Farmed oysters offer a sustainable and controlled alternative to wild oysters, reducing environmental impact and supporting consistent quality. Wild oysters often provide unique flavors influenced by their natural habitat but face risks from overharvesting and pollution. Choosing farmed or wild oysters depends on preferences for sustainability, taste variation, and ecosystem preservation.
Table of Comparison
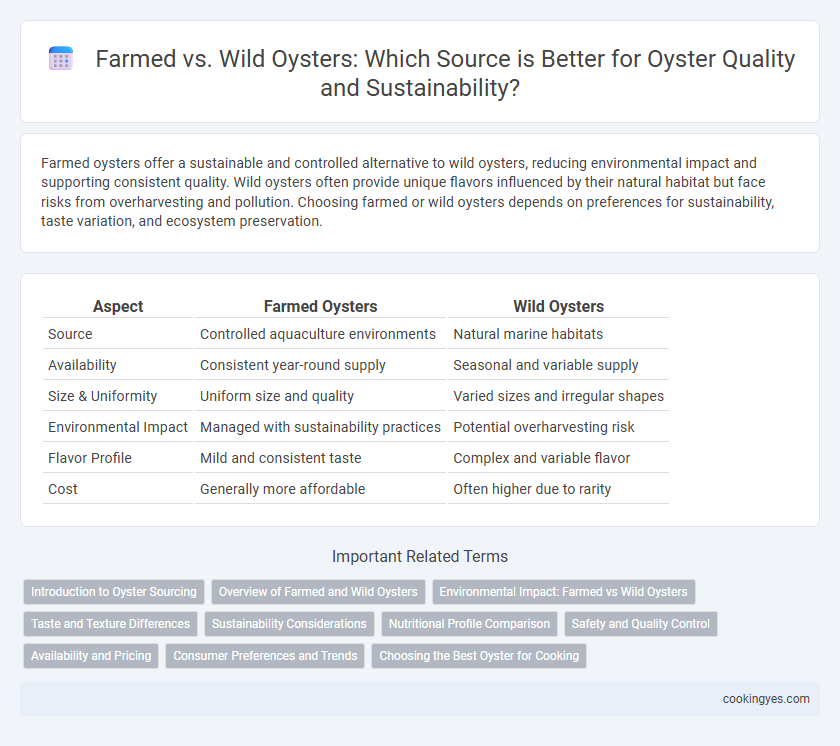
| Aspect | Farmed Oysters | Wild Oysters |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Controlled aquaculture environments | Natural marine habitats |
| Availability | Consistent year-round supply | Seasonal and variable supply |
| Size & Uniformity | Uniform size and quality | Varied sizes and irregular shapes |
| Environmental Impact | Managed with sustainability practices | Potential overharvesting risk |
| Flavor Profile | Mild and consistent taste | Complex and variable flavor |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Often higher due to rarity |
Introduction to Oyster Sourcing
Oyster sourcing involves choosing between farmed and wild oysters, each offering distinct ecological and quality factors. Farmed oysters are cultivated in controlled environments, ensuring consistent size, taste, and reduced contamination risks, while wild oysters provide natural flavor profiles influenced by their native habitats. Sustainable oyster farming supports environmental balance by filtering water and preserving wild populations, making it a preferred method in modern seafood sourcing.
Overview of Farmed and Wild Oysters
Farmed oysters are cultivated in controlled environments, optimizing growth conditions to ensure consistent size and quality, while wild oysters are harvested from natural habitats, reflecting diverse environmental influences and natural flavor profiles. Farmed oysters contribute to sustainable seafood production by reducing pressure on wild stocks and supporting ecosystem restoration through methods like reef rebuilding. Wild oysters, valued for their unique taste and texture resulting from varied water conditions, face challenges from overharvesting and habitat degradation, emphasizing the need for balanced sourcing practices.
Environmental Impact: Farmed vs Wild Oysters
Farmed oysters significantly reduce environmental impact by filtering water and improving ecosystem health without depleting wild populations. Wild oysters, while natural, often face overharvesting risks that disrupt marine habitats and reduce biodiversity. Sustainable oyster farming practices promote habitat restoration and help maintain water quality, offering a more eco-friendly source compared to wild harvesting.
Taste and Texture Differences
Farmed oysters tend to have a consistent, mild flavor with a slightly creamy texture due to controlled growing conditions and diet, while wild oysters offer a more complex, briny taste with firm and varied textures influenced by their natural environment. The mineral content and salinity of wild waters create unique flavor profiles that are often described as more intense and aromatic compared to their farmed counterparts. Texture differences arise from the natural movement and diet of wild oysters, resulting in a chewier, sometimes meatier bite compared to the typically smoother, more uniform texture of farmed oysters.
Sustainability Considerations
Farmed oysters offer sustainable advantages by reducing pressure on wild populations and enhancing water quality through their natural filtration abilities. Wild oysters face risks from overharvesting, habitat loss, and environmental changes, threatening ecosystem balance. Integrating farmed oyster production supports biodiversity and promotes long-term sustainability in oyster sourcing.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Farmed oysters typically contain higher levels of essential minerals such as zinc and iron compared to wild oysters, which can vary significantly based on their natural environment. Both farmed and wild oysters provide a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, but wild oysters may have a more diverse fatty acid profile due to their varied diet. The protein content remains comparable between the two, though farmed oysters often exhibit lower levels of contaminants, making them a safer nutritional choice.
Safety and Quality Control
Farmed oysters undergo rigorous safety and quality control measures including regular water testing and monitoring for contaminants, ensuring consistent product standards. Wild oysters may have higher variability in safety due to exposure to fluctuating environmental conditions and potential pollutants. Sourcing farmed oysters provides greater traceability and compliance with food safety regulations compared to wild-harvested oysters.
Availability and Pricing
Farmed oysters offer consistent availability year-round due to controlled cultivation environments, making them more reliable for suppliers and consumers. Wild oysters, however, are subject to seasonal fluctuations and environmental factors, leading to limited availability and higher market prices. Pricing for farmed oysters is generally more stable and affordable, while wild oysters often command premium prices driven by their natural growth conditions and rarity.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumers increasingly prefer farmed oysters due to their consistent quality, sustainable sourcing, and traceability compared to wild oysters, which can vary in flavor and availability. Market trends indicate a rising demand for farmed oysters as eco-conscious buyers prioritize sustainability and environmental impact. Wild oysters retain appeal among connoisseurs seeking unique taste profiles and natural variations linked to specific harvest locations.
Choosing the Best Oyster for Cooking
Farmed oysters offer consistent size, taste, and availability, making them ideal for reliable cooking results and sustainable sourcing. Wild oysters provide unique flavor profiles influenced by their diverse natural habitats, enhancing gourmet dishes with distinct briny and mineral notes. Choosing between farmed and wild oysters depends on the desired flavor intensity, texture, and environmental considerations in culinary applications.
Farmed vs Wild for oyster sourcing Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com