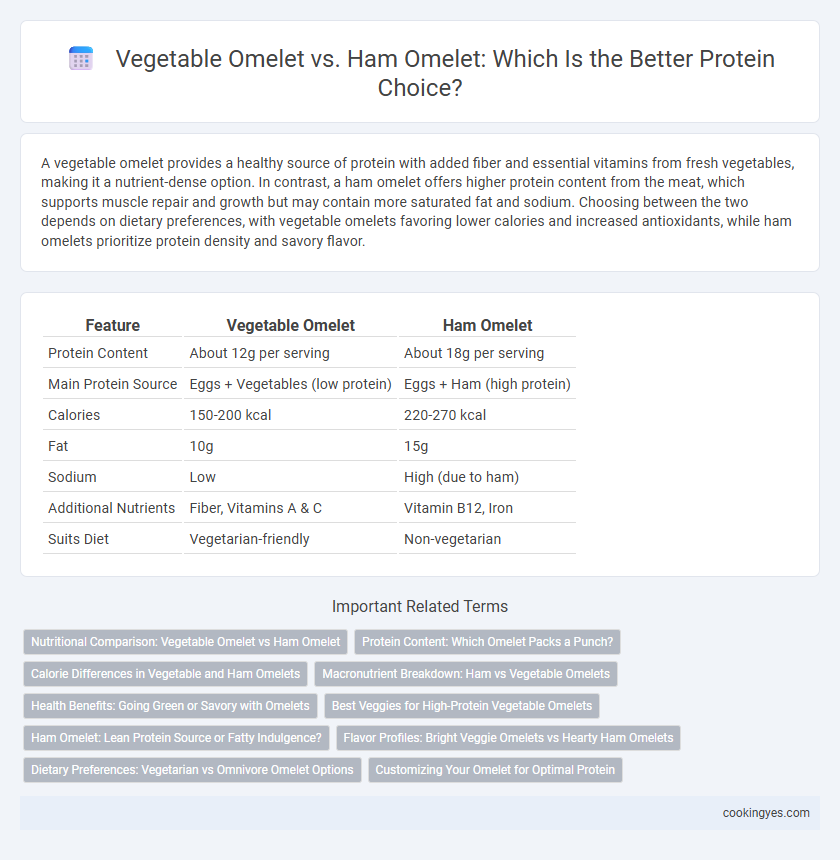
A vegetable omelet provides a healthy source of protein with added fiber and essential vitamins from fresh vegetables, making it a nutrient-dense option. In contrast, a ham omelet offers higher protein content from the meat, which supports muscle repair and growth but may contain more saturated fat and sodium. Choosing between the two depends on dietary preferences, with vegetable omelets favoring lower calories and increased antioxidants, while ham omelets prioritize protein density and savory flavor.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable Omelet | Ham Omelet |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Content | About 12g per serving | About 18g per serving |
| Main Protein Source | Eggs + Vegetables (low protein) | Eggs + Ham (high protein) |
| Calories | 150-200 kcal | 220-270 kcal |
| Fat | 10g | 15g |
| Sodium | Low | High (due to ham) |
| Additional Nutrients | Fiber, Vitamins A & C | Vitamin B12, Iron |
| Suits Diet | Vegetarian-friendly | Non-vegetarian |
Nutritional Comparison: Vegetable Omelet vs Ham Omelet
A vegetable omelet typically contains fewer calories and less saturated fat than a ham omelet while offering higher fiber content and essential vitamins such as vitamin C and antioxidants from vegetables like spinach, tomatoes, and peppers. In contrast, a ham omelet provides a higher protein content and significant amounts of vitamin B12 and iron, which are important for muscle repair and energy metabolism. Choosing between the two depends on dietary goals: prioritize a vegetable omelet for lower fat and increased micronutrients or opt for a ham omelet to boost protein intake and essential minerals.
Protein Content: Which Omelet Packs a Punch?
A ham omelet typically contains around 18-20 grams of protein per serving, making it a rich source for muscle repair and growth. In contrast, a vegetable omelet provides approximately 10-12 grams of protein but offers additional fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants from ingredients like spinach, tomatoes, and bell peppers. Choosing between the two depends on your protein requirements and nutritional goals, with ham omelets delivering higher protein density and vegetable omelets favored for overall nutrient variety.
Calorie Differences in Vegetable and Ham Omelets
Vegetable omelets typically contain fewer calories than ham omelets due to the lower fat content and reduced protein density in vegetables compared to ham. A standard vegetable omelet usually provides around 150-200 calories, whereas a ham omelet can range from 250-300 calories, mainly because ham adds extra saturated fats and protein. Choosing between these options depends on balancing calorie intake with protein needs, making vegetable omelets ideal for lower-calorie diets and ham omelets better for higher protein consumption.
Macronutrient Breakdown: Ham vs Vegetable Omelets
Ham omelets generally provide a higher protein content, averaging around 20-25 grams per serving, compared to vegetable omelets which typically contain 12-15 grams of protein due to the lower protein density of vegetables. In terms of macronutrient breakdown, ham omelets often contain more fat and calories, with approximately 250-300 calories and 15-20 grams of fat, whereas vegetable omelets tend to be lower in calories, around 150-200, and fat, usually under 10 grams. Choosing between the two depends on dietary goals: ham omelets offer more protein for muscle repair and satiety, while vegetable omelets provide fiber, vitamins, and lower calorie options.
Health Benefits: Going Green or Savory with Omelets
Vegetable omelets provide a rich source of fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins like A, C, and K, supporting heart health and immune function. Ham omelets offer high-quality complete proteins and vital minerals such as iron and zinc, promoting muscle repair and energy metabolism. Choosing between vegetable and ham omelets depends on desired nutritional benefits, with vegetables enhancing micronutrient intake and ham boosting protein density.
Best Veggies for High-Protein Vegetable Omelets
A vegetable omelet with spinach, broccoli, and peas offers a rich protein boost, rivaling the protein content found in ham omelets. Among vegetables, peas provide the highest protein per serving, followed by spinach and broccoli, making them ideal choices for a high-protein vegetable omelet. Incorporating these vegetables enhances both the protein quality and nutritional value compared to traditional ham omelets.
Ham Omelet: Lean Protein Source or Fatty Indulgence?
Ham omelets provide a rich source of lean protein, offering about 10-12 grams of protein per serving, which supports muscle repair and growth. While ham contributes essential amino acids and iron, it may also contain higher levels of sodium and saturated fat compared to vegetable omelets. Choosing leaner cuts of ham can balance protein intake with lower fat content, making it a favorable option for those seeking a satisfying yet nutritious meal.
Flavor Profiles: Bright Veggie Omelets vs Hearty Ham Omelets
Vegetable omelets offer a fresh, bright flavor profile with ingredients like bell peppers, spinach, and tomatoes that contribute vitamins and a lighter texture. Ham omelets provide a hearty, savory taste with smoky, salty notes and a substantial protein boost ideal for muscle repair and energy. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prefer a nutrient-rich, vibrant flavor or a robust, protein-dense option.
Dietary Preferences: Vegetarian vs Omnivore Omelet Options
Vegetable omelets provide a rich source of plant-based protein and essential nutrients ideal for vegetarians, incorporating ingredients like spinach, tomatoes, and bell peppers. Ham omelets offer a higher protein content from animal sources, appealing to omnivores seeking a savory, protein-dense meal with added vitamins such as B12 and iron. Choosing between these options depends on dietary preferences, where vegetable omelets suit vegetarian diets and ham omelets complement omnivorous nutrition goals.
Customizing Your Omelet for Optimal Protein
Customizing your omelet for optimal protein involves choosing ingredients like ham for a higher protein boost, as a 3-ounce serving provides roughly 18 grams of protein compared to the lower protein content in most vegetables. A vegetable omelet offers added fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants but typically delivers around 3-5 grams of protein depending on the vegetables used. Combining both ham and vegetables can maximize protein intake while enhancing nutrient diversity and flavor in your omelet.
Vegetable omelet vs Ham omelet for protein choice Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com