Pecorino Romano offers a sharper, saltier flavor that perfectly complements robust pasta dishes, adding a bold, tangy punch. Parmigiano-Reggiano provides a nuttier, more complex umami profile with a granular texture, making it ideal for enhancing delicate pasta sauces. Choosing between the two depends on whether you want a strong, savory contrast or a subtle, rich depth in your pasta.
Table of Comparison
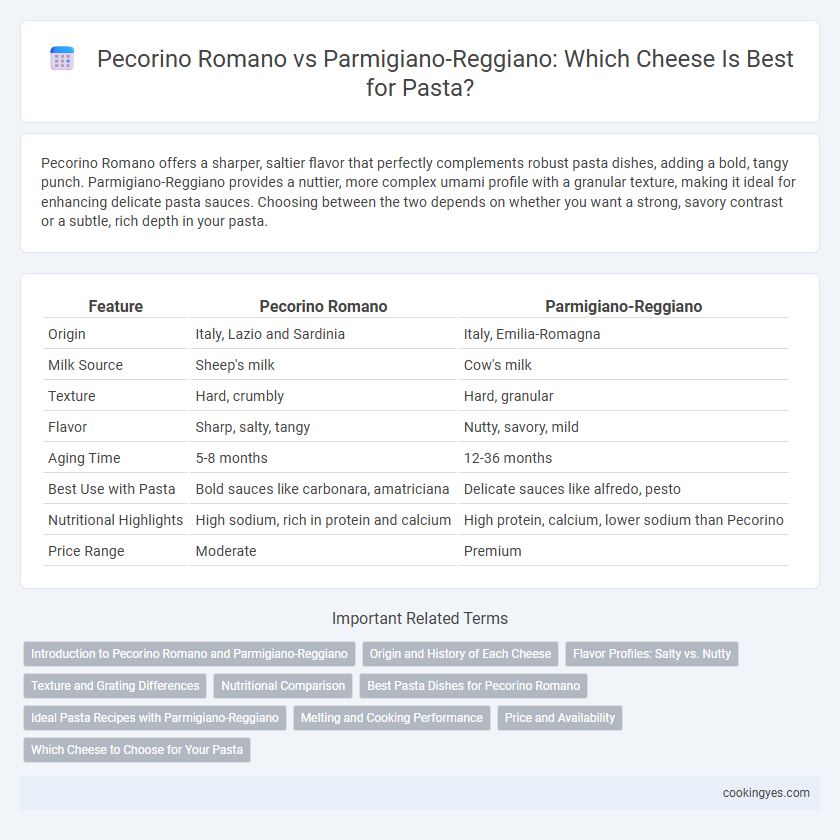
| Feature | Pecorino Romano | Parmigiano-Reggiano |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Italy, Lazio and Sardinia | Italy, Emilia-Romagna |
| Milk Source | Sheep's milk | Cow's milk |
| Texture | Hard, crumbly | Hard, granular |
| Flavor | Sharp, salty, tangy | Nutty, savory, mild |
| Aging Time | 5-8 months | 12-36 months |
| Best Use with Pasta | Bold sauces like carbonara, amatriciana | Delicate sauces like alfredo, pesto |
| Nutritional Highlights | High sodium, rich in protein and calcium | High protein, calcium, lower sodium than Pecorino |
| Price Range | Moderate | Premium |
Introduction to Pecorino Romano and Parmigiano-Reggiano
Pecorino Romano, a hard, salty Italian cheese made from sheep's milk, is known for its sharp, tangy flavor that enhances pasta dishes like Cacio e Pepe. Parmigiano-Reggiano, crafted from cow's milk and aged for a minimum of 12 months, offers a rich, nutty taste with a granular texture ideal for grating over pasta. Both cheeses are staple ingredients in Italian cuisine, but Pecorino Romano delivers a bolder, saltier punch, while Parmigiano-Reggiano provides a more mellow, complex flavor.
Origin and History of Each Cheese
Pecorino Romano, originating from Italy's Lazio region, is one of the oldest Italian cheeses, traditionally made from sheep's milk and dating back to ancient Roman times. Parmigiano-Reggiano, also known as Parmesan, hails from the Emilia-Romagna region and has been produced since the Middle Ages, made from cow's milk with a strict protected designation of origin (PDO) status. Both cheeses carry rich historical significance, influencing Italian culinary traditions, especially in pasta dishes where Pecorino Romano imparts a sharp, salty flavor, and Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a nutty, umami boost.
Flavor Profiles: Salty vs. Nutty
Pecorino Romano delivers a sharp, salty flavor with a pronounced tang that enhances pasta dishes by adding a bold, savory kick. Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a complex nutty and umami profile, featuring subtle hints of fruit and a crystalline texture that melts smoothly into sauces. Choosing between these cheeses depends on whether a recipe benefits from a robust saltiness or a rich, nutty depth to complement the pasta.
Texture and Grating Differences
Pecorino Romano exhibits a dense, crumbly texture with a sharper, saltier profile, making it ideal for coarse grating over robust pasta dishes. Parmigiano-Reggiano features a granular, slightly oily texture that softens when grated finely, lending a nutty, savory richness to delicate pasta sauces. The harder Pecorino grates into larger shards, while Parmigiano-Reggiano produces finer, fluffier flakes that melt smoothly.
Nutritional Comparison
Pecorino Romano contains higher protein and sodium levels compared to Parmigiano-Reggiano, offering a saltier taste ideal for robust pasta dishes. Parmigiano-Reggiano provides more calcium and phosphorus, supporting bone health while contributing a nutty flavor suitable for delicate pasta varieties. Both cheeses deliver essential nutrients such as vitamins A and B12, but Pecorino Romano's sheep's milk base contributes more fat, affecting calorie content in pasta recipes.
Best Pasta Dishes for Pecorino Romano
Pecorino Romano's sharp, salty flavor enhances classic Roman pasta dishes such as Cacio e Pepe and Pasta all'Amatriciana, where its bold taste cuts through rich sauces. This sheep's milk cheese melts smoothly, providing a tangy contrast that complements simple ingredients like black pepper and guanciale. Unlike Parmigiano-Reggiano, which offers a nutty and milder profile best suited for a wider range of pasta, Pecorino Romano is preferred for robust, traditional Italian recipes requiring strong seasoning.
Ideal Pasta Recipes with Parmigiano-Reggiano
Parmigiano-Reggiano enhances classic pasta recipes like spaghetti carbonara and fettuccine Alfredo with its nutty, granular texture and rich umami flavor, perfectly melting into creamy sauces. Pecorino Romano, made from sheep's milk, offers a sharper, saltier taste ideal for dishes like Cacio e Pepe, but Parmigiano-Reggiano's balanced complexity suits a wider range of creamy, tomato-based, and vegetable pasta sauces. The aging process of Parmigiano-Reggiano, typically 12 to 36 months, develops a deep flavor profile that complements fresh herbs and delicate pasta shapes such as tagliatelle or pappardelle.
Melting and Cooking Performance
Pecorino Romano melts quickly and evenly, making it ideal for recipes requiring smooth cheese integration, while Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a slightly granular texture that enhances flavor without fully melting. Pecorino Romano's higher salt content intensifies pasta dishes, complementing its superior melting properties during cooking. Parmigiano-Reggiano maintains a firmer consistency under heat, providing a distinct, nutty uplift to sauces and gratins.
Price and Availability
Pecorino Romano is generally more affordable and widely available in supermarkets compared to Parmigiano-Reggiano, which tends to be pricier due to its lengthy aging process and protected designation of origin status. Parmigiano-Reggiano's complex flavor profile and granular texture make it a premium choice but may be harder to find in some regions, especially outside Italy. Both cheeses melt well over pasta, but budget-conscious cooks often prefer Pecorino Romano for its sharp, salty punch and accessibility.
Which Cheese to Choose for Your Pasta
Pecorino Romano, made from sheep's milk, offers a sharp, salty flavor that complements robust pasta dishes like carbonara or amatriciana, providing a bold contrast to rich sauces. Parmigiano-Reggiano, aged longer and crafted from cow's milk, delivers a nutty, complex taste ideal for enhancing lighter pasta recipes such as fettuccine Alfredo or simple tomato sauces. Choosing Pecorino Romano results in a more intense, tangy bite, while Parmigiano-Reggiano contributes a creamy, savory depth to pasta dishes.
Pecorino Romano vs Parmigiano-Reggiano for pasta Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com