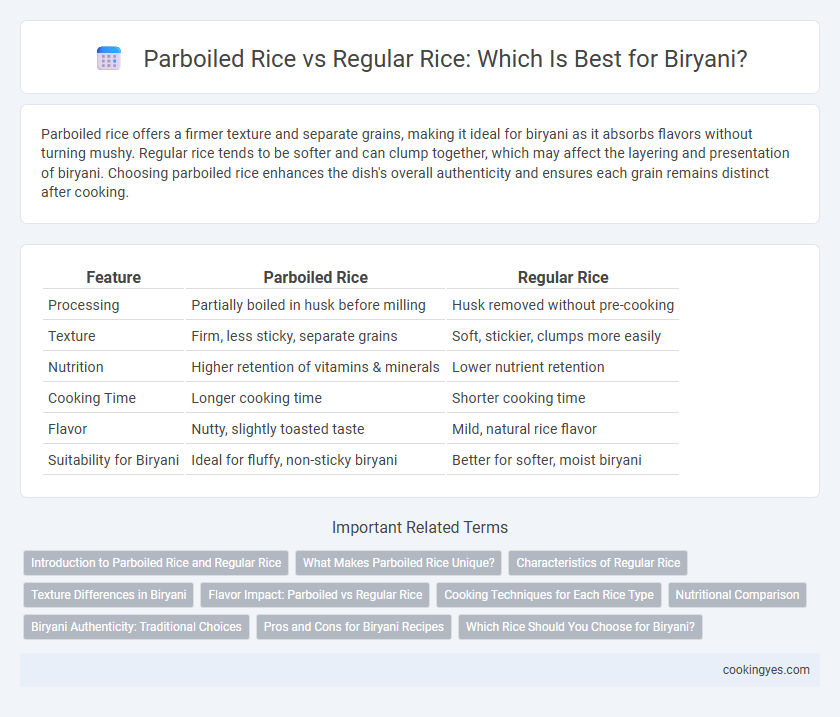
Parboiled rice offers a firmer texture and separate grains, making it ideal for biryani as it absorbs flavors without turning mushy. Regular rice tends to be softer and can clump together, which may affect the layering and presentation of biryani. Choosing parboiled rice enhances the dish's overall authenticity and ensures each grain remains distinct after cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Parboiled Rice | Regular Rice |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Partially boiled in husk before milling | Husk removed without pre-cooking |
| Texture | Firm, less sticky, separate grains | Soft, stickier, clumps more easily |
| Nutrition | Higher retention of vitamins & minerals | Lower nutrient retention |
| Cooking Time | Longer cooking time | Shorter cooking time |
| Flavor | Nutty, slightly toasted taste | Mild, natural rice flavor |
| Suitability for Biryani | Ideal for fluffy, non-sticky biryani | Better for softer, moist biryani |
Introduction to Parboiled Rice and Regular Rice
Parboiled rice undergoes a unique processing method where the rice is soaked, steamed, and dried within the husk, enhancing its nutritional profile and making it less sticky during cooking, ideal for biryani's layered texture. Regular rice, typically white or basmati, is milled and polished, resulting in a softer grain that can clump together when cooked, which may affect the distinct separation desired in biryani. Choosing parboiled rice for biryani ensures firmer, non-sticky grains that maintain their shape, while regular rice offers a more delicate texture suitable for softer rice dishes.
What Makes Parboiled Rice Unique?
Parboiled rice undergoes a hydrothermal treatment that drives nutrients from the bran into the grain, enhancing its nutritional profile and maintaining firmness during cooking. Its unique gelatinized starch structure prevents overcooking and stickiness, making it ideal for biryani where separate, fluffy grains are preferred. This contrasts with regular rice, which lacks this treatment and often results in softer, stickier textures less suitable for layered dishes like biryani.
Characteristics of Regular Rice
Regular rice for biryani typically consists of long-grain varieties like basmati known for their fragrant aroma and fluffy texture. It absorbs flavors well but tends to be softer and stickier compared to parboiled rice. The grains of regular rice break more easily during cooking, which can affect the layered consistency essential to traditional biryani.
Texture Differences in Biryani
Parboiled rice has a firmer and less sticky texture compared to regular rice, making it ideal for biryani where separate, fluffy grains are desired. The parboiling process gelatinizes the starch, resulting in grains that retain their shape and absorb flavors without becoming mushy. Regular rice tends to be softer and can clump together, which may affect the delicate layering and texture essential to authentic biryani.
Flavor Impact: Parboiled vs Regular Rice
Parboiled rice retains more nutrients and has a firmer texture, which helps absorb spices and flavors in biryani without becoming mushy. Regular rice offers a softer, more delicate bite that can highlight subtle aromatic spices but risks losing texture when cooked long. Choosing parboiled rice generally enhances the robust, layered flavors typical of biryani by maintaining grain integrity during lengthy cooking.
Cooking Techniques for Each Rice Type
Parboiled rice requires soaking and partial boiling before cooking, which helps retain nutrients and results in firmer, less sticky grains ideal for biryani layers. Regular rice, often soaked briefly and cooked with precise water control, yields softer, fluffier grains that absorb spices effectively. Understanding these cooking techniques ensures the biryani achieves the desired texture and flavor profile unique to each rice type.
Nutritional Comparison
Parboiled rice retains more nutrients compared to regular rice due to the steaming process that drives vitamins and minerals from the bran into the grain, making it richer in thiamine, niacin, and magnesium. This higher nutrient content contributes to better digestion and sustained energy release, which is beneficial in a dish like biryani that requires prolonged cooking. Regular rice, typically milled and polished, loses significant fiber and essential nutrients, resulting in lower nutritional value but a softer texture preferred by some for biryani.
Biryani Authenticity: Traditional Choices
Parboiled rice preserves more nutrients and retains firmness, making it a preferred choice in traditional biryani recipes across South Asia for authentic texture and taste. Regular rice, while softer and less sticky, can compromise the distinct grain separation crucial to classic biryani presentation. Authentic biryani often relies on the slightly aromatic and resilient qualities of parboiled rice to maintain the dish's heritage and flavor profile.
Pros and Cons for Biryani Recipes
Parboiled rice for biryani offers benefits such as enhanced nutritional value, less stickiness, and firmness, which helps maintain grain separation during cooking, making it ideal for layered biryani recipes. However, parboiled rice requires longer cooking time and may have a slightly altered texture and flavor compared to regular basmati rice, which is prized for its aromatic fragrance and delicate, fluffy grains that absorb spices well. Regular rice can sometimes become mushy in biryani, while parboiled rice's resilience ensures a consistent texture but might lack the traditional aroma cherished in classic biryani dishes.
Which Rice Should You Choose for Biryani?
Parboiled rice is preferred for biryani due to its firmer texture, less sticky grains, and ability to absorb flavors without becoming mushy, resulting in distinct, separate grains after cooking. Regular white rice tends to be softer and stickier, which can lead to a clumpy biryani lacking the ideal fluffy and layered consistency. For authentic biryani, basmati parboiled rice like Tilda or Royal is often chosen to enhance aroma, texture, and overall presentation.
Parboiled Rice vs Regular Rice for Biryani Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com