Mussels thrive in both freshwater and saltwater environments, but their habitat preferences impact their growth and reproduction. Freshwater mussels typically inhabit rivers, streams, and lakes with clean, oxygen-rich water, where they filter nutrients and provide ecosystem benefits. Saltwater mussels, found in marine environments such as coastal bays and estuaries, adapt to saline conditions and often attach to rocks or submerged structures, playing a crucial role in maintaining water quality through their filtration.
Table of Comparison
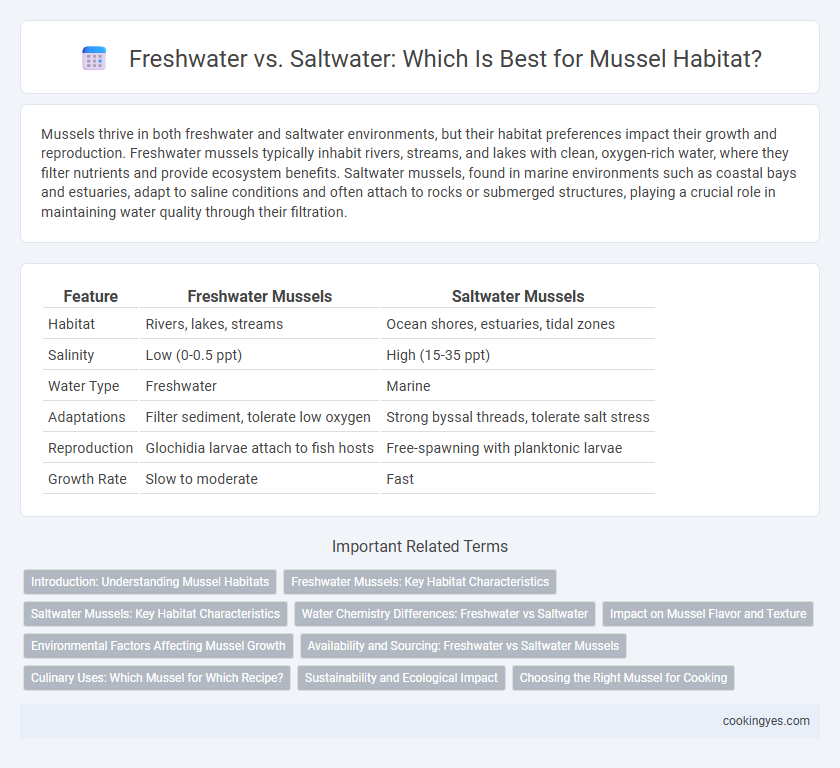
| Feature | Freshwater Mussels | Saltwater Mussels |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Rivers, lakes, streams | Ocean shores, estuaries, tidal zones |
| Salinity | Low (0-0.5 ppt) | High (15-35 ppt) |
| Water Type | Freshwater | Marine |
| Adaptations | Filter sediment, tolerate low oxygen | Strong byssal threads, tolerate salt stress |
| Reproduction | Glochidia larvae attach to fish hosts | Free-spawning with planktonic larvae |
| Growth Rate | Slow to moderate | Fast |
Introduction: Understanding Mussel Habitats
Mussels inhabit both freshwater and saltwater environments, each offering distinct conditions that influence their growth and survival. Freshwater mussels typically thrive in rivers, streams, and lakes with clean, well-oxygenated water, while saltwater mussels are commonly found attached to rocks and submerged structures in coastal and intertidal zones. Understanding the specific habitat requirements such as salinity levels, water temperature, and substrate type is essential for conserving mussel populations and maintaining ecosystem balance.
Freshwater Mussels: Key Habitat Characteristics
Freshwater mussels thrive in clean, well-oxygenated rivers and streams with stable substrates such as sand, gravel, or cobble, essential for their burrowing and feeding behaviors. These habitats often feature moderate to slow current flows that facilitate filter feeding and provide consistent nutrient sources. Freshwater mussel populations depend heavily on water quality parameters like low pollution levels and balanced pH, making them sensitive indicators of ecosystem health.
Saltwater Mussels: Key Habitat Characteristics
Saltwater mussels thrive in brackish to fully marine environments where salinity ranges between 15 to 30 parts per thousand, often attaching to rocky substrates, pilings, and submerged structures. These bivalves require well-oxygenated, nutrient-rich waters with moderate to strong tidal currents that facilitate filter feeding and waste removal. Key species such as Mytilus edulis demonstrate adaptability to varying salinity levels but depend fundamentally on stable saline conditions for optimal growth and reproduction.
Water Chemistry Differences: Freshwater vs Saltwater
Freshwater mussels thrive in environments with lower salinity levels, where ions like calcium and magnesium are less concentrated compared to saltwater habitats. Saltwater mussels require higher salinity and stable levels of sodium and chloride, adapting to the complex ionic composition of marine ecosystems. These water chemistry differences influence mussel shell formation, growth rates, and overall physiological processes.
Impact on Mussel Flavor and Texture
Freshwater mussels typically develop a milder, earthier flavor and a firmer texture due to their diet and the mineral composition of freshwater environments. Saltwater mussels, exposed to higher salinity and richer planktonic feed, often exhibit a brinier, slightly sweeter taste with a softer, more tender texture. Variations in water chemistry and habitat conditions directly influence the biochemical makeup of mussel muscle tissues, affecting both taste and mouthfeel.
Environmental Factors Affecting Mussel Growth
Mussel growth is significantly influenced by environmental factors such as water salinity, temperature, and nutrient availability, with freshwater and saltwater habitats presenting distinct conditions. Freshwater mussels thrive in stable, lower salinity environments with abundant organic matter, while saltwater mussels require higher salinity levels and benefit from tidal nutrient fluxes. Understanding the specific habitat requirements helps optimize conservation and aquaculture practices for different mussel species.
Availability and Sourcing: Freshwater vs Saltwater Mussels
Freshwater mussels primarily inhabit rivers, lakes, and streams, making them more accessible for local sourcing and sustainable harvesting compared to saltwater mussels found in oceanic environments. Saltwater mussels are generally farmed in coastal areas with higher salinity, often requiring specialized aquaculture facilities to ensure consistent availability. The availability of freshwater mussels is often limited by water quality and habitat degradation, while saltwater mussels benefit from expansive marine habitats but face challenges from pollution and overfishing.
Culinary Uses: Which Mussel for Which Recipe?
Freshwater mussels, with their milder flavor and firmer texture, are often favored in recipes requiring subtle taste profiles, such as steamed dishes or light broths, while saltwater mussels offer a brinier, richer taste ideal for robust preparations like seafood paellas or spicy marinara sauces. Saltwater varieties, especially blue mussels (Mytilus edulis), are widely used in European culinary traditions for their distinct oceanic flavor that complements garlic, white wine, and herbs. Freshwater mussels, though less common in commercial cuisine due to their tougher shells and variable flavor, are prized in regions where they are sustainably harvested and incorporated into rustic stews and chowders.
Sustainability and Ecological Impact
Freshwater and saltwater mussels differ significantly in sustainability and ecological impact, with freshwater mussels playing a crucial role in filtering pollutants and supporting biodiversity in river ecosystems, while saltwater mussels contribute to nutrient cycling and water purification in marine environments. Sustainable harvesting practices are essential in both habitats to prevent population declines and preserve ecological functions. Habitat degradation and pollution pose greater threats to freshwater mussel populations, making conservation efforts critical to maintaining their ecological benefits.
Choosing the Right Mussel for Cooking
Freshwater mussels and saltwater mussels differ significantly in taste, texture, and culinary uses, with freshwater varieties often offering a milder flavor suited for delicate dishes while saltwater mussels provide a brinier, more robust taste ideal for seafood stews and pasta. Selecting the right mussel depends on the recipe requirements and desired flavor profile, as saltwater mussels typically thrive in coastal environments with higher salinity levels, whereas freshwater mussels inhabit rivers and lakes with minimal salt content. For cooking, saltwater mussels are generally preferred due to their consistent availability, larger size, and richer mineral content that enhances their savory flavor.
Freshwater vs saltwater for mussel habitat Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com