Heritage breed chickens are prized for their genetic diversity, robust health, and ability to thrive in free-range environments, making them ideal for sustainable, small-scale farming. Commercial breeds are selectively bred for rapid growth and high egg or meat production, often requiring controlled conditions and specialized feed. Choosing heritage breeds supports biodiversity and long-term resilience, while commercial breeds maximize efficiency and yield in intensive systems.
Table of Comparison
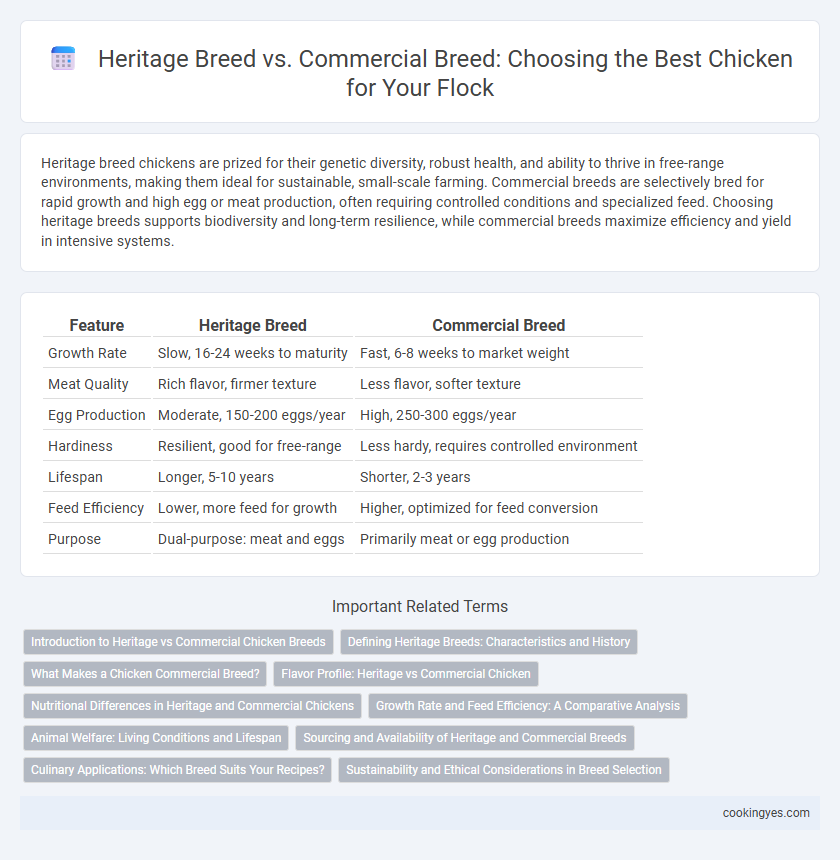
| Feature | Heritage Breed | Commercial Breed |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Slow, 16-24 weeks to maturity | Fast, 6-8 weeks to market weight |
| Meat Quality | Rich flavor, firmer texture | Less flavor, softer texture |
| Egg Production | Moderate, 150-200 eggs/year | High, 250-300 eggs/year |
| Hardiness | Resilient, good for free-range | Less hardy, requires controlled environment |
| Lifespan | Longer, 5-10 years | Shorter, 2-3 years |
| Feed Efficiency | Lower, more feed for growth | Higher, optimized for feed conversion |
| Purpose | Dual-purpose: meat and eggs | Primarily meat or egg production |
Introduction to Heritage vs Commercial Chicken Breeds
Heritage chicken breeds are traditional, slow-growing varieties known for their natural behaviors, disease resistance, and flavorful meat, often favored by small-scale farmers and backyard enthusiasts. Commercial chicken breeds are selectively bred for rapid growth, high feed efficiency, and enhanced meat or egg production, dominating large-scale poultry operations. Understanding the distinctions between heritage and commercial breeds is essential for selecting chickens based on purpose, sustainability, and production goals.
Defining Heritage Breeds: Characteristics and History
Heritage breeds of chickens are defined by their distinct traits such as slow growth, natural mating capabilities, and longevity, often tracing lineage back several generations. These breeds possess unique genetic diversity and historical significance, reflecting traditional farming practices and adaptation to local environments. Unlike commercial breeds optimized for rapid meat or egg production, heritage breeds prioritize resilience, flavor, and sustainability in poultry farming.
What Makes a Chicken Commercial Breed?
A commercial chicken breed is primarily selected for rapid growth, high feed efficiency, and maximum meat or egg production to meet large-scale agricultural demands. These breeds often result from crossbreeding specific strains like Cornish and White Leghorn to optimize traits such as body weight and egg-laying capacity. Genetic uniformity and adaptability to confined farming systems distinguish commercial breeds from heritage breeds, which emphasize genetic diversity and traditional traits.
Flavor Profile: Heritage vs Commercial Chicken
Heritage breed chickens offer a richer, more complex flavor profile due to their slower growth and diverse genetics, often resulting in firmer texture and more pronounced taste. Commercial breeds, bred for rapid growth and high yield, typically have milder flavor and softer meat, catering to mass-market preferences. Selecting heritage breeds enhances culinary experiences by providing deeper, more authentic chicken flavors favored by chefs and food connoisseurs.
Nutritional Differences in Heritage and Commercial Chickens
Heritage breed chickens typically offer higher nutritional value, including greater omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A and E, and lower fat content compared to commercial breeds. Commercial chickens, bred for rapid growth and high meat production, often have increased fat levels and lower micronutrient density due to selective breeding and diet differences. The nutrient profile in heritage birds supports better flavor and health benefits, making them a preferred choice for nutrient-conscious consumers.
Growth Rate and Feed Efficiency: A Comparative Analysis
Heritage breeds grow slower, typically reaching market weight in 16 to 24 weeks, compared to commercial broilers that achieve similar weight in 6 to 8 weeks due to selective breeding for rapid growth. Commercial breeds exhibit superior feed efficiency, converting feed to body mass at a ratio of approximately 1.5:1, while heritage breeds often require a ratio closer to 3:1. These differences influence production costs and sustainability, making commercial breeds more cost-effective for large-scale operations but less resilient than heritage breeds.
Animal Welfare: Living Conditions and Lifespan
Heritage breed chickens generally experience better animal welfare due to their adaptability to free-range living conditions, which promote natural behaviors and reduce stress compared to commercial breeds often raised in confined environments. These breeds typically have longer lifespans, averaging 6 to 8 years, whereas commercial broilers are bred for rapid growth and usually live only 6 to 8 weeks before processing. Improved living conditions and extended lifespan in heritage breeds contribute to enhanced overall health and welfare outcomes.
Sourcing and Availability of Heritage and Commercial Breeds
Heritage chicken breeds are sourced primarily from specialized breeders and small farms that focus on preserving genetic diversity, resulting in limited availability and higher costs compared to commercial breeds. Commercial breeds dominate the poultry market due to their mass production by large-scale hatcheries, ensuring widespread availability and lower prices. Procuring heritage breeds often requires advanced ordering or visiting farmer's markets, while commercial breeds are readily accessible through major suppliers and grocery stores.
Culinary Applications: Which Breed Suits Your Recipes?
Heritage chicken breeds, known for their rich flavor and firm texture, excel in slow-cooked dishes, roasting, and recipes requiring pronounced taste, making them ideal for gourmet and traditional culinary applications. Commercial breeds, bred primarily for rapid growth and high meat yield, offer a milder flavor and tender meat, suiting fast cooking methods like frying and grilling. Chefs and home cooks looking to enhance depth in recipes often prefer heritage breeds, while those seeking consistency and tenderness opt for commercial varieties.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations in Breed Selection
Heritage breeds of chickens, known for their natural resilience and slower growth rates, promote sustainability by supporting genetic diversity and reducing reliance on intensive farming practices often seen in commercial breeds. These breeds typically require fewer antibiotics and are better adapted to local environments, enhancing animal welfare and ethical farming standards. In contrast, commercial breeds prioritize rapid growth and high yield but often contribute to environmental degradation and raise ethical concerns due to crowded, industrialized conditions.
Heritage breed vs Commercial breed for chicken selection Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com