Boiled ravioli offers a tender texture with a classic, delicate flavor achieved through gentle water cooking, making it a quick and simple preparation method. Baked ravioli provides a crispy, golden crust and richer taste due to the baking process, often enhanced with sauces and cheese for added depth. Choosing between boiled and baked ravioli depends on whether you prefer a soft, traditional bite or a crunchy, savory experience.
Table of Comparison
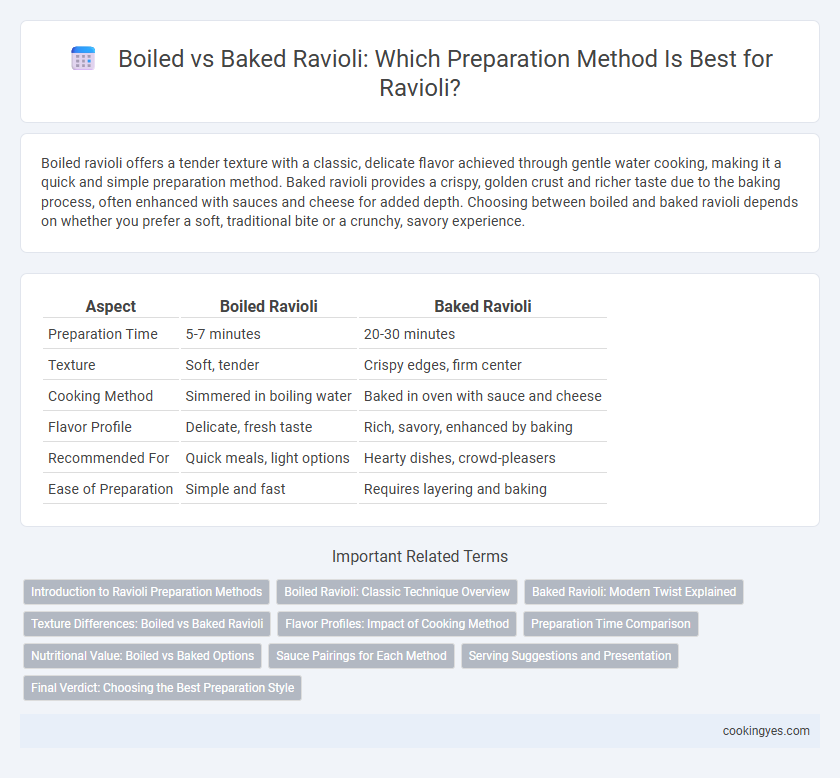
| Aspect | Boiled Ravioli | Baked Ravioli |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Time | 5-7 minutes | 20-30 minutes |
| Texture | Soft, tender | Crispy edges, firm center |
| Cooking Method | Simmered in boiling water | Baked in oven with sauce and cheese |
| Flavor Profile | Delicate, fresh taste | Rich, savory, enhanced by baking |
| Recommended For | Quick meals, light options | Hearty dishes, crowd-pleasers |
| Ease of Preparation | Simple and fast | Requires layering and baking |
Introduction to Ravioli Preparation Methods
Boiled ravioli involves cooking pasta pockets in rapidly boiling water until tender, preserving a delicate texture and allowing fillings like cheese or meat to remain moist. Baked ravioli requires breaded or sauced pockets to be layered and cooked in an oven, resulting in a crisp exterior with a warm, melted interior ideal for hearty fillings. Each method highlights different textures and flavor profiles, influencing the overall dining experience.
Boiled Ravioli: Classic Technique Overview
Boiled ravioli is the traditional preparation method involving cooking pasta pockets in rapidly boiling water until they float, signaling readiness. This technique ensures a tender texture and allows the delicate filling flavors to shine through without additional fat or toppings. The consistent heat distribution during boiling preserves the pasta integrity, making it a preferred choice for maintaining authentic ravioli taste and texture.
Baked Ravioli: Modern Twist Explained
Baked ravioli transforms traditional boiled pasta by creating a crispy, golden crust while maintaining a tender interior, offering a modern twist on classic preparation. This method enhances flavor through caramelization and allows for layered textures when combined with cheese and sauce, delivering a more indulgent dining experience. Baking also simplifies serving and presentation, making it a popular choice for contemporary Italian cuisine and casual gatherings.
Texture Differences: Boiled vs Baked Ravioli
Boiled ravioli features a tender, silky texture as the pasta softens evenly in water, preserving the delicate filling inside. Baked ravioli develops a crispy, golden exterior with a firmer, chewier bite, while the filling becomes warm and slightly caramelized. Texture preferences hinge on desired contrast, with boiled offering smoothness and baked providing a satisfying crunch.
Flavor Profiles: Impact of Cooking Method
Boiled ravioli retains a delicate, tender texture with a subtle, fresh flavor that highlights the filling's natural taste. Baked ravioli develops a crispy, golden outer layer, intensifying the savory notes and creating a rich, caramelized flavor contrast. The cooking method dramatically influences the overall taste experience, making boiled ravioli lighter and baked ravioli more robust and hearty.
Preparation Time Comparison
Boiled ravioli typically requires 4 to 6 minutes of cooking time, making it a quick method suitable for weeknight meals. Baked ravioli involves additional steps such as layering with sauce and cheese and baking for 20 to 30 minutes, resulting in a longer total preparation time. Choosing between boiled and baked ravioli depends on balancing convenience with a richer, baked flavor profile.
Nutritional Value: Boiled vs Baked Options
Boiled ravioli retains more moisture and typically has a lower fat content compared to baked ravioli, which is often brushed with oil or cheese, increasing its calorie and fat levels. Baking ravioli enhances flavor through browning and can add protein and calcium if cheese toppings are used, but it also raises sodium content due to added ingredients. Choosing boiled ravioli supports lower calorie intake, while baked ravioli offers a richer taste and higher nutrient density from toppings and browning reactions.
Sauce Pairings for Each Method
Boiled ravioli pairs well with light, fresh sauces like marinara or a simple garlic and olive oil blend, allowing the delicate pasta and filling flavors to shine. Baked ravioli, often topped with cheese and baked until golden, complements richer sauces such as creamy Alfredo or hearty meat sauce, which meld perfectly with the crispy, baked texture. Selecting the appropriate sauce enhances the overall dish, balancing the preparation method's unique characteristics.
Serving Suggestions and Presentation
Boiled ravioli offers a classic, tender texture perfect for pairing with light sauces and fresh herbs, enhancing its delicate flavor for a simple yet elegant presentation. Baked ravioli provides a crispy, golden crust that holds rich cheese and tomato sauce, making it ideal for hearty servings topped with melted mozzarella and grated Parmesan. Serving boiled ravioli on a shallow dish with a drizzle of olive oil and basil leaves creates a refined look, while baked ravioli benefits from being presented in a rustic casserole dish garnished with fresh parsley for a comforting, family-style appeal.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Preparation Style
Boiled ravioli offers a traditional, tender texture with a delicate bite, ideal for savoring the rich filling and pairing with classic sauces like marinara or Alfredo. Baked ravioli delivers a crispy, golden crust that enhances flavor complexity and adds a satisfying crunch, often topped with melted cheese and fresh herbs. The best preparation style depends on personal preference: choose boiled for authenticity and softness, or baked for a heartier, more textured dish.
Boiled ravioli vs Baked ravioli for preparation Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com