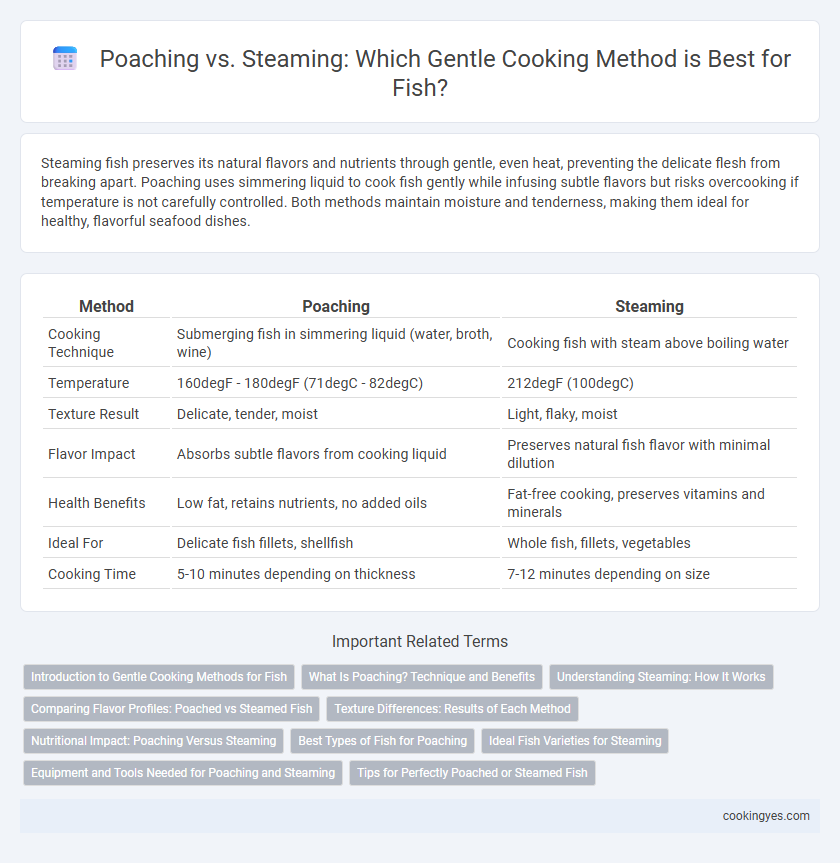
Steaming fish preserves its natural flavors and nutrients through gentle, even heat, preventing the delicate flesh from breaking apart. Poaching uses simmering liquid to cook fish gently while infusing subtle flavors but risks overcooking if temperature is not carefully controlled. Both methods maintain moisture and tenderness, making them ideal for healthy, flavorful seafood dishes.
Table of Comparison
| Method | Poaching | Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Technique | Submerging fish in simmering liquid (water, broth, wine) | Cooking fish with steam above boiling water |
| Temperature | 160degF - 180degF (71degC - 82degC) | 212degF (100degC) |
| Texture Result | Delicate, tender, moist | Light, flaky, moist |
| Flavor Impact | Absorbs subtle flavors from cooking liquid | Preserves natural fish flavor with minimal dilution |
| Health Benefits | Low fat, retains nutrients, no added oils | Fat-free cooking, preserves vitamins and minerals |
| Ideal For | Delicate fish fillets, shellfish | Whole fish, fillets, vegetables |
| Cooking Time | 5-10 minutes depending on thickness | 7-12 minutes depending on size |
Introduction to Gentle Cooking Methods for Fish
Poaching preserves the delicate texture and moisture of fish by cooking it in low-temperature liquid, such as broth or water, typically between 160degF and 180degF. Steaming uses moist heat to cook fish evenly while retaining nutrients and flavor, often involving temperatures around 212degF with minimal direct contact with water. Both methods prevent overcooking and maintain the fish's natural tenderness, making them ideal for gentle cooking approaches.
What Is Poaching? Technique and Benefits
Poaching is a gentle cooking technique that involves simmering fish in a flavorful liquid at low temperatures, typically between 160degF to 180degF, preserving its delicate texture and natural moisture. This method enhances the fish's subtle flavors without adding excess fat, making it a healthy option rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Poaching also helps retain essential nutrients like vitamin D and protein, resulting in tender, flaky fish ideal for light, nutritious meals.
Understanding Steaming: How It Works
Steaming fish involves cooking it with the heat from steam, preserving moisture and nutrients while preventing direct contact with water or oil, which helps maintain delicate textures and flavors. This gentle method uses boiling water's vapor to transfer heat evenly, reducing the risk of overcooking or drying out the fish. By retaining essential amino acids and omega-3 fatty acids, steaming promotes a healthier and more flavorful dining experience compared to more aggressive cooking techniques.
Comparing Flavor Profiles: Poached vs Steamed Fish
Poaching fish infuses it with delicate, subtle flavors from the cooking liquid, often enhanced by herbs, spices, or wine, resulting in a tender and moist texture. Steaming preserves the pure, natural taste of the fish by cooking it with moist heat without direct contact with water, retaining its freshness and clean flavors. Both methods prevent drying out, but poached fish tends to absorb more aromatic nuances, whereas steamed fish highlights the fish's inherent flavor.
Texture Differences: Results of Each Method
Poaching fish in gently simmering liquid preserves moisture, resulting in a tender, delicate texture that flakes easily without drying out. Steaming fish uses moist heat that cooks evenly while maintaining firmness and a slightly springy bite, ideal for preserving the fish's natural structure. Both methods avoid the toughness caused by high-heat cooking, but poaching yields softer, more ethereal flesh compared to the firmer, more intact texture from steaming.
Nutritional Impact: Poaching Versus Steaming
Poaching fish gently in liquid preserves delicate omega-3 fatty acids and essential vitamins such as B12 and D by minimizing nutrient loss through direct contact with water. Steaming fish retains more water-soluble nutrients like B-complex vitamins while preventing leaching into cooking liquids, enhancing the nutritional profile and moisture content. Both methods offer low-fat cooking options that help maintain protein quality and improve digestibility compared to frying or grilling.
Best Types of Fish for Poaching
Delicate fish such as sole, cod, and flounder are ideal for poaching due to their mild flavor and tender texture, which gently absorb the poaching liquid's subtle flavors. Lean fish like tilapia and halibut also respond well to poaching, maintaining moisture without becoming tough. Poaching preserves the fish's natural juiciness and is especially suited for species prone to drying out during cooking.
Ideal Fish Varieties for Steaming
Delicate fish varieties such as cod, sole, halibut, and flounder are ideal for steaming due to their tender texture and mild flavor, which the gentle cooking method preserves. Steaming maintains moisture and nutrients better than poaching, producing flakes that hold together without becoming mushy. Fish with firmer flesh like salmon and sea bass also respond well to steaming, allowing for even cooking and enhanced natural taste.
Equipment and Tools Needed for Poaching and Steaming
Poaching fish requires a wide, shallow pan with a lid to maintain a gentle simmer, along with a slotted spoon or spatula for delicate handling. Steaming fish involves a steamer basket or rack placed over boiling water, often using a pot with a tight-fitting lid to trap steam effectively. Both methods benefit from precise temperature control devices like stovetop burners or electric steamers to ensure even, gentle cooking without overcooking the fish.
Tips for Perfectly Poached or Steamed Fish
For perfectly poached fish, maintain a gentle simmer at 160-180degF (71-82degC) using a flavorful liquid like court bouillon or seasoned water to enhance taste and ensure even cooking. When steaming, use a tight-fitting lid to trap steam and cook fish evenly without drying, aiming for 8-10 minutes per inch of thickness for tender, flaky results. Always check for opaque flesh and easily flaked texture to determine doneness and avoid overcooking.
Poaching vs Steaming for gentle cooking Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com