Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, is primarily found along the Atlantic coast of North America and is prized for its large size and sweet, tender meat. Homarus gammarus, or the European lobster, inhabits the eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean seas, distinguished by its slightly smaller claws and a firmer texture. Both species offer distinct culinary experiences, with Homarus americanus favored for its rich flavor and Homarus gammarus appreciated for its delicate taste and versatility in seafood dishes.
Table of Comparison
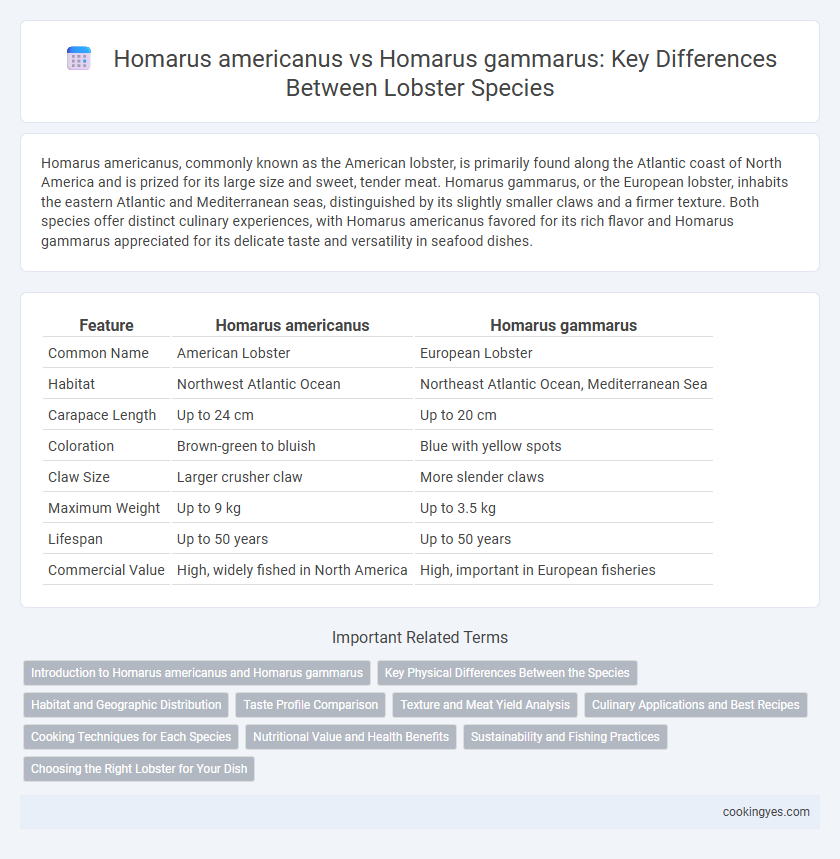
| Feature | Homarus americanus | Homarus gammarus |
|---|---|---|
| Common Name | American Lobster | European Lobster |
| Habitat | Northwest Atlantic Ocean | Northeast Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea |
| Carapace Length | Up to 24 cm | Up to 20 cm |
| Coloration | Brown-green to bluish | Blue with yellow spots |
| Claw Size | Larger crusher claw | More slender claws |
| Maximum Weight | Up to 9 kg | Up to 3.5 kg |
| Lifespan | Up to 50 years | Up to 50 years |
| Commercial Value | High, widely fished in North America | High, important in European fisheries |
Introduction to Homarus americanus and Homarus gammarus
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, is primarily found along the Atlantic coast of North America, thriving in cold, rocky marine environments, and is prized for its large claws and sweet meat. Homarus gammarus, the European lobster, inhabits the northeast Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea, recognized for its distinct dark blue shell and slightly smaller size relative to its American counterpart. Both species play significant roles in regional fisheries, with Homarus americanus dominating the North American market and Homarus gammarus being a key species in European seafood industries.
Key Physical Differences Between the Species
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, typically features a larger, more robust claw structure with one claw significantly bigger, adapted for crushing, and a dark bluish-green to brown shell. In contrast, Homarus gammarus, the European lobster, displays slightly slimmer claws that are more equal in size with brighter coloration, usually dark blue with yellow spots on the body and claws. These key physical differences help distinguish the two species, important for identification in their respective marine environments along the North Atlantic coasts.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, inhabits the cold waters of the Atlantic coast of North America, ranging from Labrador to North Carolina, thriving in rocky, sheltered seabeds. In contrast, Homarus gammarus, the European lobster, is found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and parts of the Mediterranean Sea, preferring rocky substrates from Norway to the Azores and along the coasts of Western Europe. Both species occupy similar depth ranges but differ significantly in their geographic distribution across the Atlantic basin.
Taste Profile Comparison
The taste profile of Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, is characterized by a sweet, tender, and slightly briny flavor, often described as rich and buttery. In contrast, Homarus gammarus, the European lobster, offers a firmer texture with a more pronounced, slightly mineral and oceanic taste, providing a less sweet but equally flavorful experience. Both species are highly prized in culinary traditions, but the American lobster's delicate sweetness often appeals more to those seeking a subtler lobster flavor.
Texture and Meat Yield Analysis
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, features a firmer texture with denser meat, making it preferred for its higher meat yield, particularly in the claw and tail regions. Homarus gammarus, the European lobster, offers a slightly more tender texture but generally produces less meat yield due to its thinner shells and smaller claw size. Comparative studies highlight Homarus americanus's superior volume of edible meat, which significantly impacts commercial harvesting and culinary applications.
Culinary Applications and Best Recipes
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, features sweeter, more tender meat ideal for steaming, boiling, and classic dishes such as lobster rolls and bisques. Homarus gammarus, or the European lobster, boasts firmer, slightly brinier meat perfect for grilling, baking, and Mediterranean-style recipes incorporating garlic, herbs, and olive oil. Culinary applications prioritize Homarus americanus for rich, creamy textures while Homarus gammarus is favored for robust, complex flavors in gourmet preparations.
Cooking Techniques for Each Species
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, responds well to boiling and steaming due to its thick, firm meat that retains moisture and flavor under high heat. In contrast, Homarus gammarus, or the European lobster, is better suited for grilling or baking, as its slightly more delicate texture benefits from gentler cooking methods that preserve its tender consistency. Understanding these species-specific cooking techniques enhances the culinary experience by maximizing the unique taste and texture of each lobster variety.
Nutritional Value and Health Benefits
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and essential minerals like zinc and selenium compared to Homarus gammarus, or the European lobster. Both species provide a rich source of lean protein and are low in saturated fat, promoting cardiovascular health and muscle maintenance. The American lobster's greater concentration of antioxidants and vitamins, particularly vitamin B12, supports improved immune function and neurological health.
Sustainability and Fishing Practices
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, benefits from stringent fishing regulations and well-established conservation programs that promote sustainable population levels through size limits, trap quotas, and seasonal closures. In contrast, Homarus gammarus, the European lobster, faces challenges due to less uniform fishing policies and variable enforcement across European waters, impacting its population resilience. Sustainable fishing practices such as trap modifications to reduce bycatch and adherence to marine protected areas are critical for both species to maintain ecological balance and fishery viability.
Choosing the Right Lobster for Your Dish
Homarus americanus, commonly known as the American lobster, features a sweeter, more tender meat ideal for boiling or steaming, making it a popular choice in New England cuisine. In contrast, Homarus gammarus, the European lobster, offers a firmer texture and richer flavor, preferred in Mediterranean dishes and grilling recipes. Selecting between these species depends on desired texture and flavor profile, with American lobsters suited for delicate preparations and European lobsters enhancing robust, grilled dishes.
Homarus americanus vs Homarus gammarus for lobster species Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com