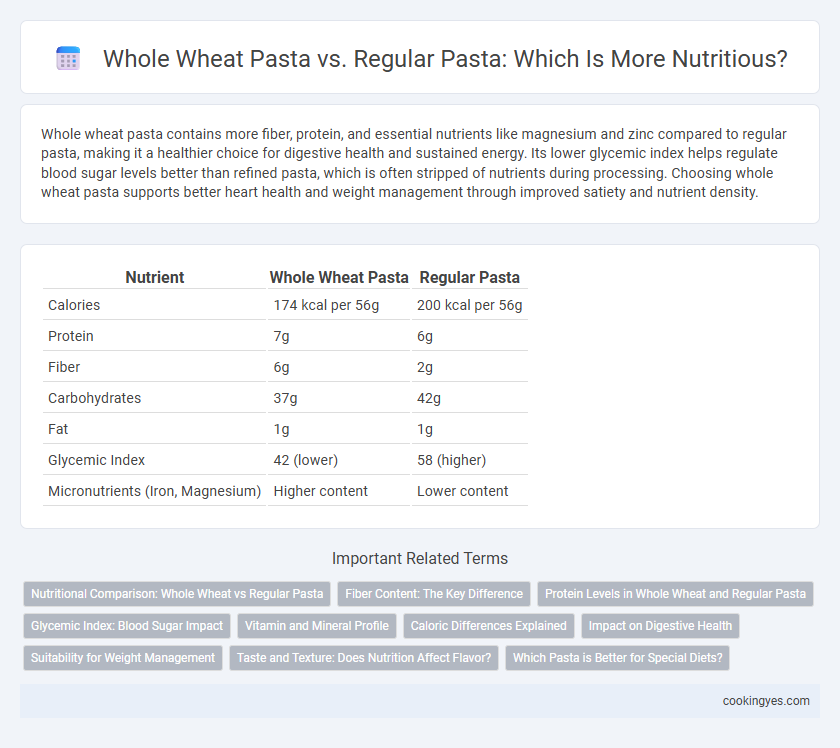
Whole wheat pasta contains more fiber, protein, and essential nutrients like magnesium and zinc compared to regular pasta, making it a healthier choice for digestive health and sustained energy. Its lower glycemic index helps regulate blood sugar levels better than refined pasta, which is often stripped of nutrients during processing. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better heart health and weight management through improved satiety and nutrient density.
Table of Comparison
| Nutrient | Whole Wheat Pasta | Regular Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 174 kcal per 56g | 200 kcal per 56g |
| Protein | 7g | 6g |
| Fiber | 6g | 2g |
| Carbohydrates | 37g | 42g |
| Fat | 1g | 1g |
| Glycemic Index | 42 (lower) | 58 (higher) |
| Micronutrients (Iron, Magnesium) | Higher content | Lower content |
Nutritional Comparison: Whole Wheat vs Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains higher dietary fiber, protein, and essential minerals such as magnesium and zinc compared to regular pasta, which is typically made from refined white flour. The increased fiber content in whole wheat pasta aids digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels, while regular pasta usually has a higher glycemic index leading to quicker blood sugar spikes. Calories and carbohydrates are similar in both, but whole wheat pasta delivers more vitamins like B-complex and antioxidants, enhancing its overall nutritional profile.
Fiber Content: The Key Difference
Whole wheat pasta contains significantly higher dietary fiber than regular pasta, offering around 6 grams of fiber per serving compared to 2 grams in traditional pasta. This increased fiber content supports digestive health, promotes satiety, and helps regulate blood sugar levels more effectively. Choosing whole wheat pasta enhances overall nutrient intake while contributing to better long-term cardiovascular and metabolic health.
Protein Levels in Whole Wheat and Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains approximately 7-8 grams of protein per 2-ounce serving, which is slightly higher than regular pasta's 5-6 grams. The increased protein in whole wheat pasta comes from the use of whole grain, preserving more of the wheat kernel's natural nutrients. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports higher protein intake alongside additional fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to regular pasta.
Glycemic Index: Blood Sugar Impact
Whole wheat pasta has a lower glycemic index (GI) than regular pasta, resulting in slower blood sugar absorption and more stable energy levels. The reduced GI in whole wheat pasta comes from its higher fiber content, which slows digestion and prevents rapid blood glucose spikes. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better blood sugar management and may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes compared to regular pasta.
Vitamin and Mineral Profile
Whole wheat pasta contains higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals compared to regular pasta, including increased amounts of B vitamins such as thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin, as well as greater magnesium, zinc, and iron content. The bran and germ retained in whole wheat pasta contribute to its richer nutrient density, supporting better metabolic and immune functions. Regular pasta, often made from refined flour, lacks these nutrients due to the removal of the outer grain layers during processing.
Caloric Differences Explained
Whole wheat pasta contains approximately 174 calories per cooked cup, offering more fiber and protein compared to regular pasta, which has about 200 calories per cooked cup. The lower calorie content in whole wheat pasta is due to its higher fiber content, which also promotes satiety and aids digestion. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better blood sugar regulation and can contribute to weight management compared to the refined carbohydrates in regular pasta.
Impact on Digestive Health
Whole wheat pasta contains higher dietary fiber, which promotes better digestive health by enhancing bowel regularity and preventing constipation compared to regular pasta. The bran and germ preserved in whole wheat pasta provide essential nutrients and prebiotics that support gut microbiota diversity. In contrast, regular pasta, made from refined flour, lacks these components, resulting in lower fiber content and minimal impact on digestive function.
Suitability for Weight Management
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber content compared to regular pasta, which aids in promoting satiety and supporting weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. It also offers a lower glycemic index, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent overeating. Regular pasta, made from refined grains, lacks these benefits and may lead to quicker spikes in blood glucose, making it less suitable for weight control.
Taste and Texture: Does Nutrition Affect Flavor?
Whole wheat pasta offers a nuttier, denser texture compared to the smoother, more neutral flavor of regular pasta, which can influence overall taste preferences. The higher fiber and protein content in whole wheat pasta contribute to a heartier mouthfeel, often perceived as more robust but less tender than the refined counterpart. While nutrition influences texture and flavor complexity, personal preference ultimately determines whether the nutritional benefits outweigh the distinct taste differences.
Which Pasta is Better for Special Diets?
Whole wheat pasta offers higher fiber content, more protein, and essential micronutrients like magnesium and zinc compared to regular pasta, making it preferable for diets focusing on blood sugar control and digestive health. Regular pasta, often made from refined wheat, has a higher glycemic index, which may lead to rapid blood sugar spikes, less ideal for diabetic or weight-management diets. For gluten-free or low-carb special diets, neither traditional nor whole wheat pasta is suitable, so alternatives like chickpea or lentil-based pasta are recommended.
Whole wheat pasta vs Regular pasta for nutrition Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com