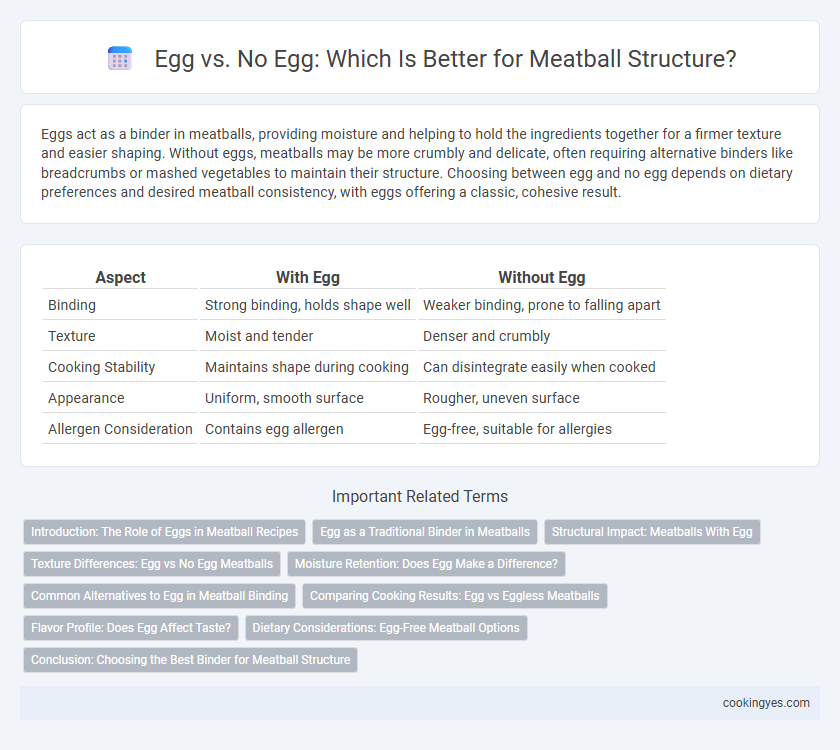
Eggs act as a binder in meatballs, providing moisture and helping to hold the ingredients together for a firmer texture and easier shaping. Without eggs, meatballs may be more crumbly and delicate, often requiring alternative binders like breadcrumbs or mashed vegetables to maintain their structure. Choosing between egg and no egg depends on dietary preferences and desired meatball consistency, with eggs offering a classic, cohesive result.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | With Egg | Without Egg |
|---|---|---|
| Binding | Strong binding, holds shape well | Weaker binding, prone to falling apart |
| Texture | Moist and tender | Denser and crumbly |
| Cooking Stability | Maintains shape during cooking | Can disintegrate easily when cooked |
| Appearance | Uniform, smooth surface | Rougher, uneven surface |
| Allergen Consideration | Contains egg allergen | Egg-free, suitable for allergies |
Introduction: The Role of Eggs in Meatball Recipes
Eggs act as a crucial binding agent in meatball recipes, helping to hold ground meat and other ingredients together during cooking. Their proteins coagulate when heated, providing structure and preventing meatballs from falling apart. While some recipes omit eggs for dietary or texture preferences, this often requires alternative binders like breadcrumbs or soaked bread to maintain firmness.
Egg as a Traditional Binder in Meatballs
Egg serves as a traditional binder in meatballs, enhancing structure by providing moisture and protein that helps maintain shape during cooking. Its coagulating properties create a firm, cohesive texture that prevents crumbling and improves overall bite. Using egg also aids in emulsifying the ingredients, resulting in a tender yet sturdy meatball.
Structural Impact: Meatballs With Egg
Eggs play a crucial role in meatball structure by acting as a binding agent that holds the meat mixture together, preventing it from falling apart during cooking. The proteins in eggs coagulate when heated, creating a firm and cohesive texture that enhances the shape retention of meatballs. Without eggs, meatballs tend to be crumbly and require alternative binders like breadcrumbs or mashed vegetables to maintain structural integrity.
Texture Differences: Egg vs No Egg Meatballs
Eggs in meatballs act as a binding agent, resulting in a firmer, more cohesive texture that holds shape during cooking. Meatballs without eggs tend to be looser and more crumbly, producing a softer bite but requiring careful handling to prevent disintegration. The presence of eggs also adds moisture, enhancing juiciness while contributing to a slightly denser texture compared to egg-free variations.
Moisture Retention: Does Egg Make a Difference?
Eggs play a crucial role in meatball structure by enhancing moisture retention, preventing dryness during cooking. The lecithin in egg yolks acts as an emulsifier, binding fat and water, which keeps meatballs tender and juicy. Without eggs, meatballs may lose more moisture, resulting in a drier texture and less cohesive bite.
Common Alternatives to Egg in Meatball Binding
Common alternatives to egg in meatball binding include breadcrumbs soaked in milk, which provide moisture and help maintain shape during cooking. Mashed potatoes or cooked rice can also serve as effective binders, adding texture and firmness without altering flavor. Ground flaxseed mixed with water offers a plant-based option that mimics egg's binding properties while enhancing nutritional value.
Comparing Cooking Results: Egg vs Eggless Meatballs
Egg meatballs tend to have a firmer, more cohesive texture due to the binding proteins in eggs that help hold the mixture together during cooking. Eggless meatballs often rely on alternative binders like breadcrumbs, flaxseed, or mashed vegetables, which can result in a softer or slightly crumbly texture but still maintain flavor and moisture. When comparing cooking results, egg meatballs typically retain shape better and have a classic chew, whereas eggless versions may be more tender and suited for specific dietary needs or preferences.
Flavor Profile: Does Egg Affect Taste?
Eggs contribute a subtle richness and moisture to meatballs, enhancing the overall flavor profile by adding a mild, creamy undertone. Without egg, meatballs may have a denser texture and a more straightforward, meat-forward taste, allowing the spices and herbs to stand out more prominently. The presence of egg slightly mellows the seasoning intensity, creating a balanced and cohesive flavor experience.
Dietary Considerations: Egg-Free Meatball Options
Egg-free meatball options cater to individuals with egg allergies, vegan diets, or cholesterol concerns by using alternatives like flaxseed meal, chia seeds, or aquafaba to bind ingredients effectively. These substitutes maintain the meatballs' structural integrity and moisture without compromising texture or flavor, ensuring a safe and delicious choice for diverse dietary needs. Selecting egg-free binders enhances dietary flexibility while preserving the traditional meatball experience.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Binder for Meatball Structure
Eggs act as a superior binder in meatballs, providing moisture, richness, and a firm texture that prevents crumbling during cooking. Without eggs, meatballs may require alternative binders such as breadcrumbs soaked in milk or mashed vegetables to maintain structure but often result in a softer, less cohesive texture. Selecting the best binder depends on dietary preferences and desired texture, with eggs offering optimal structural support for traditional meatballs.
Egg vs No Egg for meatball structure Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com