Kimchi fermentation can be done either on-the-counter or refrigerated, each method impacting flavor and fermentation speed. On-the-counter fermentation accelerates lactic acid bacteria activity, producing a tangier and more robust kimchi in a shorter time. Refrigerated fermentation slows the process, resulting in a milder taste and longer shelf life, preserving the pet-safe nutrients effectively.
Table of Comparison
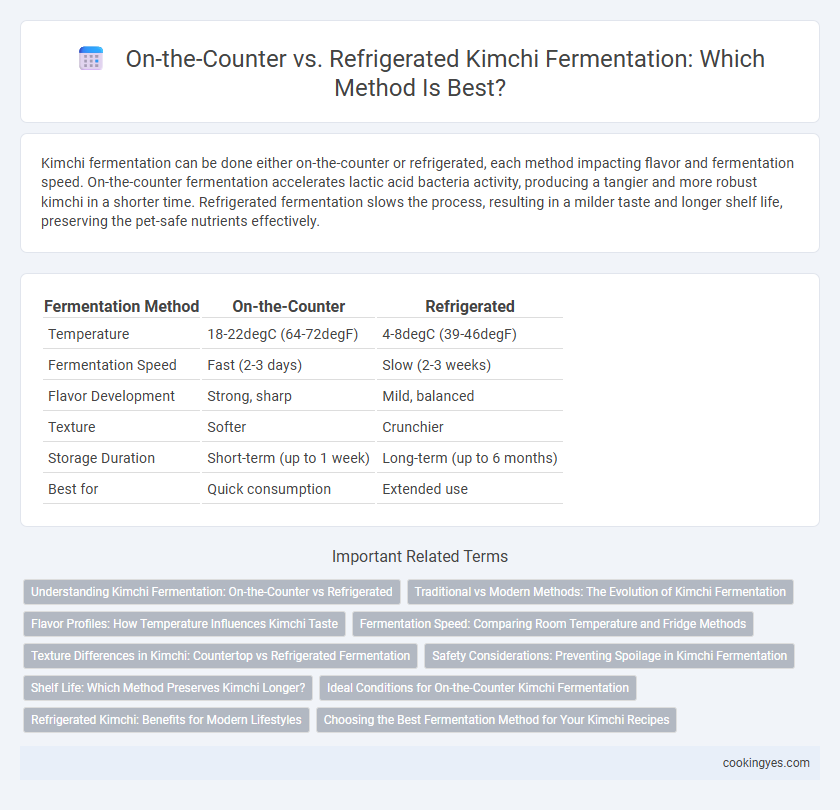
| Fermentation Method | On-the-Counter | Refrigerated |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 18-22degC (64-72degF) | 4-8degC (39-46degF) |
| Fermentation Speed | Fast (2-3 days) | Slow (2-3 weeks) |
| Flavor Development | Strong, sharp | Mild, balanced |
| Texture | Softer | Crunchier |
| Storage Duration | Short-term (up to 1 week) | Long-term (up to 6 months) |
| Best for | Quick consumption | Extended use |
Understanding Kimchi Fermentation: On-the-Counter vs Refrigerated
Kimchi fermentation varies significantly between on-the-counter and refrigerated methods, impacting flavor development and fermentation speed. On-the-counter fermentation typically occurs at room temperature around 20-22degC, accelerating microbial activity and resulting in a tangier, more pungent kimchi within 1-2 days. Refrigerated fermentation at 4degC slows down lactic acid bacteria growth, producing a milder taste and allowing kimchi to ferment gradually over 2-4 weeks, enhancing texture and complexity.
Traditional vs Modern Methods: The Evolution of Kimchi Fermentation
Traditional kimchi fermentation relies on on-the-counter methods, allowing natural ambient temperature fluctuations to develop complex flavors over weeks, often enhancing probiotic content. Modern refrigeration techniques control temperature precisely, accelerating fermentation while maintaining consistent taste and texture, reducing spoilage risks. This evolution from ambient to refrigerated fermentation reflects a balance between preserving traditional quality and improving food safety and shelf life.
Flavor Profiles: How Temperature Influences Kimchi Taste
On-the-counter fermentation accelerates kimchi's sourness by encouraging rapid lactic acid bacteria activity at room temperature, resulting in a tangier and more pungent flavor profile. Refrigerated fermentation slows down microbial metabolism, producing a milder, crispier texture with subtle, balanced flavors over an extended period. Temperature directly influences the development of organic acids and aroma compounds, shaping the distinctive taste characteristics of kimchi.
Fermentation Speed: Comparing Room Temperature and Fridge Methods
Kimchi ferments faster at room temperature, typically completing the initial fermentation within 1 to 3 days, which intensifies its tangy flavor and softens the vegetables rapidly. Refrigerated fermentation slows down the process, extending it to several weeks, allowing for a more gradual development of complex flavors and preserving the kimchi's crunchiness. Choosing room temperature accelerates lactobacillus activity, while refrigeration maintains a steady, slower fermentation rate that enhances probiotic qualities over time.
Texture Differences in Kimchi: Countertop vs Refrigerated Fermentation
Kimchi fermented on the countertop develops a softer, more effervescent texture due to warmer temperatures accelerating fermentation and enzyme activity. In contrast, refrigerated fermentation slows these processes, resulting in crisper cabbage and a firmer overall bite. Temperature control directly influences lactic acid bacteria growth, which is critical for achieving the desired texture in traditional kimchi.
Safety Considerations: Preventing Spoilage in Kimchi Fermentation
On-the-counter fermentation of kimchi requires careful monitoring of temperature and hygiene to prevent spoilage and ensure safety, as ambient conditions can promote harmful bacterial growth. Refrigerated fermentation slows down microbial activity, reducing the risk of spoilage and extending shelf life while maintaining safe lactic acid fermentation. Proper sealing and consistent cold storage temperatures below 5degC are critical in preventing contamination and preserving the quality of kimchi during fermentation.
Shelf Life: Which Method Preserves Kimchi Longer?
Refrigerated fermentation of kimchi significantly extends shelf life by maintaining a consistent low temperature that slows microbial activity, allowing preservation for several months without spoilage. On-the-counter fermentation accelerates fermentation due to warmer ambient temperatures, resulting in a shorter shelf life typically lasting one to two weeks before sourness intensifies. For prolonged storage and flavor stability, refrigeration remains the preferred method to preserve kimchi's texture and taste.
Ideal Conditions for On-the-Counter Kimchi Fermentation
On-the-counter kimchi fermentation thrives at room temperatures of 18-22degC (64-72degF), which promote moderate fermentation speed, enhancing flavor complexity and texture. Ideal conditions include storing kimchi in airtight containers to minimize oxygen exposure and placing them away from direct sunlight to maintain consistent temperature. Controlled humidity around 60-70% helps prevent drying out while allowing natural fermentation processes driven by lactobacillus bacteria to develop optimal tang and umami notes.
Refrigerated Kimchi: Benefits for Modern Lifestyles
Refrigerated kimchi fermentation offers precise temperature control, preserving the optimal balance of beneficial probiotics like Lactobacillus strains for enhanced gut health. This method extends shelf life by slowing fermentation, reducing spoilage risks and maintaining consistent flavor profiles suited for modern consumers. Convenient refrigeration aligns with busy lifestyles, enabling ready-to-eat kimchi that supports nutritious, time-efficient meal options.
Choosing the Best Fermentation Method for Your Kimchi Recipes
Choosing the best fermentation method for kimchi depends on the desired flavor profile and fermentation speed. On-the-counter fermentation at room temperature accelerates the process, producing tangier and more robust flavors within 1-3 days, ideal for quick consumption. Refrigerated fermentation slows down bacterial activity, extending the aging process over several weeks to develop complex, mellow flavors while maintaining optimal food safety and texture.
On-the-counter vs Refrigerated for kimchi fermentation method Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com