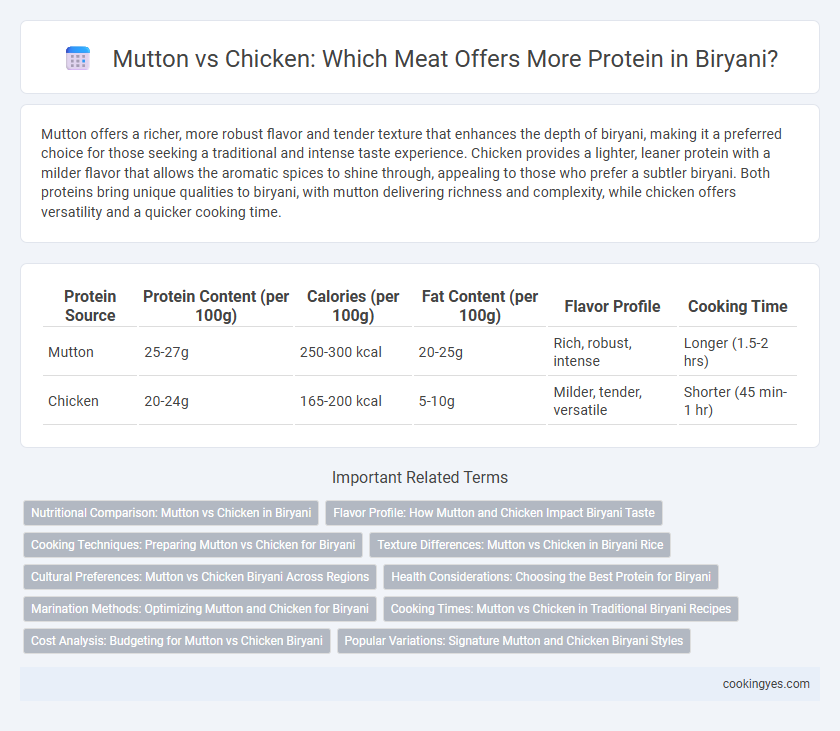
Mutton offers a richer, more robust flavor and tender texture that enhances the depth of biryani, making it a preferred choice for those seeking a traditional and intense taste experience. Chicken provides a lighter, leaner protein with a milder flavor that allows the aromatic spices to shine through, appealing to those who prefer a subtler biryani. Both proteins bring unique qualities to biryani, with mutton delivering richness and complexity, while chicken offers versatility and a quicker cooking time.
Table of Comparison
| Protein Source | Protein Content (per 100g) | Calories (per 100g) | Fat Content (per 100g) | Flavor Profile | Cooking Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutton | 25-27g | 250-300 kcal | 20-25g | Rich, robust, intense | Longer (1.5-2 hrs) |
| Chicken | 20-24g | 165-200 kcal | 5-10g | Milder, tender, versatile | Shorter (45 min-1 hr) |
Nutritional Comparison: Mutton vs Chicken in Biryani
Mutton Biryani contains higher levels of iron and zinc compared to Chicken Biryani, supporting better immune function and oxygen transport. Chicken Biryani is lower in saturated fat and calories, making it a leaner option beneficial for heart health and weight management. Both proteins provide essential amino acids, but mutton offers richer content in vitamin B12, contributing to improved energy metabolism.
Flavor Profile: How Mutton and Chicken Impact Biryani Taste
Mutton imparts a rich, robust, and slightly gamy flavor to biryani, enhancing its depth and complexity with a hearty, savory profile that stands out against the aromatic spices. Chicken offers a lighter, milder taste that absorbs the blend of spices more evenly, providing a tender, juicy texture without overpowering the dish's aromatic character. The choice between mutton and chicken significantly influences the biryani's flavor intensity, with mutton delivering a bold, intense taste while chicken offers a balanced, subtler flavor experience.
Cooking Techniques: Preparing Mutton vs Chicken for Biryani
Mutton requires longer marination and slow-cooking techniques such as pressure cooking or simmering to achieve tenderness and deep flavor absorption in biryani. Chicken cooks faster and benefits from quick marination with yogurt and spices, followed by gentle steaming to retain juiciness and texture. Adjusting cooking times and layering methods is crucial to harmonize protein texture with aromatic rice in both mutton and chicken biryani recipes.
Texture Differences: Mutton vs Chicken in Biryani Rice
Mutton in biryani offers a rich, tender texture that becomes succulent after slow cooking, creating a hearty mouthfeel that deeply infuses the rice with robust flavors. Chicken provides a lighter, softer texture that absorbs spices quickly, resulting in a delicate and moist bite within the biryani rice. The contrasting textures of mutton and chicken significantly influence the overall sensory experience, with mutton lending a firmer chew and chicken delivering a more tender, juicy finish.
Cultural Preferences: Mutton vs Chicken Biryani Across Regions
Mutton biryani holds strong cultural significance in regions like Hyderabad and Lucknow, where its rich, robust flavor is preferred for traditional feasts and celebrations. Chicken biryani is more popular in South Indian states such as Tamil Nadu and Kerala, favored for its lighter taste and quicker cooking time. Regional preferences often reflect local customs and ingredient availability, influencing the choice between mutton and chicken proteins in biryani recipes.
Health Considerations: Choosing the Best Protein for Biryani
Mutton Biryani provides higher iron and zinc content, supporting immune function and energy metabolism, while chicken Biryani offers leaner protein with lower saturated fat, making it a heart-healthier choice. Opting for chicken reduces calorie intake and cholesterol levels, suitable for those managing weight or cardiovascular concerns. Balancing flavor preference with nutritional needs can guide selecting the best protein for a health-conscious Biryani.
Marination Methods: Optimizing Mutton and Chicken for Biryani
Mutton for biryani requires a longer marination time, often overnight, using yogurt, ginger-garlic paste, and robust spices like garam masala to tenderize the tougher meat and infuse deeper flavors. Chicken marination is typically shorter, around 1-2 hours, emphasizing lighter spice blends and citrus elements like lemon juice to maintain its tender texture without overpowering the delicate meat. Optimizing marination enhances the distinct protein profiles, ensuring mutton delivers a rich, hearty taste while chicken remains succulent and flavorful in biryani.
Cooking Times: Mutton vs Chicken in Traditional Biryani Recipes
Mutton requires a longer cooking time than chicken in traditional biryani recipes, often needing 1.5 to 2 hours to become tender, while chicken typically cooks within 30 to 45 minutes. The extended cooking duration for mutton enhances its rich, deep flavor, allowing the meat to absorb more spices and aromatics. Chicken biryani, with its shorter cooking time, delivers a lighter texture and tends to retain more moisture, resulting in a juicier final dish.
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Mutton vs Chicken Biryani
Mutton biryani generally incurs a higher cost than chicken biryani due to the premium price of mutton meat, which can be two to three times more expensive per kilogram. Budget-conscious consumers often prefer chicken biryani for its affordability while still delivering rich flavors and protein content. Evaluating local market prices and portion sizes is essential for accurate budgeting when choosing between mutton and chicken for biryani preparation.
Popular Variations: Signature Mutton and Chicken Biryani Styles
Mutton biryani is renowned for its rich, intense flavor and tender meat, often featured in signature styles like Kolkata and Hyderabadi mutton biryani, prized for their aromatic spices and slow-cooked depth. Chicken biryani offers a lighter, more versatile protein option with popular variations such as Lucknowi (Awadhi) and Andhra chicken biryani, recognized for their vibrant spices and slightly shorter cooking times. Both proteins contribute distinct textures and flavors, driving regional preferences and unique culinary traditions in their respective biryani styles.
Mutton vs Chicken for Biryani protein Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com