Low-fat muffin recipes use ingredients like applesauce or yogurt to reduce fat content while maintaining moisture, making them a healthier option. Full-fat muffins typically include butter or oil, resulting in a richer texture and enhanced flavor profile. Choosing between low-fat and full-fat muffins depends on dietary preferences and desired taste and texture.
Table of Comparison
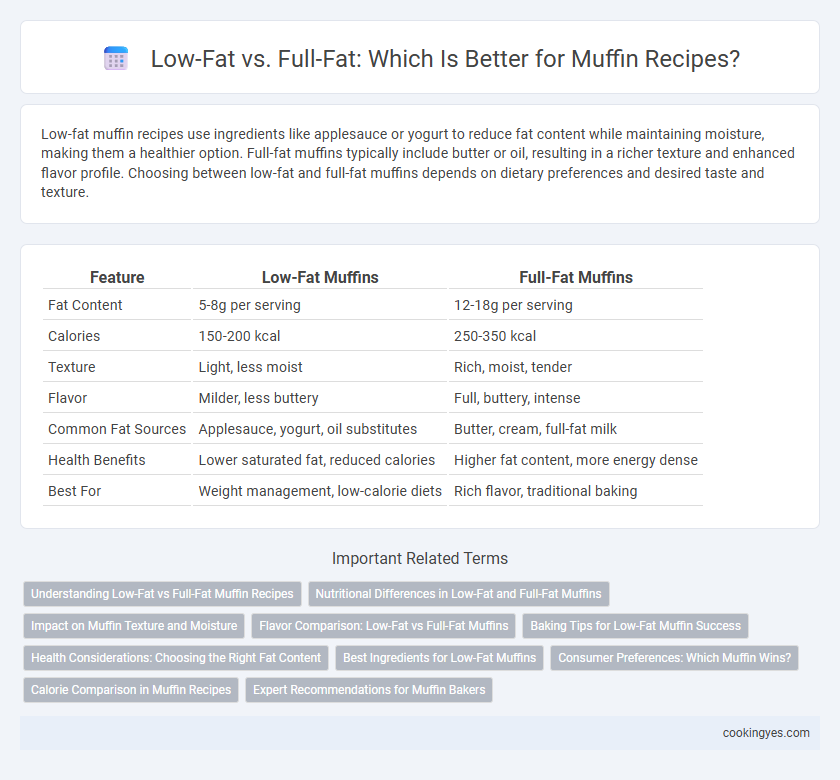
| Feature | Low-Fat Muffins | Full-Fat Muffins |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | 5-8g per serving | 12-18g per serving |
| Calories | 150-200 kcal | 250-350 kcal |
| Texture | Light, less moist | Rich, moist, tender |
| Flavor | Milder, less buttery | Full, buttery, intense |
| Common Fat Sources | Applesauce, yogurt, oil substitutes | Butter, cream, full-fat milk |
| Health Benefits | Lower saturated fat, reduced calories | Higher fat content, more energy dense |
| Best For | Weight management, low-calorie diets | Rich flavor, traditional baking |
Understanding Low-Fat vs Full-Fat Muffin Recipes
Low-fat muffin recipes typically use ingredients like applesauce, yogurt, or skim milk to reduce fat content while maintaining moisture and tenderness. Full-fat muffin recipes rely on butter, cream, or whole milk, providing richer flavor and denser crumb texture. Understanding the balance between fat types affects texture, taste, and calorie content, crucial for tailoring muffins to dietary needs or flavor preferences.
Nutritional Differences in Low-Fat and Full-Fat Muffins
Low-fat muffins typically contain reduced amounts of butter or oil, leading to lower calorie and saturated fat content compared to full-fat muffins. Full-fat muffins provide higher levels of fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids, contributing to richer texture and flavor. Nutritionally, choosing low-fat muffins can support calorie control and heart health, while full-fat options offer more energy-dense nutrition beneficial for certain dietary needs.
Impact on Muffin Texture and Moisture
Low-fat muffin recipes often yield a denser and drier texture due to reduced fat content, which is essential for tenderness and moisture retention. Full-fat muffins benefit from the fat's ability to coat flour proteins, limiting gluten formation and resulting in a softer crumb with enhanced moisture. Choosing full-fat ingredients like butter or cream creates a richer mouthfeel and prevents the muffin from becoming crumbly or overly firm.
Flavor Comparison: Low-Fat vs Full-Fat Muffins
Full-fat muffins deliver a richer, more indulgent flavor due to higher butter or oil content, enhancing moistness and mouthfeel. Low-fat muffins often have a lighter texture and subtle taste but may lack the depth of buttery richness found in full-fat versions. Using alternatives like applesauce or yogurt can improve moistness in low-fat muffins without compromising flavor as much.
Baking Tips for Low-Fat Muffin Success
Using low-fat ingredients in muffin recipes often requires adjustments in texture and moisture to prevent dryness; incorporating applesauce, yogurt, or mashed bananas can help retain moisture while reducing fat content. Opt for whole wheat or oat flour to increase fiber, enhancing the nutritional profile and providing a tender crumb in low-fat muffins. Baking at a slightly lower temperature and avoiding overmixing ensures a soft, fluffy texture while maintaining structure without the richness of full-fat ingredients.
Health Considerations: Choosing the Right Fat Content
Low-fat muffin recipes typically reduce calories and saturated fat intake, making them suitable for heart health and weight management. Full-fat muffins retain more natural moisture and flavor, but higher saturated fat content may impact cholesterol levels and cardiovascular risk. Selecting the appropriate fat content depends on individual dietary goals and health conditions, balancing taste preferences with nutritional needs.
Best Ingredients for Low-Fat Muffins
Low-fat muffins benefit from ingredients such as applesauce, mashed bananas, or Greek yogurt to maintain moisture while reducing fat content. Using whole wheat flour or oat flour enhances fiber, improving the muffin's nutritional profile without compromising texture. Incorporating natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup minimizes refined sugars, making these muffins healthier yet flavorful.
Consumer Preferences: Which Muffin Wins?
Consumer preferences in muffin recipes often lean toward full-fat versions due to their richer flavor and moist texture, which enhance overall taste satisfaction. Low-fat muffins appeal to health-conscious individuals seeking reduced calorie and fat intake but may sacrifice some depth of flavor and crumb tenderness. Market studies reveal that while low-fat muffins attract a niche audience, full-fat muffins generally dominate sales by delivering superior sensory qualities.
Calorie Comparison in Muffin Recipes
Low-fat muffin recipes typically contain 100 to 150 fewer calories per serving compared to full-fat versions, primarily due to reduced butter or oil content. Full-fat muffins, often prepared with whole milk, butter, or cream, contribute to higher saturated fat levels, increasing their calorie density by about 20-30%. Choosing low-fat alternatives like applesauce or yogurt can significantly decrease calorie intake while maintaining moisture and flavor in muffins.
Expert Recommendations for Muffin Bakers
Expert recommendations for muffin bakers emphasize choosing low-fat ingredients to create moist, tender muffins with fewer calories, aiding in healthier recipe adaptations. Incorporating low-fat dairy such as yogurt or buttermilk maintains texture while reducing saturated fat, enhancing flavor without compromising richness. Full-fat options are suggested only when intense flavor and richer crumb are desired, though they increase calorie content and should be balanced with overall dietary goals.
Low-fat vs full-fat for muffin recipes Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com