Potato flour enhances doughnut texture by adding moisture and softness, creating a tender crumb with a slight chewiness, while wheat flour provides essential gluten that gives doughnuts their traditional structure and elasticity. Using potato flour in combination with wheat flour can improve doughnut freshness and extend shelf life without compromising firmness. This blend balances lightness and chew, resulting in a doughnut that is both fluffy and structurally sound.
Table of Comparison
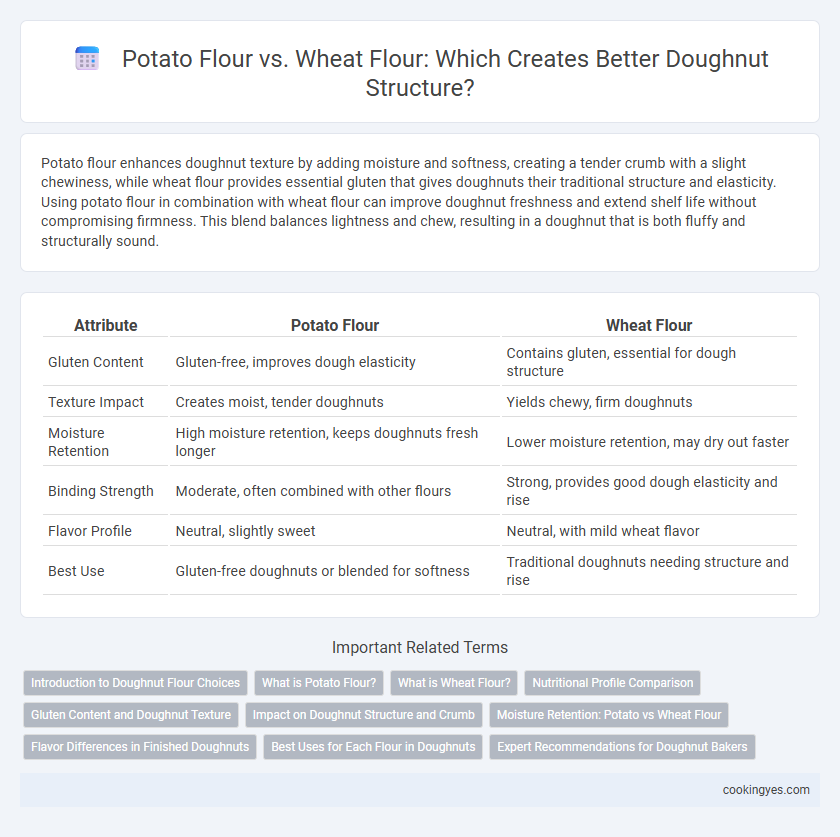
| Attribute | Potato Flour | Wheat Flour |
|---|---|---|
| Gluten Content | Gluten-free, improves dough elasticity | Contains gluten, essential for dough structure |
| Texture Impact | Creates moist, tender doughnuts | Yields chewy, firm doughnuts |
| Moisture Retention | High moisture retention, keeps doughnuts fresh longer | Lower moisture retention, may dry out faster |
| Binding Strength | Moderate, often combined with other flours | Strong, provides good dough elasticity and rise |
| Flavor Profile | Neutral, slightly sweet | Neutral, with mild wheat flavor |
| Best Use | Gluten-free doughnuts or blended for softness | Traditional doughnuts needing structure and rise |
Introduction to Doughnut Flour Choices
Potato flour enhances doughnut structure by improving moisture retention and creating a tender, light crumb compared to wheat flour, which provides stronger gluten development and a chewier texture. The unique starch properties in potato flour promote a softer interior and extended freshness, making it a preferred choice for fluffy, melt-in-mouth doughnuts. Wheat flour varieties, especially all-purpose or bread flour, contribute to dough elasticity and rise, balancing doughnut volume and structural integrity.
What is Potato Flour?
Potato flour is a fine powder made from whole peeled potatoes that are cooked, dried, and ground, offering high moisture retention and a light texture ideal for doughnut batter. Unlike wheat flour, potato flour contains no gluten, which results in a softer, denser doughnut structure and can improve shelf life by keeping the doughnut moist. Using potato flour in doughnut recipes enhances crispiness on the outside while maintaining a tender, fluffy interior.
What is Wheat Flour?
Wheat flour, derived from grinding wheat grains, contains gluten proteins that provide elasticity and strength crucial for doughnut structure and texture. This gluten network traps air during frying, resulting in a light, airy, and chewy doughnut crumb. Compared to potato flour, which lacks gluten, wheat flour offers superior dough elasticity and rise, essential for traditional doughnut dough consistency.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Potato flour enhances doughnut texture by adding moisture and a tender crumb, while wheat flour provides essential gluten for structural support. Nutritionally, potato flour is higher in potassium and vitamin C but lower in protein compared to wheat flour, which offers more dietary fiber and B vitamins crucial for energy metabolism. Choosing between the two affects both the doughnut's nutritional value and its overall mouthfeel.
Gluten Content and Doughnut Texture
Potato flour, with its lack of gluten, produces doughnuts that are softer and more tender but have less structural elasticity compared to wheat flour. Wheat flour contains gluten proteins that form a strong, elastic network, giving doughnuts a chewy texture and well-defined shape. Balancing potato flour with wheat flour can yield doughnuts that combine lightness with enough firmness for a desirable bite.
Impact on Doughnut Structure and Crumb
Potato flour enhances doughnut structure by imparting increased moisture retention and a tender crumb, resulting from its higher starch content and excellent gel-forming ability. Wheat flour, with its gluten proteins, provides the essential elasticity and chewiness needed for dough development, producing a firmer crumb and better rise. Combining potato flour with wheat flour can optimize doughnut texture by balancing softness and structural integrity.
Moisture Retention: Potato vs Wheat Flour
Potato flour enhances doughnut moisture retention due to its high starch content, which absorbs and holds water effectively, resulting in a softer and moister texture. Wheat flour, containing gluten, provides elasticity and structure but retains less moisture, often causing a drier doughnut crumb over time. Using potato flour in doughnut recipes optimizes moisture balance, prolonging freshness and improving overall mouthfeel.
Flavor Differences in Finished Doughnuts
Potato flour enhances doughnut flavor by imparting a subtle earthiness and natural sweetness, creating a distinct taste profile compared to wheat flour. Wheat flour offers a more traditional, mild flavor that acts as a neutral base, allowing other ingredients like sugar and spices to shine. The use of potato flour results in doughnuts with a richer, slightly tangy flavor, while wheat flour yields a classic, familiar doughnut taste.
Best Uses for Each Flour in Doughnuts
Potato flour enhances doughnut texture by providing a soft, moist crumb and a tender bite, making it ideal for cake-style doughnuts. Wheat flour, especially all-purpose or bread flour, contributes elasticity and structure due to its gluten content, resulting in chewier, yeast-raised doughnuts. Combining both flours can balance softness and chewiness, optimizing doughnut quality for varied recipes.
Expert Recommendations for Doughnut Bakers
Potato flour enhances doughnut texture by providing greater moisture retention and a tender crumb, making it a preferred choice for achieving soft, fluffy doughnuts. Expert doughnut bakers recommend blending potato flour with wheat flour to balance gluten development, ensuring optimal elasticity and structure while maintaining lightness. Using a precise ratio of 10-20% potato flour in wheat-based dough yields superior doughnut shelf life and a satisfying mouthfeel favored in artisanal baking.
Potato flour vs Wheat flour for doughnut structure Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com