Turkey bacon offers a leaner alternative to pork bacon, making it ideal for low-fat dishes while still providing a satisfying smoky flavor. Its reduced fat content helps lower overall calorie intake, which supports weight management and heart health. Although turkey bacon has a different texture, it can be easily incorporated into recipes without compromising taste or culinary appeal.
Table of Comparison
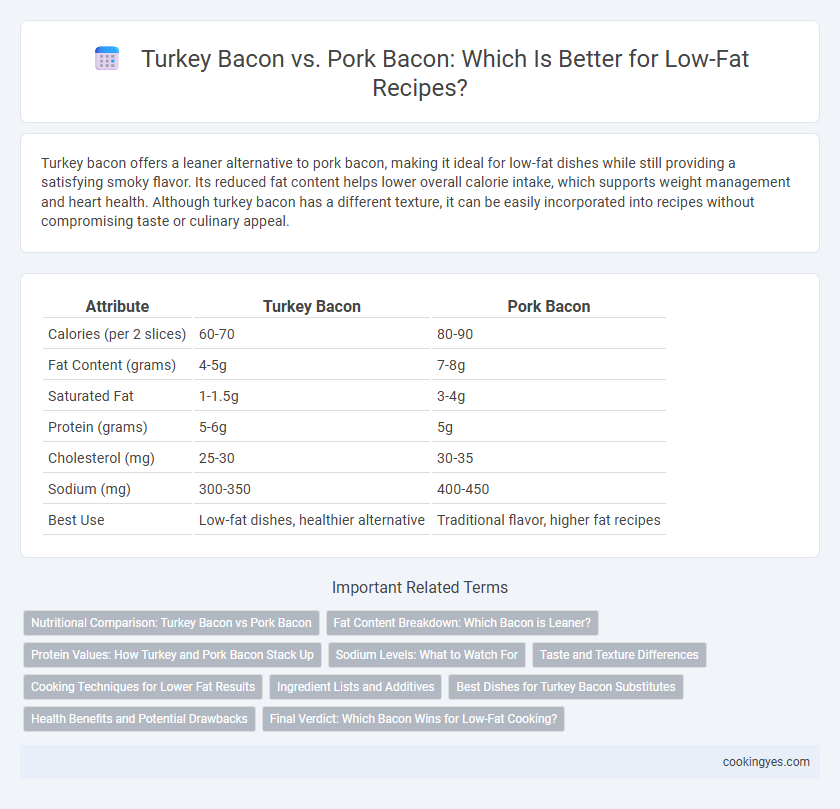
| Attribute | Turkey Bacon | Pork Bacon |
|---|---|---|
| Calories (per 2 slices) | 60-70 | 80-90 |
| Fat Content (grams) | 4-5g | 7-8g |
| Saturated Fat | 1-1.5g | 3-4g |
| Protein (grams) | 5-6g | 5g |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 25-30 | 30-35 |
| Sodium (mg) | 300-350 | 400-450 |
| Best Use | Low-fat dishes, healthier alternative | Traditional flavor, higher fat recipes |
Nutritional Comparison: Turkey Bacon vs Pork Bacon
Turkey bacon contains significantly less fat than pork bacon, with approximately 3 grams of fat per serving compared to pork bacon's 12 grams. It also offers fewer calories, typically around 30 calories per slice versus 42 calories in pork bacon, making it a better option for low-fat dishes. Additionally, turkey bacon contains less saturated fat, supporting heart-healthier meal choices without compromising the smoky, savory flavor.
Fat Content Breakdown: Which Bacon is Leaner?
Turkey bacon contains significantly less total fat, averaging about 3 grams per slice, compared to pork bacon which can have 8 to 12 grams per slice. The saturated fat content in turkey bacon is also notably lower, making it a leaner option ideal for low-fat dishes and heart-health-conscious diets. Despite lower fat, turkey bacon provides similar protein levels, supporting its use as a healthier alternative without sacrificing savory flavor.
Protein Values: How Turkey and Pork Bacon Stack Up
Turkey bacon contains approximately 10 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a leaner alternative to pork bacon, which offers around 12 grams per 100 grams but with higher fat content. The lower fat percentage in turkey bacon supports low-fat dish preparation without significantly sacrificing protein intake, ideal for health-conscious consumers. Opting for turkey bacon can enhance protein value in meals while reducing saturated fat intake compared to traditional pork bacon.
Sodium Levels: What to Watch For
Turkey bacon typically contains less fat than pork bacon, making it a popular choice for low-fat dishes, though its sodium levels can be significantly higher. Monitoring sodium intake is crucial, as turkey bacon often compensates for reduced fat with added salt and preservatives, which may affect heart health. Choosing lower-sodium turkey bacon brands or rinsing slices before cooking can help manage sodium consumption without sacrificing flavor.
Taste and Texture Differences
Turkey bacon offers a leaner alternative to pork bacon, containing significantly less fat and calories, ideal for low-fat dishes. The taste of turkey bacon is milder and less smoky compared to the rich, savory flavor of pork bacon, making it a subtler option for recipes. Texture-wise, turkey bacon tends to be chewier and less crispy, whereas pork bacon delivers a satisfying crispiness and melt-in-your-mouth fat that enhances flavor complexity.
Cooking Techniques for Lower Fat Results
Turkey bacon offers a leaner alternative to traditional pork bacon, containing significantly less saturated fat and fewer calories, making it ideal for low-fat dishes. Cooking techniques such as baking or grilling turkey bacon on a rack allow excess fat to drip away, reducing overall fat content compared to pan-frying. Using non-stick cookware and blotting with paper towels after cooking further minimizes fat retention, ensuring healthier, flavorful results.
Ingredient Lists and Additives
Turkey bacon typically contains fewer calories and less fat than pork bacon, making it a preferred choice for low-fat dishes. Ingredient lists for turkey bacon often include turkey meat, water, salt, sugar, and preservatives like sodium nitrite, while pork bacon tends to have pork belly, salt, curing agents, and sometimes added sugars or smoke flavorings. Additives in turkey bacon may include binders and fillers to mimic the texture of pork bacon, whereas pork bacon generally relies on natural curing and smoking processes.
Best Dishes for Turkey Bacon Substitutes
Turkey bacon is an excellent low-fat alternative to traditional pork bacon, containing significantly less saturated fat and calories, making it ideal for health-conscious recipes. Best dishes for turkey bacon substitutes include breakfast scrambles, salads, and lean protein sandwiches where its smoky flavor complements fresh, nutrient-rich ingredients without the greasiness of pork bacon. Incorporating turkey bacon in wraps and grain bowls enhances texture and flavor while maintaining a lower fat profile, perfect for balanced, nutritious meals.
Health Benefits and Potential Drawbacks
Turkey bacon contains significantly less saturated fat and calories compared to pork bacon, making it a preferred choice for low-fat dishes aimed at heart health and weight management. It offers a leaner protein source, though it often contains higher levels of sodium and preservatives, which can affect cardiovascular health if consumed excessively. Pork bacon, while richer in flavor and essential nutrients like B vitamins and zinc, tends to be higher in saturated fats and cholesterol, which may contribute to increased risks of heart disease when eaten in large quantities.
Final Verdict: Which Bacon Wins for Low-Fat Cooking?
Turkey bacon contains significantly less fat and fewer calories than traditional pork bacon, making it a superior choice for low-fat dishes. Its lean protein content supports healthier meal options while maintaining a smoky flavor, ideal for those seeking to reduce saturated fat intake. For low-fat cooking, turkey bacon wins as the optimal bacon variant due to its improved nutritional profile and lower fat content.
Turkey bacon vs pork bacon for low-fat dishes Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com