Gluten-free macaroni offers a suitable alternative for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease, providing similar texture and taste without harming their digestive system. Traditional macaroni, made from wheat flour, contains gluten which can cause adverse reactions in sensitive individuals but offers a familiar, chewy consistency favored in many classic recipes. Choosing between gluten-free and traditional macaroni depends on dietary needs, with gluten-free options ensuring safe consumption while maintaining versatility in pasta dishes.
Table of Comparison
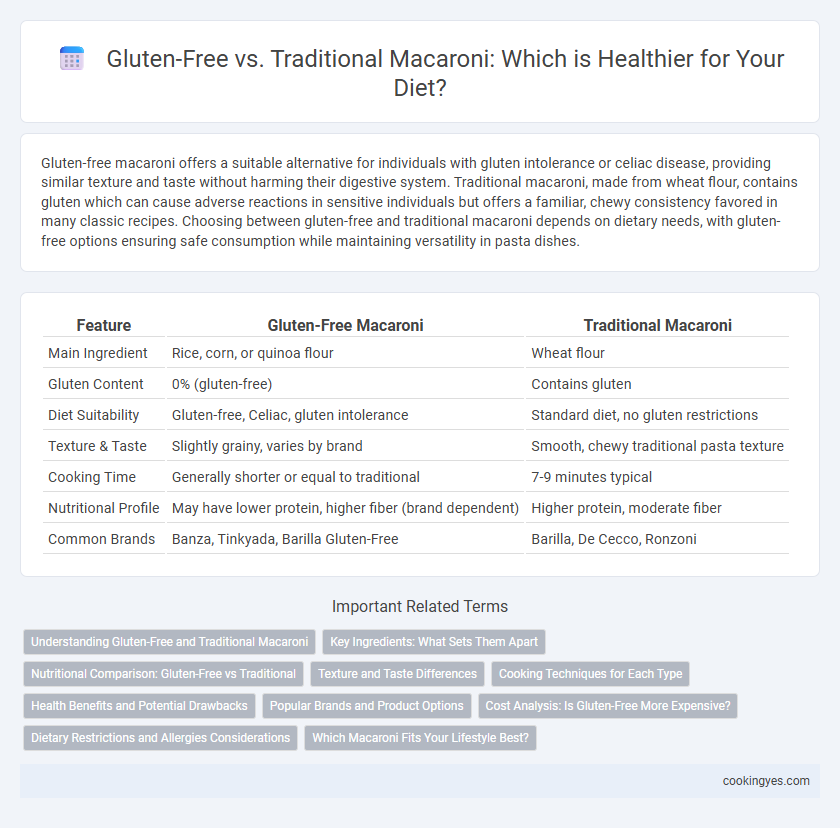
| Feature | Gluten-Free Macaroni | Traditional Macaroni |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredient | Rice, corn, or quinoa flour | Wheat flour |
| Gluten Content | 0% (gluten-free) | Contains gluten |
| Diet Suitability | Gluten-free, Celiac, gluten intolerance | Standard diet, no gluten restrictions |
| Texture & Taste | Slightly grainy, varies by brand | Smooth, chewy traditional pasta texture |
| Cooking Time | Generally shorter or equal to traditional | 7-9 minutes typical |
| Nutritional Profile | May have lower protein, higher fiber (brand dependent) | Higher protein, moderate fiber |
| Common Brands | Banza, Tinkyada, Barilla Gluten-Free | Barilla, De Cecco, Ronzoni |
Understanding Gluten-Free and Traditional Macaroni
Gluten-free macaroni is made from alternative flours such as rice, corn, or quinoa, catering to those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease, while traditional macaroni primarily uses wheat flour containing gluten. The nutritional profile of gluten-free macaroni often varies, sometimes including higher fiber or protein depending on the base ingredient, whereas traditional macaroni provides a familiar texture and protein content. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right type to suit dietary needs and preferences without compromising on taste or nutrition.
Key Ingredients: What Sets Them Apart
Gluten-free macaroni is typically made from alternative flours such as rice, corn, or quinoa, which replace traditional wheat flour and eliminate gluten proteins. Traditional macaroni contains wheat flour, providing gluten that contributes to its elasticity and chewy texture. The absence of gluten in gluten-free varieties often requires the addition of binding agents like xanthan gum to mimic the texture of conventional pasta.
Nutritional Comparison: Gluten-Free vs Traditional
Gluten-free macaroni often contains alternative flours such as rice, corn, or quinoa, which can result in a different nutrient profile compared to traditional wheat-based macaroni. Traditional macaroni generally provides higher protein content and more B vitamins due to the presence of wheat gluten and enriched flour. However, gluten-free versions may offer higher fiber levels and are suitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, making them a viable option for balanced diets requiring gluten avoidance.
Texture and Taste Differences
Gluten-free macaroni often features a denser texture and a slightly grainier mouthfeel compared to traditional wheat-based varieties, which offer a firm yet tender bite due to gluten's elastic properties. Taste differences arise as gluten-free options, commonly made from rice, corn, or quinoa flour, present a nuttier or earthier flavor profile, contrasting with the neutral, milder taste of traditional macaroni. These variations impact the overall eating experience, influencing suitability for gluten-sensitive diets without compromising essential nutritional benefits like carbohydrate content.
Cooking Techniques for Each Type
Gluten-free macaroni requires careful boiling with constant stirring and shorter cook times to prevent mushiness, while traditional macaroni benefits from prolonged boiling in salted water to achieve firm al dente texture. Rinsing gluten-free pasta after cooking reduces starchiness, improving texture and preventing clumping, a step unnecessary for traditional wheat-based macaroni. Using precise timing and water-to-pasta ratios is critical for both types to optimize cooking consistency and enhance nutrient retention.
Health Benefits and Potential Drawbacks
Gluten-free macaroni offers significant advantages for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, reducing digestive discomfort and inflammation linked to gluten intake. Traditional macaroni, typically made from wheat, provides higher protein and fiber content but may trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals. Careful consideration of dietary needs and ingredient quality is essential when choosing between gluten-free and traditional macaroni for a balanced diet.
Popular Brands and Product Options
Popular gluten-free macaroni brands like Tinkyada and Barilla offer a variety of rice, corn, or legume-based options catering to dietary restrictions without sacrificing texture or flavor. Traditional macaroni brands such as De Cecco and Ronzoni maintain classic wheat-based recipes favored for their firm bite and culinary versatility. Consumers seeking gluten-free alternatives can choose from diverse product lines that replicate traditional macaroni's cooking performance while meeting gluten intolerance needs.
Cost Analysis: Is Gluten-Free More Expensive?
Gluten-free macaroni often carries a higher price tag compared to traditional wheat-based varieties due to specialized ingredients like rice, corn, or quinoa flour and smaller production scales. Bulk purchasing and brand selection can influence the cost discrepancy, but overall, gluten-free options tend to be more expensive, impacting diet budgeting for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Traditional macaroni benefits from established mass production and raw materials typically sourced at lower costs, making it the more economical choice for consumers without dietary restrictions.
Dietary Restrictions and Allergies Considerations
Gluten-free macaroni caters to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity by eliminating wheat-based ingredients, preventing adverse reactions and digestive discomfort. Traditional macaroni, typically made from durum wheat semolina, provides a higher protein content but poses risks for those with gluten allergies or intolerances. Selecting gluten-free pasta ensures safety and inclusivity for dietary restrictions while maintaining the versatility of macaroni in numerous recipes.
Which Macaroni Fits Your Lifestyle Best?
Gluten-free macaroni offers a suitable alternative for those with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, made from rice, corn, or quinoa flours that provide similar texture and taste to traditional wheat-based macaroni. Traditional macaroni is rich in gluten, which gives it elasticity and a chewy bite, preferred by many for classic pasta dishes and better nutrient absorption. Choosing between gluten-free and traditional macaroni depends on digestive health, dietary restrictions, and personal taste preferences to best fit your lifestyle and nutritional needs.
Gluten-Free vs Traditional for Macaroni Diet Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com