Choosing between Atlantic and Pacific crabs for pets depends on species availability and environmental conditions. Atlantic crabs, such as the Atlantic blue crab, are known for their vibrant colors and adaptability to cooler waters, while Pacific crabs often include varieties like the Dungeness, prized for their size and hardiness in diverse habitats. Understanding these differences helps hobbyists select the ideal crab species that thrives best in their home aquarium environment.
Table of Comparison
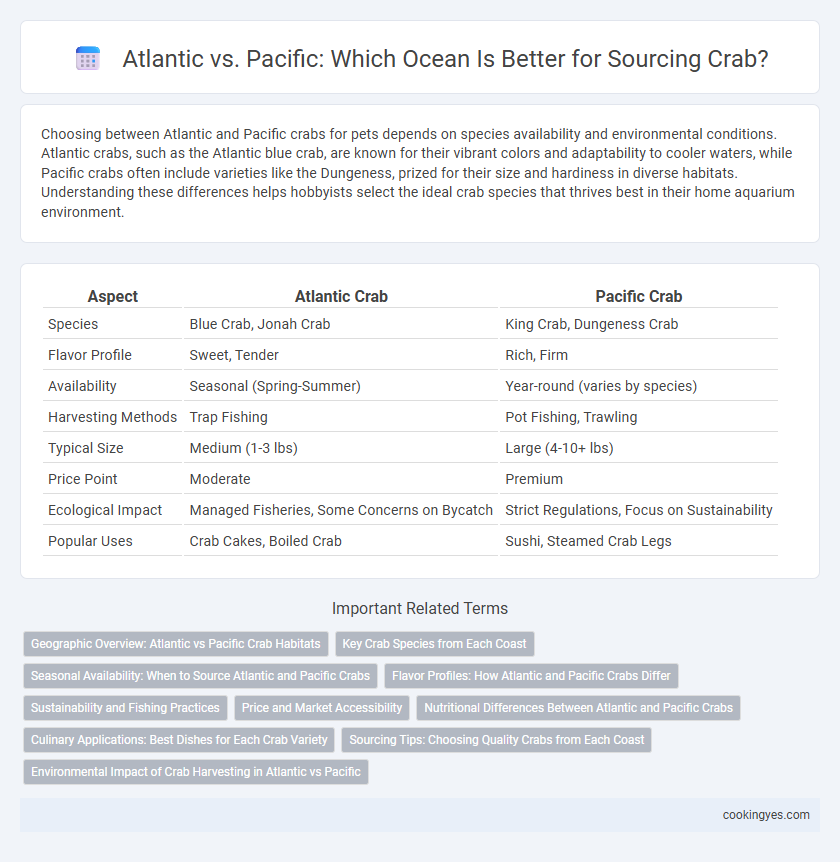
| Aspect | Atlantic Crab | Pacific Crab |
|---|---|---|
| Species | Blue Crab, Jonah Crab | King Crab, Dungeness Crab |
| Flavor Profile | Sweet, Tender | Rich, Firm |
| Availability | Seasonal (Spring-Summer) | Year-round (varies by species) |
| Harvesting Methods | Trap Fishing | Pot Fishing, Trawling |
| Typical Size | Medium (1-3 lbs) | Large (4-10+ lbs) |
| Price Point | Moderate | Premium |
| Ecological Impact | Managed Fisheries, Some Concerns on Bycatch | Strict Regulations, Focus on Sustainability |
| Popular Uses | Crab Cakes, Boiled Crab | Sushi, Steamed Crab Legs |
Geographic Overview: Atlantic vs Pacific Crab Habitats
Atlantic crab habitats predominantly span the colder waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, including regions off the coasts of New England, Canada, and parts of Europe, known for species like the Atlantic blue crab and snow crab. Pacific crab environments are typically found along the coasts of Alaska, British Columbia, and the Pacific Northwest, with a rich presence of Dungeness crab and king crab thriving in the nutrient-rich waters of the Bering Sea and Pacific Ocean. These distinct geographic zones influence crab species diversity, population density, and seasonal availability, shaping sourcing strategies for commercial fisheries.
Key Crab Species from Each Coast
Atlantic crab sourcing primarily centers on the Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus), known for its sweet, tender meat and significant commercial value along the U.S. East Coast. Conversely, the Pacific Coast is renowned for the Dungeness Crab (Metacarcinus magister), prized for its large size and rich flavor, widely harvested from Alaska to California. Key species from each coast highlight regional differences in climate, habitat, and culinary preferences, influencing the crab industry's economic and ecological dynamics.
Seasonal Availability: When to Source Atlantic and Pacific Crabs
Atlantic crabs, particularly blue crabs, are primarily available in the late spring through early fall, peaking from May to October, aligning with their molting and breeding cycles. Pacific crabs, such as Dungeness crabs, are most abundant during the late fall and winter months, typically from November to January, making their harvest seasonal and weather-dependent. Sourcing decisions should consider these distinct seasonal windows to ensure optimal freshness and supply for Atlantic and Pacific crab varieties.
Flavor Profiles: How Atlantic and Pacific Crabs Differ
Atlantic crabs are known for their sweet, delicate flavor with a slightly briny undertone, making them ideal for dishes that emphasize subtle seafood tastes. Pacific crabs tend to have a richer, more robust flavor with a firmer texture, often preferred for hearty recipes and bold seasoning. The distinct flavor profiles of Atlantic and Pacific crabs directly influence culinary applications and consumer preferences across different gastronomic regions.
Sustainability and Fishing Practices
Atlantic crab fisheries often implement rigorous sustainability measures, including strict quotas and seasonal closures to prevent overfishing and protect juvenile crabs. In contrast, Pacific crab sourcing tends to emphasize trap fishing techniques that reduce bycatch and minimize habitat damage, supporting ecosystem health. Both regions are increasingly adopting certification programs like MSC to ensure responsible harvesting and traceability in the crab supply chain.
Price and Market Accessibility
Atlantic crab generally commands higher prices due to its perceived superior flavor and firmer texture, making it a premium product in seafood markets. Pacific crab offers greater market accessibility because of its larger supply volume and widespread harvesting regions along the west coast of North America and Asia. Price-sensitive buyers often prefer Pacific crab for its affordability, while luxury markets tend to favor the Atlantic variety despite limited sourcing areas.
Nutritional Differences Between Atlantic and Pacific Crabs
Atlantic crabs generally offer higher omega-3 fatty acid levels, contributing to improved heart health compared to Pacific crabs. Pacific crabs are often richer in certain vitamins such as vitamin B12 and selenium, which support energy metabolism and antioxidant functions. These nutritional variations influence consumer choices based on specific dietary needs and health benefits.
Culinary Applications: Best Dishes for Each Crab Variety
Atlantic crabs, particularly Blue Crabs, are prized for their sweet, tender meat, making them ideal for classic dishes like Maryland crab cakes and crab boils that highlight delicate flavors. Pacific crabs, such as Dungeness and King crab, offer firmer, more robust meat perfect for grilling, steaming, or incorporating into rich bisques and seafood chowders. Each variety brings unique textures and flavor profiles that influence optimal culinary applications in coastal and gourmet cuisine.
Sourcing Tips: Choosing Quality Crabs from Each Coast
When sourcing crabs, Atlantic crabs, particularly Blue Crabs, offer a sweeter, tender meat ideal for delicate recipes, while Pacific crabs like Dungeness provide a firmer texture suited for hearty dishes. Prioritize freshness by selecting crabs harvested during peak seasons--spring to early summer on the East Coast and late fall through winter on the West Coast--to ensure optimal flavor and sustainability. Verify sourcing practices by choosing suppliers committed to sustainable fishing methods certified by organizations such as the Marine Stewardship Council for Atlantic crabs and the Pacific Seafood Processors Association for West Coast varieties.
Environmental Impact of Crab Harvesting in Atlantic vs Pacific
Harvesting crabs in the Atlantic typically has a lower environmental impact due to stricter regulations and sustainable practices such as size limits and seasonal closures, which help preserve crab populations and marine ecosystems. In contrast, some Pacific crab fisheries face challenges like habitat disruption and bycatch, although efforts are underway to improve management and reduce ecological footprints. The Atlantic's implementation of quota systems and habitat protection measures advances conservation, making its crab sourcing generally more environmentally sustainable than certain Pacific fisheries.
Atlantic vs Pacific for crab sourcing Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com