When choosing between a male and female crab as a pet, male crabs tend to be more aggressive and territorial, making them suitable for experienced handlers. Female crabs are generally calmer and less likely to fight, which can be beneficial in community tanks or for beginners. Physical differences, such as the shape of the abdomen, help identify gender and influence their behavior and care needs.
Table of Comparison
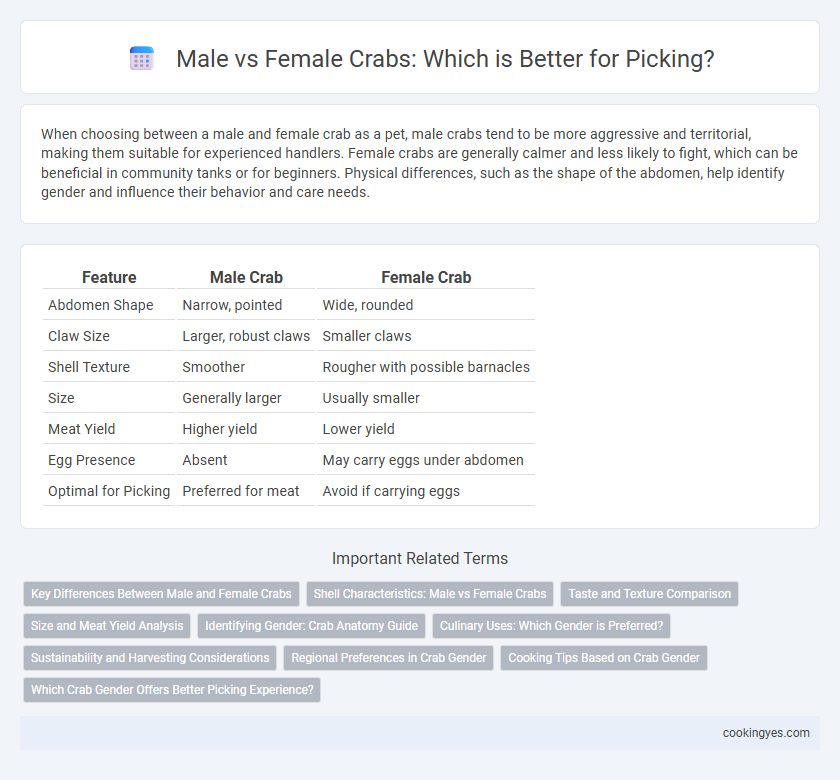
| Feature | Male Crab | Female Crab |
|---|---|---|
| Abdomen Shape | Narrow, pointed | Wide, rounded |
| Claw Size | Larger, robust claws | Smaller claws |
| Shell Texture | Smoother | Rougher with possible barnacles |
| Size | Generally larger | Usually smaller |
| Meat Yield | Higher yield | Lower yield |
| Egg Presence | Absent | May carry eggs under abdomen |
| Optimal for Picking | Preferred for meat | Avoid if carrying eggs |
Key Differences Between Male and Female Crabs
Male and female crabs can be distinguished by the shape of their abdominal flaps; males typically have a narrow, pointed flap while females possess a broader, rounded one designed to carry eggs. The size and claw strength in males are often more prominent, used for fighting and mating displays, whereas females are generally smaller but crucial for reproduction. These key morphological differences aid in identifying crabs for sustainable harvesting and conservation purposes.
Shell Characteristics: Male vs Female Crabs
Male crabs typically have a narrow, pointed abdominal apron on their underside, resembling an inverted T or V shape, while female crabs feature a wider, rounded apron that protects their eggs. The shell of male crabs often appears thicker and more robust, reflecting their role in territorial defense, whereas female crabs may have a smoother, less pronounced shell texture. These distinct shell characteristics are crucial for identifying gender during crab picking, ensuring sustainable harvesting practices by protecting egg-bearing females.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Male crab meat typically offers a firmer texture and a slightly sweeter taste, making it ideal for dishes requiring distinct, robust flavors. Female crabs often have softer meat with a creamier texture due to the presence of roe, which adds a rich, briny flavor prized in certain culinary applications. Understanding these differences helps chefs select the appropriate crab based on desired taste profiles and texture preferences.
Size and Meat Yield Analysis
Male crabs generally exhibit larger size and a higher meat yield compared to female crabs, making them the preferred choice for harvesting. Their broader claws and thicker shells contribute to increased edible portions, particularly in species like blue crabs and Dungeness crabs. Female crabs, often smaller and carrying roe, provide lower meat volume but are valued for their eggs in culinary applications.
Identifying Gender: Crab Anatomy Guide
Male crabs can be identified by their narrow, pointed abdomen, often described as a T-shaped or triangular apron, while female crabs have a broader, rounded apron used for carrying eggs. Male crabs typically have larger claws and a more robust body suited for territorial defense, whereas females tend to have a smoother carapace and are generally smaller. Understanding these anatomical differences is crucial for sustainable crab picking, ensuring the protection of breeding females to maintain population balance.
Culinary Uses: Which Gender is Preferred?
Female crabs are often preferred in culinary uses due to their rich roe, which adds a distinct flavor and texture to dishes. Male crabs generally offer more meat, prized for its firm texture and mild taste, making them ideal for meat-centric recipes. Chefs select based on recipe needs: roe-rich female crabs enhance flavor complexity, while meatier males provide substance.
Sustainability and Harvesting Considerations
Male crabs are generally preferred for harvesting due to their larger size and higher meat yield, which supports more efficient and sustainable fishing practices. Female crabs, especially those carrying eggs, play a critical role in sustaining crab populations and must be protected to ensure long-term ecological balance. Sustainable crab harvesting guidelines emphasize releasing egg-bearing females and adhering to size limits to promote population recovery and maintain healthy marine ecosystems.
Regional Preferences in Crab Gender
Regional preferences in crab selection vary significantly, with female crabs often favored in Asian markets for their roe, prized as a delicacy, while male crabs are preferred in Western countries due to their larger meat yield. In Chesapeake Bay, female blue crabs are harvested before spawning to ensure sustainability, whereas in the Gulf of Mexico, male crabs dominate crab picking because of their robust claws and meat quality. These regional distinctions influence crab fisheries management and consumer demand, reflecting cultural and culinary traditions tied to crab gender.
Cooking Tips Based on Crab Gender
Male crabs typically have firmer meat and are preferred for cooking methods like grilling or steaming, which highlight their dense texture and robust flavor. Female crabs often contain roe, making them ideal for recipes requiring richer, creamier ingredients such as crab bisque or crab cakes. Selecting crabs based on gender can enhance the taste and texture of dishes, optimizing the culinary experience.
Which Crab Gender Offers Better Picking Experience?
Male crabs generally offer a better picking experience due to their larger claws and higher meat yield, especially in species like blue crabs and Dungeness crabs. Female crabs often carry roe, which is prized in culinary uses but can make the picking process more delicate and less meat-intensive. Therefore, for meat quantity and ease of extraction, male crabs are preferred by many seafood enthusiasts and professional pickers.
Male vs female crab for picking Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com