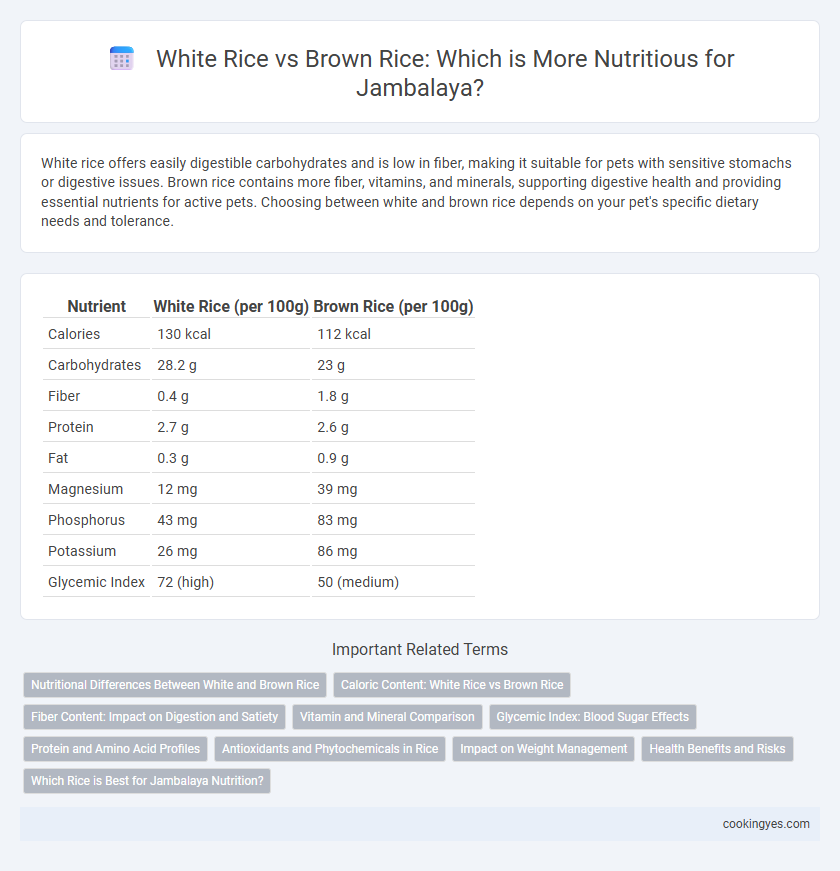
White rice offers easily digestible carbohydrates and is low in fiber, making it suitable for pets with sensitive stomachs or digestive issues. Brown rice contains more fiber, vitamins, and minerals, supporting digestive health and providing essential nutrients for active pets. Choosing between white and brown rice depends on your pet's specific dietary needs and tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Nutrient | White Rice (per 100g) | Brown Rice (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 130 kcal | 112 kcal |
| Carbohydrates | 28.2 g | 23 g |
| Fiber | 0.4 g | 1.8 g |
| Protein | 2.7 g | 2.6 g |
| Fat | 0.3 g | 0.9 g |
| Magnesium | 12 mg | 39 mg |
| Phosphorus | 43 mg | 83 mg |
| Potassium | 26 mg | 86 mg |
| Glycemic Index | 72 (high) | 50 (medium) |
Nutritional Differences Between White and Brown Rice
Brown rice contains higher amounts of fiber, vitamins, and minerals such as magnesium and phosphorus compared to white rice, which undergoes milling that removes the bran and germ. The increased fiber in brown rice supports better digestion and prolonged satiety, making it a nutritious choice for balanced meals like jambalaya. White rice provides quicker energy due to its higher glycemic index but lacks the nutrient density found in brown rice.
Caloric Content: White Rice vs Brown Rice
White rice contains approximately 130 calories per 100 grams, while brown rice has about 110 calories per 100 grams, making brown rice the lower-calorie option. Brown rice retains its bran and germ, contributing to higher fiber and nutrient content despite fewer calories. Choosing brown rice in jambalaya enhances its nutritional profile with added vitamins and minerals while slightly reducing caloric intake.
Fiber Content: Impact on Digestion and Satiety
White rice contains significantly less fiber than brown rice, which retains its bran and germ layers rich in dietary fiber. Higher fiber content in brown rice promotes better digestion by aiding bowel regularity and increasing satiety, helping to control appetite and prevent overeating. Choosing brown rice in jambalaya enhances its nutritional profile by supporting digestive health and prolonging fullness.
Vitamin and Mineral Comparison
White rice in jambalaya provides a milder flavor and softer texture but has lower vitamin and mineral content compared to brown rice. Brown rice retains the bran and germ, offering higher amounts of magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and B vitamins like niacin, thiamin, and vitamin B6, which support energy metabolism and cardiovascular health. Choosing brown rice enhances jambalaya's nutritional profile by supplying more essential nutrients and dietary fiber.
Glycemic Index: Blood Sugar Effects
White rice has a higher glycemic index (GI) ranging from 70 to 89, causing quicker spikes in blood sugar levels when used in jambalaya. Brown rice's GI is significantly lower, around 50 to 55, resulting in slower digestion and a more gradual blood sugar rise. Choosing brown rice in jambalaya can aid in better glycemic control and sustained energy release.
Protein and Amino Acid Profiles
White rice in jambalaya offers a moderate protein content with a less diverse amino acid profile, often lacking in essential amino acids like lysine. Brown rice provides higher protein levels and a more complete amino acid spectrum due to retained bran and germ components, enhancing the dish's nutritional value. Choosing brown rice boosts jambalaya's protein quality and supports better muscle repair and overall health.
Antioxidants and Phytochemicals in Rice
Brown rice contains higher levels of antioxidants and phytochemicals compared to white rice, due to its intact bran and germ layers that preserve essential nutrients. These compounds, including ferulic acid and phytic acid, contribute to reduced oxidative stress and support overall cellular health. Incorporating brown rice into jambalaya enhances its nutritional profile by providing more fiber, vitamins, and bioactive plant compounds.
Impact on Weight Management
White rice and brown rice differ significantly in fiber content, with brown rice containing more dietary fiber, which promotes satiety and aids in weight management. The higher fiber and lower glycemic index of brown rice help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing hunger spikes and calorie intake. White rice, having fewer nutrients and higher glycemic load, may contribute to quicker digestion and potentially increased appetite, impacting weight control negatively.
Health Benefits and Risks
White rice offers quick energy due to its high glycemic index but lacks fiber and essential nutrients, potentially causing blood sugar spikes. Brown rice contains more fiber, vitamins, and minerals, promoting better digestion and lower cholesterol levels while sustaining energy longer. However, brown rice may contain higher levels of arsenic and phytic acid, which can affect mineral absorption if consumed excessively.
Which Rice is Best for Jambalaya Nutrition?
White rice offers a softer texture and cooks faster, making it traditional for classic jambalaya, but it has lower fiber and fewer nutrients compared to brown rice. Brown rice contains higher amounts of fiber, magnesium, and antioxidants, supporting better digestion and sustained energy levels, enhancing the nutritional profile of jambalaya. For optimal nutrition, brown rice is the superior choice due to its richness in vitamins and minerals, though it may slightly alter the traditional taste and texture.
White Rice vs Brown Rice for nutrition Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com