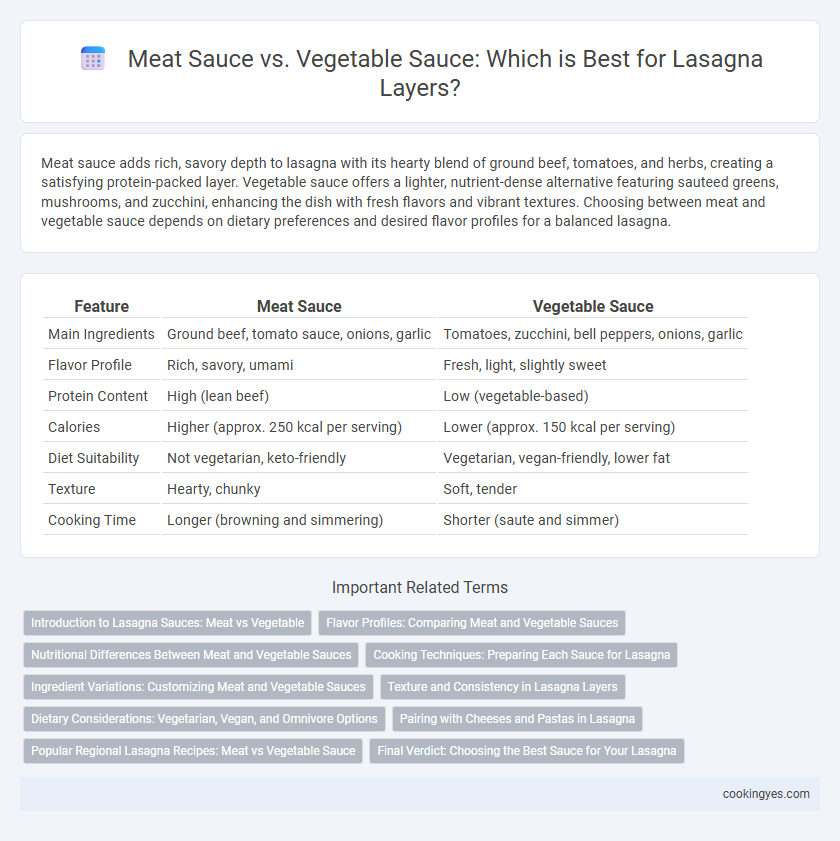
Meat sauce adds rich, savory depth to lasagna with its hearty blend of ground beef, tomatoes, and herbs, creating a satisfying protein-packed layer. Vegetable sauce offers a lighter, nutrient-dense alternative featuring sauteed greens, mushrooms, and zucchini, enhancing the dish with fresh flavors and vibrant textures. Choosing between meat and vegetable sauce depends on dietary preferences and desired flavor profiles for a balanced lasagna.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Meat Sauce | Vegetable Sauce |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredients | Ground beef, tomato sauce, onions, garlic | Tomatoes, zucchini, bell peppers, onions, garlic |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, savory, umami | Fresh, light, slightly sweet |
| Protein Content | High (lean beef) | Low (vegetable-based) |
| Calories | Higher (approx. 250 kcal per serving) | Lower (approx. 150 kcal per serving) |
| Diet Suitability | Not vegetarian, keto-friendly | Vegetarian, vegan-friendly, lower fat |
| Texture | Hearty, chunky | Soft, tender |
| Cooking Time | Longer (browning and simmering) | Shorter (saute and simmer) |
Introduction to Lasagna Sauces: Meat vs Vegetable
Lasagna layers can be enhanced by choosing between rich meat sauce and flavorful vegetable sauce, each offering distinct textures and nutritional profiles. Meat sauce typically includes ground beef or Italian sausage simmered with tomatoes and herbs, contributing a hearty, protein-rich base. Vegetable sauce incorporates ingredients like spinach, mushrooms, zucchini, and bell peppers, providing a lighter, nutrient-dense alternative that complements the creamy cheese layers.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Meat and Vegetable Sauces
Meat sauce for lasagna delivers a rich, savory flavor profile with deep umami notes from the combination of ground beef, pork, or sausage simmered with tomatoes and aromatic herbs like oregano and basil. Vegetable sauce offers a lighter, fresher taste, characterized by the natural sweetness and earthiness of ingredients such as zucchini, mushrooms, spinach, and bell peppers, often enhanced with garlic and rosemary for complexity. The choice between meat and vegetable sauce affects the overall depth and texture of the lasagna, catering to preferences for robust, hearty flavors versus vibrant, garden-fresh tastes.
Nutritional Differences Between Meat and Vegetable Sauces
Meat sauce for lasagna provides higher protein content and essential nutrients such as iron and vitamin B12, which support muscle health and energy metabolism. Vegetable sauce, rich in dietary fiber, antioxidants, and vitamins A and C, promotes digestive health and boosts the immune system. Choosing between meat and vegetable sauces affects calorie intake and fat content, with vegetable sauces generally offering a lower-calorie, heart-healthy alternative.
Cooking Techniques: Preparing Each Sauce for Lasagna
Meat sauce for lasagna typically requires browning ground beef or pork to develop deep, savory flavors and simmering with tomatoes, onions, garlic, and herbs to create a rich, thick consistency that complements pasta layers. Vegetable sauce preparation involves sauteing a mix of finely chopped vegetables such as zucchini, mushrooms, and bell peppers until tender, then simmering them with crushed tomatoes or tomato puree to maintain moisture and enhance sweetness without overpowering the dish. Both sauces benefit from slow cooking to fully meld flavors and achieve the ideal texture, ensuring the lasagna layers remain moist yet structured during baking.
Ingredient Variations: Customizing Meat and Vegetable Sauces
Meat sauce for lasagna typically includes ground beef, pork, or veal combined with tomatoes, onions, garlic, and herbs like basil and oregano, offering a rich, savory flavor profile. Vegetable sauce variations often feature ingredients such as zucchini, mushrooms, bell peppers, spinach, and eggplant, enhanced with garlic, tomatoes, and Italian seasonings to create a lighter, nutrient-dense layer. Customizing sauces allows for flexibility in texture, flavor intensity, and dietary preferences, enabling a balanced combination of protein-rich meat sauces and antioxidant-packed vegetable options in the lasagna layers.
Texture and Consistency in Lasagna Layers
Meat sauce in lasagna layers offers a rich, hearty texture with a thick, chunky consistency that adds substantial body and depth to each bite. Vegetable sauce provides a lighter, smoother texture with a more uniform consistency, allowing the layers to remain tender and moist without overwhelming heaviness. The choice between meat and vegetable sauce directly impacts the lasagna's overall mouthfeel and layer cohesion, enhancing either robust heartiness or delicate softness.
Dietary Considerations: Vegetarian, Vegan, and Omnivore Options
Meat sauce for lasagna offers high protein and essential nutrients suitable for omnivores but excludes vegetarians and vegans due to animal content. Vegetable sauces, rich in fiber and antioxidants, cater to vegetarian and vegan diets while providing a lighter alternative that supports digestive health. Choosing between meat and vegetable sauces allows customization based on dietary preferences, ensuring inclusivity for diverse nutritional needs in lasagna layers.
Pairing with Cheeses and Pastas in Lasagna
Meat sauce pairs well with robust cheeses like mozzarella, ricotta, and Parmesan, enhancing the rich, savory flavors and complementing thick pasta sheets such as traditional lasagna noodles. Vegetable sauce, often made with zucchini, spinach, or eggplant, works best with lighter cheeses like ricotta and goat cheese, balancing freshness and creaminess while pairing smoothly with thinner or more delicate pasta layers like fresh egg pasta. Choosing the right cheese and pasta texture optimizes the harmony between layers, creating a balanced and flavorful lasagna experience.
Popular Regional Lasagna Recipes: Meat vs Vegetable Sauce
Traditional Italian lasagna recipes from Emilia-Romagna prominently feature rich meat sauce made with ground beef, pork, and tomatoes, creating a hearty and savory flavor profile. In contrast, Southern Italian and Mediterranean-inspired lasagna variations often use vegetable sauces with ingredients like zucchini, eggplant, spinach, and mozzarella, catering to lighter and vegetarian preferences. Popular regional lasagna dishes highlight the distinct textures and tastes brought by meat-based ragu versus vegetable-rich sauces, reflecting local agricultural products and culinary traditions.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Sauce for Your Lasagna
Meat sauce offers a rich, savory depth that enhances the traditional lasagna's hearty flavor profile, making it ideal for those seeking a classic, protein-packed meal. Vegetable sauce provides a lighter, nutrient-dense alternative packed with vitamins and antioxidants, perfect for health-conscious or vegetarian diners. The best sauce choice depends on personal dietary preferences and desired flavor intensity, with meat sauce delivering robust taste and vegetable sauce offering freshness and nutrition.
Meat Sauce vs Vegetable Sauce for Lasagna Layer Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com