Processed cheddar is mass-produced with additives and emulsifiers to ensure a consistent texture and longer shelf life, making it ideal for convenience and affordability. Artisanal cheddar is crafted using traditional methods, often aged longer and made from high-quality milk, resulting in complex flavors and a richer mouthfeel. Choosing between processed and artisanal cheddar depends on the desired taste experience and usage, with artisanal typically favored for gourmet consumption and processed for everyday cooking.
Table of Comparison
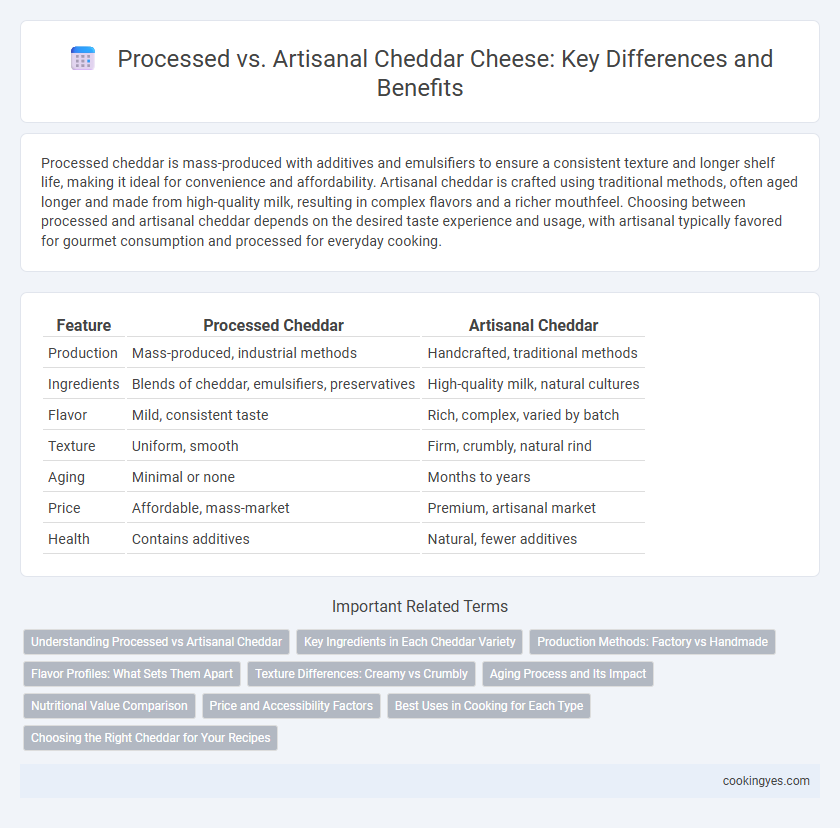
| Feature | Processed Cheddar | Artisanal Cheddar |
|---|---|---|
| Production | Mass-produced, industrial methods | Handcrafted, traditional methods |
| Ingredients | Blends of cheddar, emulsifiers, preservatives | High-quality milk, natural cultures |
| Flavor | Mild, consistent taste | Rich, complex, varied by batch |
| Texture | Uniform, smooth | Firm, crumbly, natural rind |
| Aging | Minimal or none | Months to years |
| Price | Affordable, mass-market | Premium, artisanal market |
| Health | Contains additives | Natural, fewer additives |
Understanding Processed vs Artisanal Cheddar
Processed Cheddar undergoes extensive melting and blending with emulsifiers to ensure uniform texture, longer shelf life, and consistent flavor, while artisanal Cheddar is crafted using traditional methods, emphasizing natural aging and regional milk qualities. Artisanal Cheddar often exhibits complex, nuanced flavors and varying textures influenced by aging times, specific terroirs, and handcrafted techniques. Understanding these differences aids consumers seeking authentic taste experiences or convenient, stable cheese products.
Key Ingredients in Each Cheddar Variety
Processed cheddar typically contains emulsifiers, preservatives, and dairy derivatives that enhance texture and shelf life, while artisanal cheddar emphasizes high-quality milk, natural cultures, and traditional aging methods. The key ingredient in processed cheddar is often dairy blends combined with stabilizers, whereas artisanal cheddar relies on raw or pasteurized milk from specific breeds, natural enzymes, and minimal additives. Flavor complexity in artisanal cheddar results from the natural fermentation and aging, compared to the consistent but milder taste of processed cheddar due to its controlled ingredient profile.
Production Methods: Factory vs Handmade
Processed cheddar is produced in factories using automated machines that blend cheese with emulsifiers, preservatives, and other additives to ensure uniform texture and extended shelf life. Artisanal cheddar is handmade in small batches, often using traditional techniques such as hand-cut curds and natural aging processes that enhance flavor complexity and texture. Factory production prioritizes efficiency and consistency, while artisanal methods emphasize craftsmanship, natural ingredients, and unique regional characteristics.
Flavor Profiles: What Sets Them Apart
Processed cheddar offers a consistent, mild flavor with a smooth, creamy texture due to its pasteurization and emulsifiers, making it ideal for mass consumption and cooking. Artisanal cheddar delivers complex, bold flavor profiles characterized by sharpness, nuttiness, and earthy undertones, developed through traditional aging processes and natural bacterial cultures. The distinct taste nuances in artisanal cheddar result from variations in milk source, aging duration, and handmade techniques, setting it apart from the uniformity of processed varieties.
Texture Differences: Creamy vs Crumbly
Processed Cheddar cheese has a creamy texture due to emulsifiers and heat treatment, creating a smooth, uniform consistency ideal for melting. Artisanal Cheddar exhibits a crumbly texture, reflecting traditional aging and natural curd formation that results in a complex, granular mouthfeel. The choice between creamy and crumbly textures significantly influences culinary applications and flavor perception in Cheddar cheese.
Aging Process and Its Impact
Aging plays a crucial role in defining the flavor and texture of Cheddar cheese, with artisanal Cheddar undergoing a natural, longer aging process that develops complex, sharp, and nuanced taste profiles. Processed Cheddar typically bypasses extended aging, relying on additives and emulsifiers to achieve a consistent, mild flavor and smoother texture. The traditional aging environment of artisanal Cheddar promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, enhancing depth and character, whereas processed variants often lack this rich sensory dimension.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Processed Cheddar cheese often contains added preservatives and emulsifiers, which can reduce its overall nutritional quality compared to artisanal Cheddar. Artisanal Cheddar typically boasts higher protein content, richer calcium levels, and fewer additives, offering a more natural nutrient profile. Vitamins A and B12 are more bioavailable in artisanal varieties, enhancing their health benefits over processed counterparts.
Price and Accessibility Factors
Processed cheddar cheese is generally more affordable and widely accessible due to mass production techniques, making it a staple in supermarkets and fast-food chains. Artisanal cheddar commands a higher price reflecting traditional craftsmanship, aged quality, and limited production, often found in specialty stores or farmers' markets. Price differences between processed and artisanal cheddar largely stem from ingredient quality, aging time, and production scale, influencing consumer accessibility.
Best Uses in Cooking for Each Type
Processed cheddar melts uniformly, making it ideal for creamy sauces, grilled cheese sandwiches, and casseroles that require smooth texture and easy blending. Artisanal cheddar offers complex flavors and a firmer texture, perfect for cheese boards, salads, and dishes where distinct taste and bite are desired. Choosing processed cheddar enhances meltability, while artisanal cheddar elevates flavor profiles in more sophisticated recipes.
Choosing the Right Cheddar for Your Recipes
Processed cheddar offers consistent flavor and smooth texture, ideal for melting in dishes like grilled cheese or casseroles, while artisanal cheddar provides complex, nuanced flavors with varied aging profiles that enhance salads, cheese boards, and gourmet recipes. Selecting the right cheddar depends on the intended use: processed cheddar excels in recipes requiring uniform meltability, whereas artisanal cheddar adds depth and distinctive taste for more refined culinary creations. Understanding cheddar's production methods and flavor characteristics helps tailor your choice to achieve optimal taste and texture outcomes in cooking.
Processed vs Artisanal for Cheddar Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com