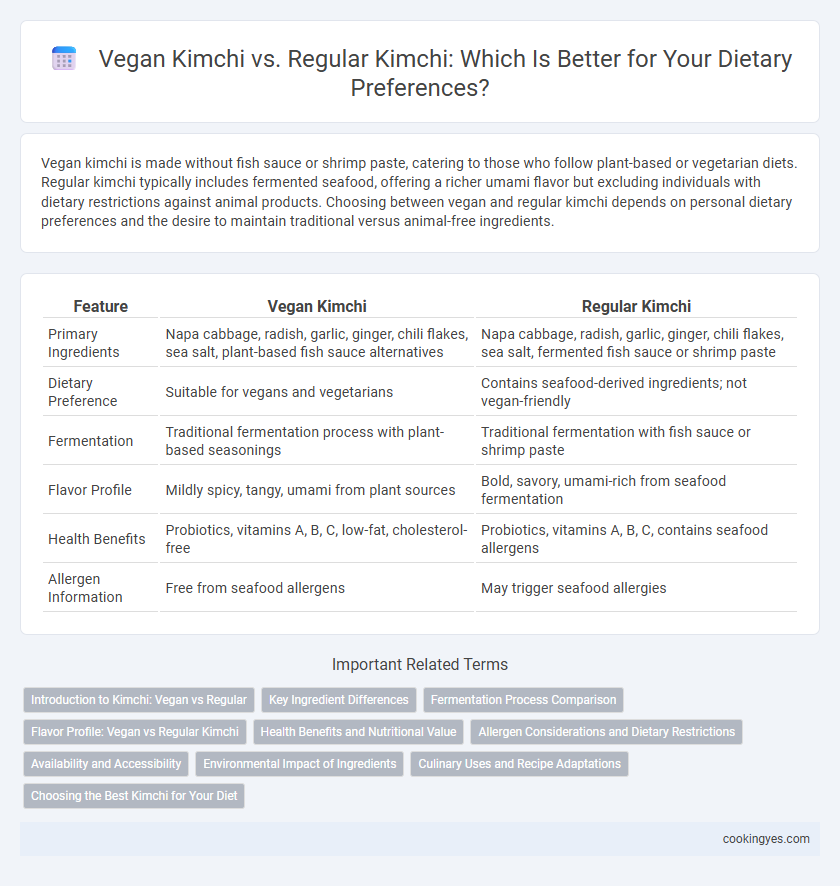
Vegan kimchi is made without fish sauce or shrimp paste, catering to those who follow plant-based or vegetarian diets. Regular kimchi typically includes fermented seafood, offering a richer umami flavor but excluding individuals with dietary restrictions against animal products. Choosing between vegan and regular kimchi depends on personal dietary preferences and the desire to maintain traditional versus animal-free ingredients.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegan Kimchi | Regular Kimchi |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Ingredients | Napa cabbage, radish, garlic, ginger, chili flakes, sea salt, plant-based fish sauce alternatives | Napa cabbage, radish, garlic, ginger, chili flakes, sea salt, fermented fish sauce or shrimp paste |
| Dietary Preference | Suitable for vegans and vegetarians | Contains seafood-derived ingredients; not vegan-friendly |
| Fermentation | Traditional fermentation process with plant-based seasonings | Traditional fermentation with fish sauce or shrimp paste |
| Flavor Profile | Mildly spicy, tangy, umami from plant sources | Bold, savory, umami-rich from seafood fermentation |
| Health Benefits | Probiotics, vitamins A, B, C, low-fat, cholesterol-free | Probiotics, vitamins A, B, C, contains seafood allergens |
| Allergen Information | Free from seafood allergens | May trigger seafood allergies |
Introduction to Kimchi: Vegan vs Regular
Kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented dish, varies between vegan and regular versions based on ingredients used; vegan kimchi excludes fish sauce and seafood, relying on plant-based seasonings like soy sauce or miso, while regular kimchi typically contains anchovy or shrimp paste for fermentation and flavor. This variation significantly impacts dietary preferences, with vegan kimchi catering to plant-based diets and regular kimchi serving omnivorous consumers. Nutritional profiles differ, with vegan kimchi offering lower cholesterol and animal protein content, aligning with vegan dietary restrictions.
Key Ingredient Differences
Vegan kimchi omits traditional seafood-based ingredients like fish sauce or shrimp paste, relying instead on substitutes such as soy sauce or seaweed extract to achieve umami flavor. Regular kimchi typically includes these fermented seafood components, contributing to its distinctive savory taste and probiotic profile. The absence of animal-derived ingredients in vegan kimchi aligns with plant-based dietary preferences while maintaining the vital fermentation process using napa cabbage and Korean chili flakes.
Fermentation Process Comparison
Vegan kimchi excludes fish sauce and shrimp paste, using plant-based alternatives like seaweed or soy sauce, which alters the fermentation process by fostering different microbial communities. Regular kimchi relies on seafood-based ingredients that promote Lactobacillus species, resulting in a distinct flavor profile and probiotic content. These variations impact both the fermentation time and the balance of beneficial bacteria, influencing taste, texture, and health benefits tailored to dietary preferences.
Flavor Profile: Vegan vs Regular Kimchi
Vegan kimchi often features a flavor profile that is tangy, spicy, and slightly sweet, relying on fermented vegetables, garlic, ginger, and chili powder without the traditional fish sauce or fermented seafood used in regular kimchi. Regular kimchi delivers a more complex umami depth and savory richness due to anchovy or shrimp paste, intensifying its bold, pungent taste. Consumers seeking a plant-based diet appreciate vegan kimchi for its cleaner, fresher taste, while those favoring traditional flavor enjoy the robust, layered umami characteristic of classic kimchi.
Health Benefits and Nutritional Value
Vegan kimchi excludes fish sauce and shrimp paste, making it suitable for plant-based diets while maintaining rich probiotics that support gut health. Regular kimchi contains fermented seafood ingredients, which contribute additional protein and omega-3 fatty acids but may trigger allergies or sensitivities in some individuals. Both varieties offer high levels of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as antioxidants, promoting immune function and reducing inflammation.
Allergen Considerations and Dietary Restrictions
Vegan kimchi excludes fish sauce and seafood-based ingredients commonly found in regular kimchi, making it suitable for those with shellfish allergies and strict plant-based diets. Regular kimchi often contains anchovy or shrimp paste, which can trigger allergic reactions and violate dietary restrictions such as veganism or certain religious practices. Choosing vegan kimchi supports allergen management and accommodates diverse dietary preferences without compromising traditional fermentation flavors.
Availability and Accessibility
Vegan kimchi, made without fish sauce or shrimp paste, is increasingly available in specialty health food stores and online retailers catering to plant-based diets, whereas regular kimchi remains widely accessible in most Asian grocery stores due to traditional recipes. The rising demand for vegan alternatives has expanded distribution channels, improving accessibility for those following vegan or vegetarian lifestyles. Regular kimchi, however, benefits from broader mainstream presence and cultural familiarity, making it easier to find in diverse markets worldwide.
Environmental Impact of Ingredients
Vegan kimchi excludes fish sauce and shrimp paste commonly found in regular kimchi, significantly reducing its environmental footprint by lowering reliance on overfished marine resources. Plant-based fermenting agents promote sustainability by decreasing water usage and greenhouse gas emissions associated with seafood production. Choosing vegan kimchi supports biodiversity and aligns with environmentally conscious dietary preferences.
Culinary Uses and Recipe Adaptations
Vegan kimchi replaces traditional fish sauce or shrimp paste with soy sauce, miso, or seaweed to maintain umami flavors, making it suitable for plant-based diets without sacrificing authenticity. Regular kimchi, rich in fermented seafood ingredients, offers robust flavors that enhance dishes like Korean stews, bibimbap, and pancakes. Recipe adaptations for vegan kimchi require careful balancing of saltiness and depth, ensuring versatile culinary uses across vegan and vegetarian Korean cuisine.
Choosing the Best Kimchi for Your Diet
Vegan kimchi excludes fish sauce and shrimp paste, making it ideal for plant-based diets and those avoiding animal products, while regular kimchi typically contains fermented seafood enhancing its umami flavor. When choosing the best kimchi for your diet, consider ingredients, fermentation methods, and personal health goals such as sodium content and probiotic benefits. Opting for vegan kimchi supports ethical and allergen-conscious choices without sacrificing the traditional tangy taste associated with kimchi.
Vegan Kimchi vs Regular Kimchi for Dietary Preference Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com