppt) | Moderate tolerance (10-30 ppt) |
| Commercial Importance | Most widely farmed oyster globally | Major species in US Atlantic coast aquaculture |
Key Differences Between Pacific and Atlantic Oysters
Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) exhibit faster growth rates and higher salinity tolerance compared to Atlantic oysters (Crassostrea virginica), which thrive in lower salinity environments. Pacific oysters feature ruffled, fluted shells with a more uniform gray-green coloring, while Atlantic oysters have rougher, more irregular shells with brown or tan hues. Flavor profiles differ, as Pacific oysters offer a sweet, mild taste with a creamy texture, whereas Atlantic oysters present a brinier, more robust flavor with a firmer bite.
Taste Profiles: Pacific vs Atlantic Oysters
Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) typically offer a sweeter, fruitier flavor with a creamy texture, often accompanied by melon or cucumber notes. Atlantic oysters (Crassostrea virginica) are known for their brinier, saltier taste with a firmer texture and pronounced mineral undertones. The distinct taste profiles are influenced by their native waters, where Pacific oysters thrive in cooler, nutrient-rich Pacific Ocean environments and Atlantic oysters develop flavor complexity from the dynamic salinity and temperature variations of the Atlantic coastline.
Shell Characteristics and Identification
Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) display deeply fluted, rough shells with an irregular profile, often exhibiting a greenish or bluish hue. Atlantic oysters (Crassostrea virginica) have smoother, more rounded shells with less pronounced ridges and typically a grayish or brown coloration. Identification relies on shell texture, shape, and color, where Pacific oysters' robust, rugged appearance contrasts with the Atlantic oysters' subtler, more uniform shell features.
Ideal Cooking Methods for Each Species
Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) are prized for their milder, sweeter flavor and plumper texture, making them ideal for grilling or baking, which enhances their natural brininess while maintaining juiciness. Atlantic oysters (Crassostrea virginica) have a brinier, more robust taste and firmer flesh, best suited for roasting or frying methods that complement their bold flavor and preserve their structure. Both species benefit from quick, high-heat cooking to avoid toughness, but Pacific oysters excel with gentle heat, whereas Atlantic oysters withstand more intense preparation.
Nutritional Comparison of Pacific and Atlantic Oysters
Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, compared to Atlantic oysters (Crassostrea virginica), promoting cardiovascular health. Atlantic oysters provide more zinc and vitamin B12, essential for immune function and energy metabolism. Both species offer a rich source of protein and essential minerals, but Pacific oysters have slightly higher caloric and fat content, enhancing their nutritional profile.
Best Recipes for Showcasing Each Oyster Variety
Pacific oysters, known for their sweet, mild flavor and firm texture, are best showcased in recipes like grilled oysters with garlic butter or lightly pickled in ceviche, which highlight their delicate nuances. Atlantic oysters offer a brinier, more robust taste and creamier texture, making them ideal for classic dishes such as oyster stew or Rockefeller, where rich ingredients complement their natural saltiness. Utilizing these recipes accentuates the unique qualities of each oyster species, enhancing flavor profiles that cater to diverse palates and culinary preferences.
Sourcing and Sustainability: Pacific vs Atlantic Oysters
Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) are widely farmed due to their fast growth rates and adaptability, making them a sustainable choice with lower environmental impact compared to wild harvesting. Atlantic oysters (Crassostrea virginica) are often sourced from wild populations or traditional aquaculture, which can lead to overharvesting risks and habitat degradation if not managed responsibly. Sustainable sourcing favors Pacific oyster farms that implement eco-friendly practices such as water filtration and habitat restoration, contributing to balanced marine ecosystems and consistent production.
Oyster Farming Practices in the Pacific and Atlantic
Pacific oyster farming primarily involves the species Crassostrea gigas, known for its fast growth and adaptability to varied saline conditions, making it a preferred choice in regions like Japan, Australia, and the US West Coast. Atlantic oyster farming often centers on Crassostrea virginica, native to the East Coast of North America, where practices emphasize maintaining water quality and managing diseases such as Dermo and MSX to sustain production. Both regions utilize techniques like rack-and-bag and off-bottom culture, but Pacific farms tend to employ more hatchery-based seed production, while Atlantic farms often rely on wild seed collection alongside hatchery methods.
Pairing Beverages with Pacific and Atlantic Oysters
Pacific oysters, known for their briny and mildly sweet flavor, pair exceptionally well with crisp, dry white wines like Sauvignon Blanc or sparkling wines that enhance their subtle mineral notes. Atlantic oysters, often saltier and meatier, complement richer beverages such as buttery Chardonnay or full-bodied lagers that balance their intense oceanic taste. Craft beers with citrus undertones also highlight the unique flavor profiles of both Pacific and Atlantic oyster varieties.
Choosing the Right Oyster for Your Culinary Needs
Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) are prized for their sweeter, creamier flavor and plump texture, making them ideal for raw consumption and delicate dishes. Atlantic oysters (Crassostrea virginica), known for a brinier taste with a firmer texture, excel in cooked preparations like grilling or frying. Selecting the right oyster depends on your desired flavor profile and cooking method, with Pacific oysters offering a milder experience and Atlantic oysters providing a robust, oceanic bite.
Pacific vs Atlantic for oyster species Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com