Cream creates a richer, silkier quiche filling due to its higher fat content, resulting in a custard that's smooth and indulgent. Milk produces a lighter, less dense texture, which can highlight the flavors of added ingredients without overwhelming them. Choosing between cream and milk depends on desired richness and calorie preferences for the quiche.
Table of Comparison
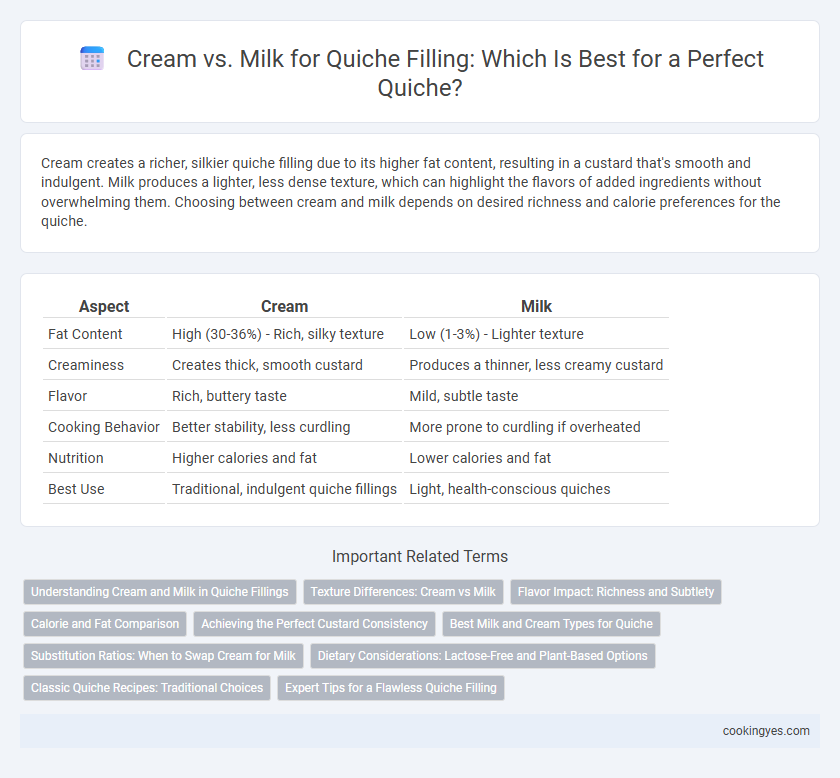
| Aspect | Cream | Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | High (30-36%) - Rich, silky texture | Low (1-3%) - Lighter texture |
| Creaminess | Creates thick, smooth custard | Produces a thinner, less creamy custard |
| Flavor | Rich, buttery taste | Mild, subtle taste |
| Cooking Behavior | Better stability, less curdling | More prone to curdling if overheated |
| Nutrition | Higher calories and fat | Lower calories and fat |
| Best Use | Traditional, indulgent quiche fillings | Light, health-conscious quiches |
Understanding Cream and Milk in Quiche Fillings
Cream provides a richer, silkier texture and higher fat content essential for a custard-like quiche filling, enhancing flavor and mouthfeel. Milk offers a lighter, more delicate consistency with lower fat, resulting in a less dense but still tender quiche custard. Balancing cream and milk ratios directly influences the quiche's richness, creaminess, and overall decadence.
Texture Differences: Cream vs Milk
Using cream in quiche filling results in a richer, silkier texture due to its higher fat content, which creates a smooth and custardy consistency. Milk, with lower fat, produces a lighter and less dense filling, offering a more delicate mouthfeel but less creaminess. Choosing cream enhances the quiche's velvety texture, while milk yields a softer, more fragile custard.
Flavor Impact: Richness and Subtlety
Using cream in quiche filling enhances richness and creates a velvety texture, contributing to a deeply indulgent flavor profile. Milk imparts a lighter, subtler taste, allowing other ingredients like cheese and vegetables to shine through more distinctly. The choice between cream and milk significantly influences the overall mouthfeel and flavor intensity of the quiche.
Calorie and Fat Comparison
Quiche filling made with heavy cream contains significantly more calories and fat compared to using milk, with heavy cream averaging about 50 calories and 5 grams of fat per tablespoon, whereas whole milk has approximately 9 calories and 0.5 grams of fat per tablespoon. Opting for milk reduces the overall calorie and fat content of the quiche, making it a lighter option without sacrificing the creamy texture essential for a rich filling. This calorie and fat difference is crucial for those managing dietary intake while still enjoying traditional quiche flavors.
Achieving the Perfect Custard Consistency
Using heavy cream in quiche filling creates a rich, velvety custard with a dense texture, while whole milk results in a lighter, more delicate consistency. The fat content in cream stabilizes the eggs and enhances the smoothness, preventing curdling and ensuring a creamy finish. Balancing cream and milk allows control over custard firmness, making it essential for achieving the perfect quiche texture.
Best Milk and Cream Types for Quiche
Heavy cream provides the richest and creamiest texture for quiche filling, enhancing flavor and consistency. Whole milk offers a lighter alternative while maintaining smoothness and moisture without overwhelming the egg base. For optimal results, use heavy cream or a combination of half-and-half and whole milk to balance richness and tenderness in the quiche custard.
Substitution Ratios: When to Swap Cream for Milk
Use cream in quiche fillings for a richer, silkier texture due to its higher fat content, typically around 35-40%, while milk, with 3-4% fat, creates a lighter, less creamy result. Substitute milk for cream at a 1:1 ratio when aiming to reduce calories or fat, but expect a slightly firmer quiche structure and less custard-like consistency. Combining half cream and half milk balances richness and weight, preserving smoothness while cutting calories effectively.
Dietary Considerations: Lactose-Free and Plant-Based Options
Using lactose-free milk or plant-based alternatives such as almond, soy, or oat milk offers a suitable option for quiche fillings for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Coconut cream or cashew cream serve as effective substitutes for traditional heavy cream, providing a rich texture while maintaining a dairy-free profile. These alternatives ensure the quiche remains creamy and flavorful without compromising dietary restrictions related to lactose intolerance or vegan preferences.
Classic Quiche Recipes: Traditional Choices
Classic quiche recipes traditionally favor heavy cream over milk for the filling due to its rich texture and ability to create a custard that holds together well during baking. Heavy cream's higher fat content results in a smoother, silkier quiche with a velvety mouthfeel, while milk can produce a lighter, less stable custard that may curdle or become watery. For authentic French quiche Lorraine or classic vegetable quiches, using cream ensures the ideal balance of richness and structural integrity.
Expert Tips for a Flawless Quiche Filling
Using heavy cream in quiche filling results in a rich, velvety texture with a higher fat content that enhances flavor and provides a custard-like consistency. Milk creates a lighter, less dense filling but may yield a slightly watery texture if used alone or in high proportions. Experts recommend combining cream and milk, typically in a 1:1 ratio, to balance richness and moisture for a perfectly smooth and stable quiche filling.
Cream vs milk for quiche filling Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com