Wheat pancakes offer a classic texture and a slightly sweet flavor, making them a popular choice for breakfast. Oatmeal pancakes provide a heartier, denser bite with added fiber and nutrients, appealing to those seeking a healthier grain option. Both options deliver distinct taste profiles, with wheat pancakes being lighter and oatmeal pancakes promoting better digestion and sustained energy.
Table of Comparison
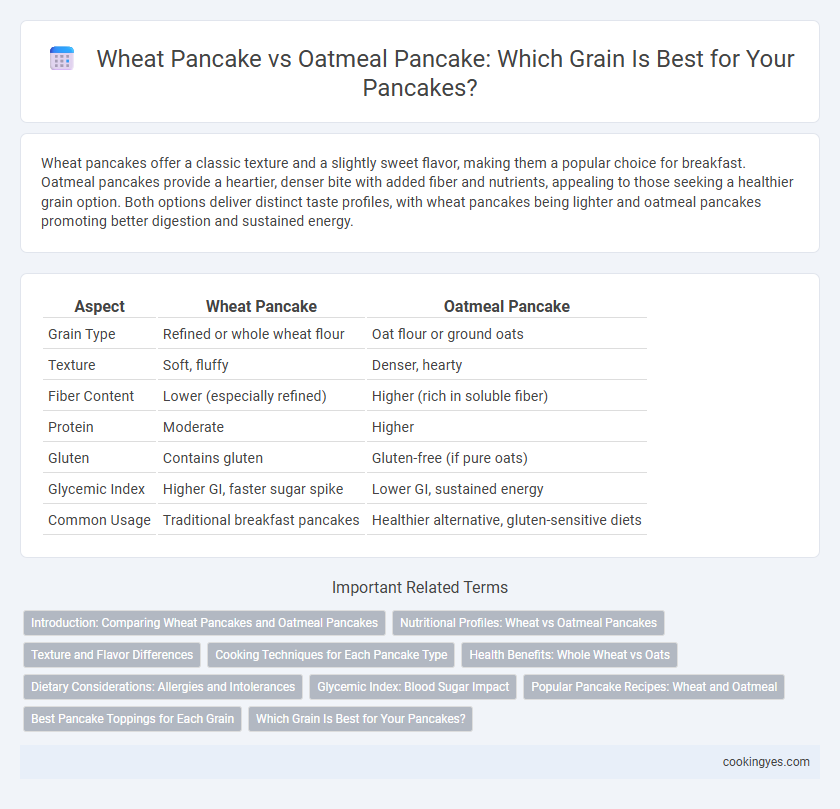
| Aspect | Wheat Pancake | Oatmeal Pancake |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Type | Refined or whole wheat flour | Oat flour or ground oats |
| Texture | Soft, fluffy | Denser, hearty |
| Fiber Content | Lower (especially refined) | Higher (rich in soluble fiber) |
| Protein | Moderate | Higher |
| Gluten | Contains gluten | Gluten-free (if pure oats) |
| Glycemic Index | Higher GI, faster sugar spike | Lower GI, sustained energy |
| Common Usage | Traditional breakfast pancakes | Healthier alternative, gluten-sensitive diets |
Introduction: Comparing Wheat Pancakes and Oatmeal Pancakes
Wheat pancakes offer a classic texture with a soft, fluffy interior and a slightly sweet, mild flavor due to refined wheat flour. Oatmeal pancakes provide a heartier, denser bite rich in soluble fiber and beta-glucans, known to support heart health and improve digestion. Choosing between wheat and oatmeal pancakes hinges on dietary goals, as oatmeal pancakes often deliver higher protein and fiber content, while wheat pancakes excel in lightness and traditional taste.
Nutritional Profiles: Wheat vs Oatmeal Pancakes
Wheat pancakes typically contain more gluten and provide a higher protein content, essential for muscle repair and growth, while oatmeal pancakes offer increased dietary fiber, promoting better digestion and sustained energy release. Oatmeal pancakes are richer in beta-glucans, which can help lower cholesterol levels and support heart health, whereas wheat pancakes contain more iron and B vitamins crucial for energy metabolism. Choosing between wheat and oatmeal pancakes depends on individual nutritional needs, with oatmeal pancakes favored for fiber and cholesterol benefits and wheat pancakes preferred for protein and micronutrient density.
Texture and Flavor Differences
Wheat pancakes feature a light, fluffy texture with a slightly sweet, mild flavor that enhances traditional pancake recipes. In contrast, oatmeal pancakes provide a denser, heartier bite with a nutty, earthy taste, offering increased fiber and a richer mouthfeel. Choosing between wheat and oatmeal grains directly impacts the pancake's softness and depth of flavor, catering to different preferences and nutritional goals.
Cooking Techniques for Each Pancake Type
Wheat pancakes require a lighter batter and moderate heat to ensure a fluffy texture without burning, while oatmeal pancakes benefit from longer soaking times to soften the grains and produce a denser, chewy consistency. Flipping wheat pancakes is typically faster, occurring once bubbles form and edges set, whereas oatmeal pancakes need slower cooking on lower heat to fully cook through the coarser oats. Adjusting cooking temperature and time is crucial in optimizing texture and taste based on the grain used.
Health Benefits: Whole Wheat vs Oats
Whole wheat pancakes provide higher levels of fiber and essential nutrients such as iron and magnesium compared to oatmeal pancakes, supporting digestive health and sustained energy release. Oatmeal pancakes contain beta-glucan, a soluble fiber known to reduce cholesterol and improve heart health, making them an excellent choice for cardiovascular benefits. Choosing between whole wheat and oatmeal pancakes depends on prioritizing either mineral content and sustained fullness or cardiovascular support and cholesterol management.
Dietary Considerations: Allergies and Intolerances
Wheat pancakes, made from common wheat flour, contain gluten, making them unsuitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, while oatmeal pancakes, derived from oats, offer a gluten-free alternative if certified gluten-free oats are used. Oats provide higher fiber content and may be better tolerated by those with wheat allergies, although cross-contamination must be considered. Choosing between wheat and oatmeal pancakes depends on specific dietary restrictions, with oatmeal pancakes often favored for those avoiding gluten-related disorders.
Glycemic Index: Blood Sugar Impact
Wheat pancakes generally have a higher glycemic index (GI) compared to oatmeal pancakes, leading to a quicker spike in blood sugar levels. Oatmeal pancakes, made from whole oats, offer a lower GI due to their higher fiber content, promoting more stable blood glucose control. Choosing oatmeal pancakes can be beneficial for managing blood sugar and reducing the risk of insulin resistance.
Popular Pancake Recipes: Wheat and Oatmeal
Wheat pancakes are favored for their classic texture and fluffy consistency, made primarily from refined or whole wheat flour rich in gluten, which provides elasticity and rise. Oatmeal pancakes offer a heartier, denser bite with higher dietary fiber and beta-glucan content, supporting digestive health and cholesterol reduction. Popular pancake recipes often combine wheat and oatmeal to balance taste, texture, and nutritional benefits, appealing to diverse dietary preferences.
Best Pancake Toppings for Each Grain
Wheat pancakes pair exceptionally well with classic toppings like maple syrup, fresh berries, and whipped cream, enhancing their soft texture and mild flavor. Oatmeal pancakes benefit from heartier toppings such as chopped nuts, Greek yogurt, and honey, which complement their denser, nuttier profile and add nutritional value. Choosing toppings that align with the grain's texture and flavor profile ensures the best pancake experience for each option.
Which Grain Is Best for Your Pancakes?
Wheat pancakes offer a classic texture and rich gluten structure, ideal for fluffy stacks, while oatmeal pancakes provide higher fiber content and a nuttier flavor, enhancing nutritional value and digestion. Oatmeal's beta-glucan helps reduce cholesterol, making it a heart-healthy choice, whereas wheat offers essential B vitamins and protein for energy. Choosing between wheat and oatmeal depends on dietary goals: opt for wheat for traditional taste and structure, or oatmeal for fiber boost and a whole-grain alternative.
Wheat Pancake vs Oatmeal Pancake for grain choice Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com